[toc]
1. 概述
Codec2.0在Android12需要进行对接,本文以AOSP源码分析,简单分析其运行逻辑,具体代码可参考https://cs.android.com/进行查阅。Codec2的Android架构可如下图所示:
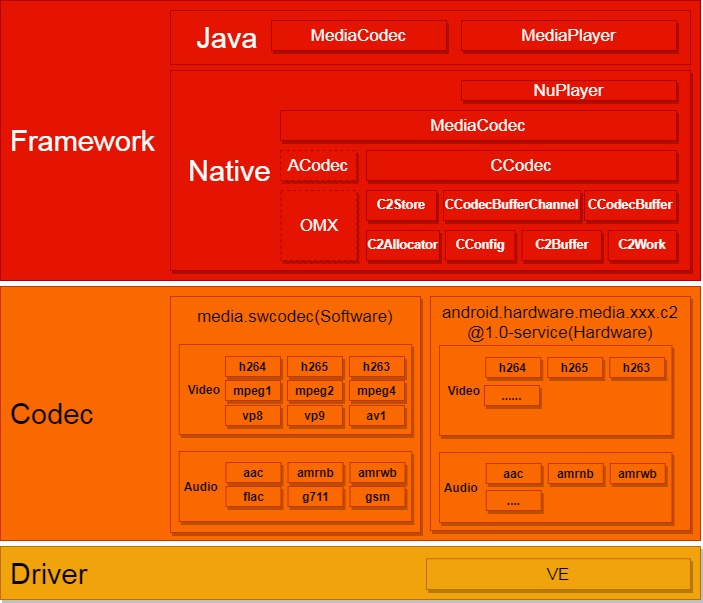
其中Framework层要使用Codec2可通过MediaCodec或者MediaPlayer(使用NuPlayer),Omx在Android12后已弃用,Codec层可分为Android原生的软件编解码和硬件编解码,本文只涉及Android原生代码。
2. MediaCodec流程
分析Codec2.0时,需要重温下MediaCodec的状态机,如下图所示:
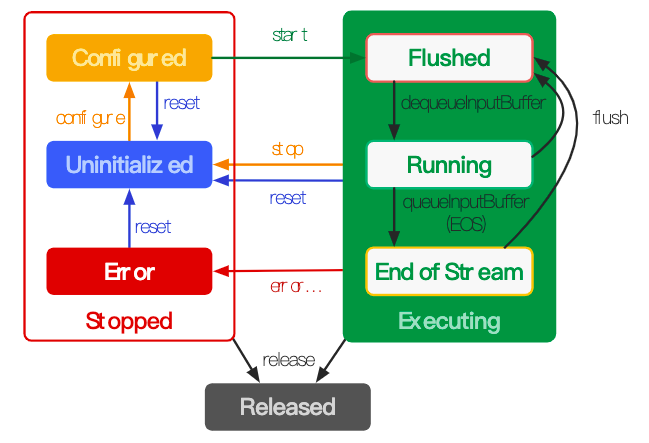
- 开始处于uninitialized状态,调用configure即进入Configured状态,然后调用start进入Executing状态。此时可以进行Buffer处理。
- Executing状态又可细分为三个子状态,Flushed,Running,EndOfStream。当调用start后,MediaCodec已经申请了所有的Buffer,并等待数据的”装载”,此时短暂为Flushed状态。当第一次调用dequeueInputBuffer后获取一个Buffer,进入Running状态。此后会通过queueInputBuffer将数据装载到之前dequeueInputBuffer的Buffer中进行处理。输出端也会获取MediaCodec处理后的Buffers用于送显,并将buffer返回给MediaCodec。最后将带有eos标记的inputBuffer给到MediaCodec后,会进入EndOfStream状态,此时MediaCodec不会再处理输入Buffer了,但仍然会输出Output Buffer直到最后一组Input Buffer处理完毕。具体的Buffer流转图可以查看下图。
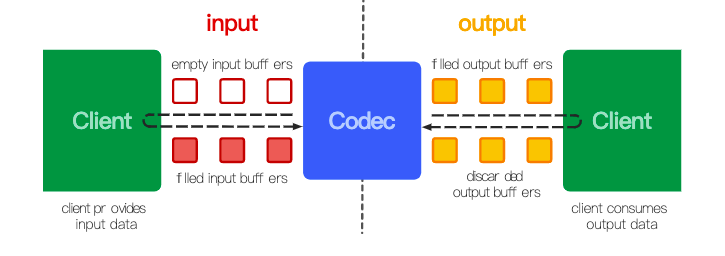
MediaCodec分为同步和异步的模式,以一段同步模式的流程为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
// 同步例子
...
for (int i = 0; i < mExtractor.getTrackCount(); i++) {
//通过解封装获取每一路的媒体信息
MediaFormat format = mExtractor.getTrackFormat(i);
String mime = format.getString(MediaFormat.KEY_MIME);
if (mime.startsWith("video/")) {
mExtractor.selectTrack(i);
try {
// 对每一路单独创建解码器
mDecoder = MediaCodec.createDecoderByType(mime);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//调用configure接口,进入Configured状态
mDecoder.configure(format, mSurfaceHolder.getSurface(), null, 0);
break;
}
}
//调用start接口, 进入 Flushed状态
mDecoder.start();
MediaCodec.BufferInfo info = new MediaCodec.BufferInfo();
boolean isEOS = false;
while (!Thread.interrupted() && !isStopped) {
if(isPaused){
try {
sleep(timeOutUs);
continue;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (!isEOS) {
//dequeueInputBuffer获取对应的下标, 像是从搬运公司要过来搬东西的汽车的车牌号
//此时进入Running状态
int inIndex = mDecoder.dequeueInputBuffer(timeOutUs);
if (inIndex >= 0) {
//获取用于放输入数据的buffer。通过车牌号找到对应的汽车, 准备用于装载货物
ByteBuffer buffer = mDecoder.getInputBuffer(inIndex);
//将解封装的数据即码流放入buffer中。将货物放在该汽车上
int sampleSize = mExtractor.readSampleData(buffer, 0);
if (sampleSize < 0) {
//搬完了,会设置一个EOS的标志位,告诉搬家公司已经全部搬完了
mDecoder.queueInputBuffer(inIndex, 0, 0, 0, MediaCodec.BUFFER_FLAG_END_OF_STREAM);
isEOS = true;
} else {
//将带有码流数据的buffer传入解码器中进行解码。让搬运汽车去到目标位置
mDecoder.queueInputBuffer(inIndex, 0, sampleSize, mExtractor.getSampleTime(), 0);
mExtractor.advance();
}
}
}
//获取解码器已经解码完成的数据,获取其下标。这里的搬家汽车卸货完成之后,还获得了报酬。
int outIndex = mDecoder.dequeueOutputBuffer(info, timeOutUs);
if(outIndex >= 0){
//通过下标获取解码后的数据buffer,用于送显。
ByteBuffer buffer = mDecoder.getOutputBuffer(outIndex);
//releaseOutputBuffer会调用BufferChannel的renderOutputBuffer,送给显示
mDecoder.releaseOutputBuffer(outIndex, true);
}
if ((info.flags & MediaCodec.BUFFER_FLAG_END_OF_STREAM) != 0) {
break;
}
...
}
以上为同步的流程,但实际上一般会采用异步的方式实现, NuPlayer也是使用如下方式去进行的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// 异步例子
Bufferodec codec = MediaCodec.createByCodecName(name);
MediaFormat mOutputFormat;
codec.setCallback(new MediaCodec.Callback() {
@Override
void onInputBufferAvailable(MediaCodec mc, int inputBufferId) {
//当输入Buffer准备好后,就可以异步地将输入Buffer给到解码器
ByteBuffer inputBuffer = codec.getInputBuffer(inputBufferId);
...
codec.queueInputBuffer(inputBufferId, …);
}
@Override
void onOutputBufferAvailable(MediaCodec mc, int outputBufferId, ...) {
//当输出Buffer准备好后,即已经解码的数据,可用于送显。
ByteBuffer outputBuffer = codec.getOutputBuffer(outputBufferId);
MediaFormat bufferFormat = codec.getOutputFormat(outputBufferId); // option A
...
codec.releaseOutputBuffer(outputBufferId, …);
}
});
初步了解了MediaCodec的工作方式,也就可以清楚码流是如何传入给解码器,然后再从解码器获取数据进行送显了。更详细的MediaCodec介绍可以查看官网https://developer.android.com/reference/android/media/MediaCodec
3. media.swcodec服务
Codec2编解码服务如概述所述,分为软件实现和硬件实现,其中软件编解码是Android原生的实现。Codec2软解的服务名为media.swcodec, 首先分析它的rc文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# frameworks/av/apex/mediaswcodec.rc
service media.swcodec /apex/com.android.media.swcodec/bin/mediaswcodec
class main
user mediacodec
group camera drmrpc mediadrm
ioprio rt 4
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
mediaswcodec.rc定义了服务名media.swcodec, 运行的binary文件为/apex/com.android.media.swcodec/bin/mediaswcodec,class为main,说明在开机就会跟随main类的服务一同启动,用户类型为mediacodec,组为camera,drmrpc以及mediadrm。
在Android11中,MainLine已经变为必须要支持了,所以实际运行media.swcodec是mainline的压缩包,但media.swcodec的代码仍可以在frameworks/av/services/mediacodec看得到,从Android.bp分析其依赖文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# frameworks/av/services/mediacodec/Android.bp
cc_binary {
name: "mediaswcodec",
vendor_available: true,
min_sdk_version: "29",
srcs: [
"main_swcodecservice.cpp",
],
shared_libs: [
"libavservices_minijail",
"libbase",
"libhidlbase",
"liblog",
"libmedia_codecserviceregistrant",
],
header_libs: [
"libmedia_headers",
],
cflags: [
"-Werror",
"-Wall",
"-Wno-error=deprecated-declarations",
],
}
由Android.bp可知服务的源文件为main_swcodecservice.cpp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# frameworks/av/services/mediacodec/main_swcodecservice.cpp
static const char kSystemSeccompPolicyPath[] =
"/apex/com.android.media.swcodec/etc/seccomp_policy/mediaswcodec.policy";
static const char kVendorSeccompPolicyPath[] =
"/vendor/etc/seccomp_policy/mediaswcodec.policy";
extern "C" void RegisterCodecServices();
int main(int argc __unused, char** argv)
{
LOG(INFO) << "media swcodec service starting";
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
// Minijail是Google用于Chrome和Android的沙盒工具,只有定义在policy后缀文件中的操作才能够被执行。
// 有兴趣可以查阅https://google.github.io/minijail/
SetUpMinijail(kSystemSeccompPolicyPath, kVendorSeccompPolicyPath);
strcpy(argv[0], "media.swcodec");
// 定义最大用于HIDL通信的线程为64
::android::hardware::configureRpcThreadpool(64, false);
// 3.4 注册Codec2服务
RegisterCodecServices();
// 加入线程池
::android::hardware::joinRpcThreadpool();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# frameworks/av/services/mediacodec/registrant/CodecServiceRegistrant.cpp
extern "C" void RegisterCodecServices() {
LOG(INFO) << "Creating software Codec2 service...";
// 3.5 获取C2ComponentStore
std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentStore> store =
android::GetCodec2PlatformComponentStore();
if (!store) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to create Codec2 service.";
return;
}
using namespace ::android::hardware::media::c2;
//平台版本决定Codec2 HAL版本2
int platformVersion = android_get_device_api_level();
// 对Q,R,S以上的服务使用software名称对软解服务进行注册
if (platformVersion >= __ANDROID_API_S__) {
android::sp<V1_2::IComponentStore> storeV1_2 =
new V1_2::utils::ComponentStore(store);
//将store作为以“software”的名称注册到服务中。
if (storeV1_2->registerAsService("software") != android::OK) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Cannot register software Codec2 v1.2 service.";
return;
}
} else if (platformVersion == __ANDROID_API_R__) {
android::sp<V1_1::IComponentStore> storeV1_1 =
new V1_1::utils::ComponentStore(store);
if (storeV1_1->registerAsService("software") != android::OK) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Cannot register software Codec2 v1.1 service.";
return;
}
} else if (platformVersion == __ANDROID_API_Q__) {
android::sp<V1_0::IComponentStore> storeV1_0 =
new V1_0::utils::ComponentStore(store);
if (storeV1_0->registerAsService("software") != android::OK) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Cannot register software Codec2 v1.0 service.";
return;
}
} else { // platformVersion < __ANDROID_API_Q__
LOG(ERROR) << "The platform version " << platformVersion <<
" is not supported.";
return;
}
if (!ionPropertiesDefined()) {
using IComponentStore =
::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore;
std::string const preferredStoreName = "default";
sp<IComponentStore> preferredStore =
IComponentStore::getService(preferredStoreName.c_str());
if (preferredStore) {
::android::SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore(
std::make_shared<H2C2ComponentStore>(preferredStore));
LOG(INFO) <<
"Preferred Codec2 store is set to \"" <<
preferredStoreName << "\".";
} else {
LOG(INFO) <<
"Preferred Codec2 store is defaulted to \"software\".";
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "Software Codec2 service created and registered.";
}
3.5 GetCodec2PlatformComponentStore
GetCodec2PlatformComponentStore可以理解为获取Codec2的PlatformComponentStore(平台组件的便利店,里面有很多组件)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/vndk/C2Store.cpp
std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentStore> GetCodec2PlatformComponentStore() {
static std::mutex mutex;
static std::weak_ptr<C2ComponentStore> platformStore;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex);
std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentStore> store = platformStore.lock();
if (store == nullptr) {
store = std::make_shared<C2PlatformComponentStore>();
platformStore = store;
}
return store;
}
在分析C2PlatformComponentStore构造函数前,先看看mComponents的类型:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/vndk/C2Store.cpp
// mComponents是为了建立库的路径名和ComponentLoader的关系。
std::map<C2String, ComponentLoader> mComponents; ///< path -> component module
/**
* Creates a component loader for a specific library path (or name).
*/
// ComponentLoader将参数libPath传入到mLibPath保存起来,为后续的初始化做准备。
ComponentLoader(std::string libPath)
: mLibPath(libPath) {}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/vndk/C2Store.cpp
C2PlatformComponentStore::C2PlatformComponentStore()
: mVisited(false),
mReflector(std::make_shared<C2ReflectorHelper>()),
mInterface(mReflector) {
// lambda函数emplace,将mComponents结构体进行填充。
auto emplace = [this](const char *libPath) {
mComponents.emplace(libPath, libPath);
};
// TODO: move this also into a .so so it can be updated
emplace("libcodec2_soft_aacdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_aacenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrnbdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrnbenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrwbdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrwbenc.so");
//emplace("libcodec2_soft_av1dec_aom.so"); // deprecated for the gav1 implementation
emplace("libcodec2_soft_av1dec_gav1.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_avcdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_avcenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_flacdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_flacenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_g711alawdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_g711mlawdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_gsmdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_h263dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_h263enc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_hevcdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_hevcenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mp3dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mpeg2dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mpeg4dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mpeg4enc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_opusdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_opusenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_rawdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vorbisdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp8dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp8enc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp9dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp9enc.so");
}
4. 编解码器组件配置
以软编解码配置为例,一个解码器需要按照如下方式进行配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/data/media_codecs_google_c2_video.xml
<Included>
<Decoders>
<MediaCodec name="c2.android.mpeg4.decoder" type="video/mp4v-es">
<Alias name="OMX.google.mpeg4.decoder" />
<!-- profiles and levels: ProfileSimple : Level3 -->
<Limit name="size" min="2x2" max="352x288" />
<Limit name="alignment" value="2x2" />
<Limit name="block-size" value="16x16" />
<Limit name="blocks-per-second" range="12-11880" />
<Limit name="bitrate" range="1-384000" />
<Feature name="adaptive-playback" />
</MediaCodec>
</Decoders>
从上面我们可以得知,该组件名为”c2.android.mpeg4.decoder”, 类型为mpeg4, 同时别名为”OMX.google.mpeg4.decoder”。其大小为最小2x2,最大为352x288(因此软解也只能处理低分辨率的片源)。 后面还有包括对齐,宏块大小,码率范围等信息,支持自适应播放等等。由此看来,当播放的分辨率符合,或者指定使用了组件名等,就能够确定使用哪个组件进行播放。值得注意的是,CTS测试也会根据xml中编解码器所支持的特性选择测试的内容。
2.2 选择最优的编解码组件
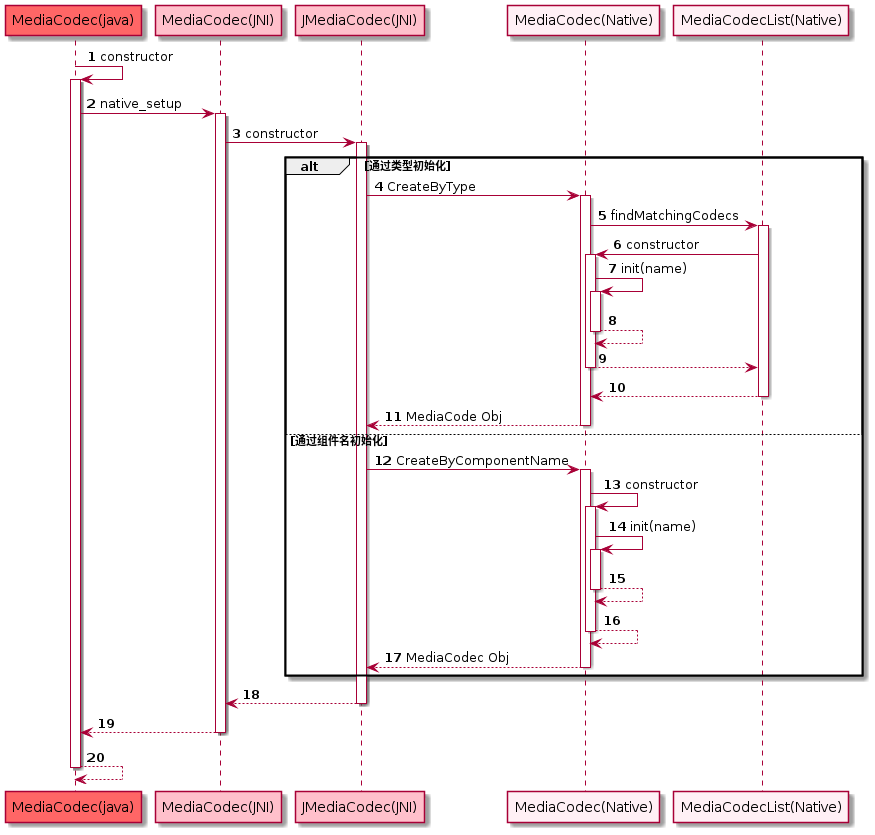
MediaCodec到实际组件的创建一般有两种方式,如上图的CreateByType和CreateByComponentName,一般来说,前者使用频率更大,通过MediaCodecList解析并得出最适合的组件进行初始化。
以findMatchingCodecs为起点进行追踪,其流程图大致如下所示,接下来将会跟踪代码。
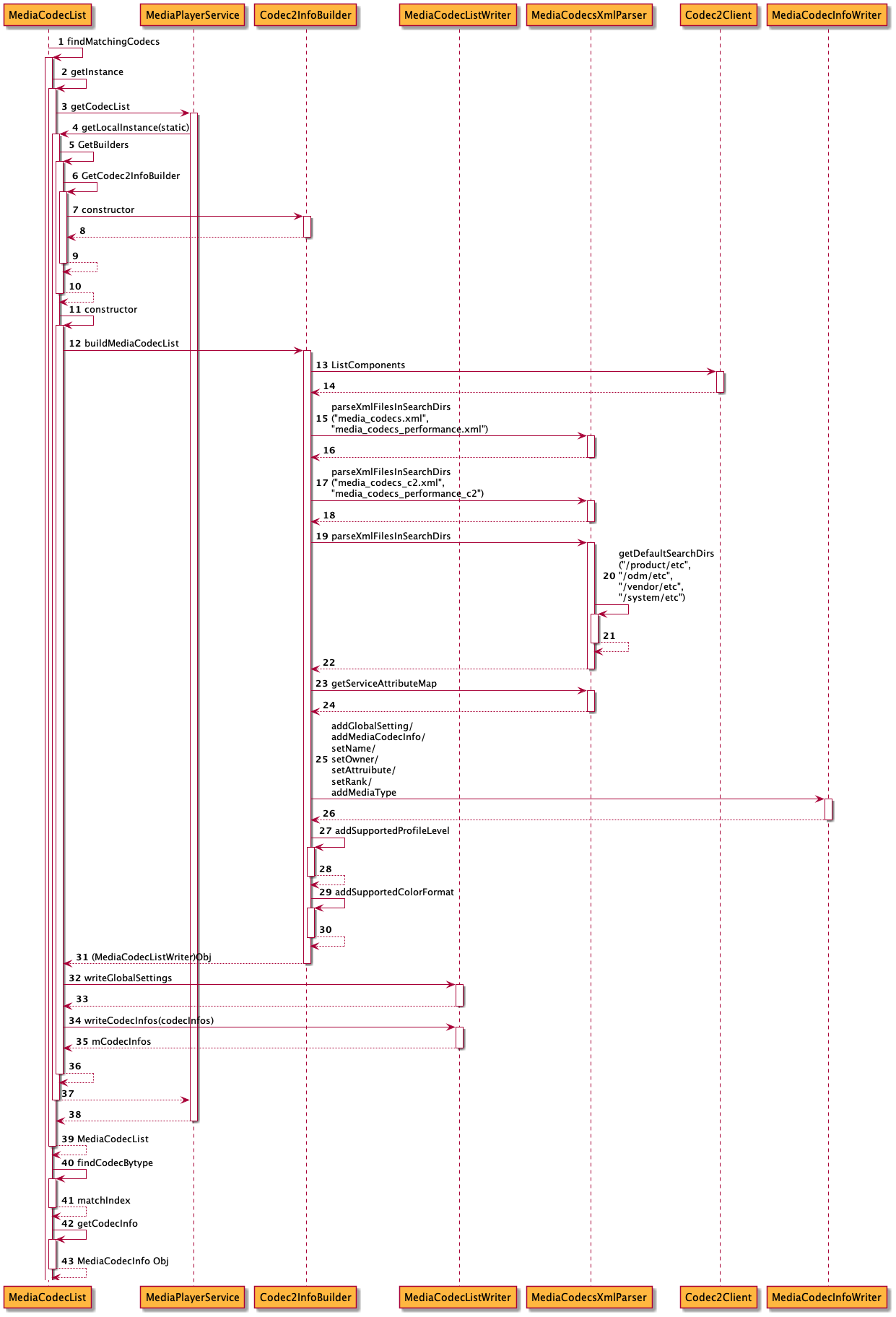
代码流程如下:
- (0) MediaCodecList::findMatchingCodecs
- (1) MediaCodecList::getInstance
- (1.1) MediaPlayerService::getCodecList
- (1.1.1) MediaCodecList::getLocalInstance
- (1.1.1.1) MediaCodecList GetBuilders
- (1.1.1.1.1) MediaCodecList GetCodec2InfoBuilder
- (1.1.1.1.1.1) Codec2InfoBuilder
- (1.1.1.1.1) MediaCodecList GetCodec2InfoBuilder
- (1.1.1.2) new MediaCodecList
- (1.1.1.2.1)Codec2InfoBuilder::buildMediaCodecList
- (1.1.1.2.1.1) Codec2Client::ListComponents
- (A) Cache::List
- (B) Cache::getTraits
- (1.1.1.2.1.1) Codec2Client::ListComponents
- (1.1.1.2.2) MediaCodecListWriter::writeCodecInfos
- (1.1.1.2.1)Codec2InfoBuilder::buildMediaCodecList
- (1.1.1.1) MediaCodecList GetBuilders
- (1.1.1) MediaCodecList::getLocalInstance
- (1.1) MediaPlayerService::getCodecList
- (2) MediaCodecList::findCodecByType
- (3) getCodecInfo
下面来跟踪代码:
(0) findMatchingCodecs: 找到合适的组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp
void MediaCodecList::findMatchingCodecs(
const char *mime, bool encoder, uint32_t flags, sp<AMessage> format,
Vector<AString> *matches) {
//matches是一个Vector容器
matches->clear();
// (1) 通过MediaPlayerService服务获取当前的MediaCodecList
const sp<IMediaCodecList> list = getInstance();
if (list == nullptr) {
return;
}
size_t index = 0;
for (;;) {
// (2) 根据初始化的MediaCodecList, 对配置文件等进行了一系列初始化
// 再从中根据mime,是否为encoder等信息找到对应的组件下标。
ssize_t matchIndex =
list->findCodecByType(mime, encoder, index);
if (matchIndex < 0) {
break;
}
index = matchIndex + 1;
// (3) 根据获取的下标,得到对应的MediaCodecInfo(步骤1的时候进行了MediaCodecInfo初始化)
const sp<MediaCodecInfo> info = list->getCodecInfo(matchIndex);
CHECK(info != nullptr);
// 获取具体组件的名字
AString componentName = info->getCodecName();
if (!codecHandlesFormat(mime, info, format)) {
ALOGV("skipping codec '%s' which doesn't satisfy format %s",
componentName.c_str(), format->debugString(2).c_str());
continue;
}
// 加入输入参数flag设置为了kHardwareCodecsOnly, 要求指定使用硬件Codec
if ((flags & kHardwareCodecsOnly) && isSoftwareCodec(componentName)) {
ALOGV("skipping SW codec '%s'", componentName.c_str());
continue;
}
// 将符合的组件名加入到Vector类型的matches中。
matches->push(componentName);
ALOGV("matching '%s'", componentName.c_str());
}
// 通过设置属性debug.stagefright.swcodec,可以使得软解优先。
if (flags & kPreferSoftwareCodecs ||
property_get_bool("debug.stagefright.swcodec", false)) {
// 排序, compareSoftwareCodecsFirst为具体的排序规则
matches->sort(compareSoftwareCodecsFirst);
}
}
(1) MediaCodecList::getInstance
MediaCodecList::getInstance实质是通过Binder与MediaPlayer Service进行进程间通信,获取需要的MeidaCodecList信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp
sp<IMediaCodecList> MediaCodecList::getInstance() {
Mutex::Autolock _l(sRemoteInitMutex);
if (sRemoteList == nullptr) {
// 获取MediaPlayerService服务
sMediaPlayer = defaultServiceManager()->getService(String16("media.player"));
sp<IMediaPlayerService> service =
interface_cast<IMediaPlayerService>(sMediaPlayer);
if (service.get() != nullptr) {
// (1.1) 调用服务的getCodecList获取MediaCodecList
// 但其实质,也是获取MediaCodecList的本地实例。
sRemoteList = service->getCodecList();
if (sRemoteList != nullptr) {
// 只要远程的MediaCodecList存在,就建立一个Binder的死亡观察者(Observer)用于
// 监听MediaPlayerService的状态,以便在其挂的时候及时收到死亡通知。
sBinderDeathObserver = new BinderDeathObserver();
sMediaPlayer->linkToDeath(sBinderDeathObserver.get());
}
}
if (sRemoteList == nullptr) {
// if failed to get remote list, create local list
// 假如通过MediaPlayerService无法获取,说明本地实例还没创建
//此时再创建,懒汉模式
sRemoteList = getLocalInstance();
}
}
return sRemoteList;
}
(1.1) MediaPlayerService::getCodecList
1
2
3
4
5
6
// frameworks/av/media/libmediaplayerservice/MediaPlayerService.cpp
sp<IMediaCodecList> MediaPlayerService::getCodecList() const {
// 这里可以看出,在(1)中,无论如何都是调用MediaCodecList的getLocalInstance方法
// (1.1.1)
return MediaCodecList::getLocalInstance();
}
(1.1.1) MediaCodecList::getLocalInstance
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp
sp<IMediaCodecList> MediaCodecList::getLocalInstance() {
Mutex::Autolock autoLock(sInitMutex);
if (sCodecList == nullptr) {
// (1.1.1.1) GetBuilders获取的建造器,对应的是CodecInfoBuilder
// (1.1.1.2) MediaCodecList应当是单例模式,只要为空时,会创建一个MediaCodecList对象
MediaCodecList *codecList = new MediaCodecList(GetBuilders());
if (codecList->initCheck() == OK) {
sCodecList = codecList;
if (isProfilingNeeded()) {
ALOGV("Codec profiling needed, will be run in separated thread.");
pthread_t profiler;
if (pthread_create(&profiler, nullptr, profilerThreadWrapper, nullptr) != 0) {
ALOGW("Failed to create thread for codec profiling.");
}
}
} else {
// failure to initialize may be temporary. retry on next call.
delete codecList;
}
}
return sCodecList;
}
至此,我们得知,只要调用了MediaCodceList的方法,就会和MediaPlayerService交互,希望通过MediaPlayerService服务获取MediaCodecList的对象,但实质其最终还是获取MediaCodecList的本地对象,那么为什么还要通过MeidaPlayerService获取多此一举?原因是因为MediapPlayerService的内部也需要使用到MediaCodecList的对象,主要是在dump的时候需要看到这些信息。那么MediaCodecList和MediaPlayerService进行通信就有必要了,否则MediaCodecList信息只能够在调用者一方知道而已了。
(1.1.1.1) MediaCodecList GetBuilders获取构建器器
Builders让我想起了Builder设计模式,在Codec2之前,用的是OMX,所以以后即使有新的框架,也可以设计对应的Builder, 适合以后的扩展。 这里获取Builder的方法名为GetCodec2InfoBuilder。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp
std::vector<MediaCodecListBuilderBase *> GetBuilders() {
std::vector<MediaCodecListBuilderBase *> builders;
// ...
// (1.1.1.1.1) GetCodec2InfoBuilder
builders.push_back(GetCodec2InfoBuilder());
return builders;
}
(1.1.1.1.1)MediaCodecList GetCodec2InfoBuilder
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
MediaCodecListBuilderBase *GetCodec2InfoBuilder() {
Mutex::Autolock _l(sCodec2InfoBuilderMutex);
if (!sCodec2InfoBuilder) {
// (1.1.1.1.1.1) Codec2InfoBuilder
sCodec2InfoBuilder.reset(new Codec2InfoBuilder);
}
return sCodec2InfoBuilder.get();
}
(1.1.1.1.1.1) Codec2InfoBuilder
Codec2InfoBuilder即为Codec2的Info的构建器。其并没有实现自定义的构造函数(默认构造函数)。当MediaCodecList首次初始化时将会用到这个构建器,继续向后跟踪流程。
接着1.1.1.1.1的流程,当Codec2InfoBuilder创建后,将作为参数传入到MediaCodecList中,意义是使用特定的建造器进行初始化。其中的buildMediaCodecList方法,对配置文件进行了初始化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp
MediaCodecList::MediaCodecList(std::vector<MediaCodecListBuilderBase*> builders) {
mGlobalSettings = new AMessage();
mCodecInfos.clear();
MediaCodecListWriter writer;
for (MediaCodecListBuilderBase *builder : builders) {
if (builder == nullptr) {
ALOGD("ignored a null builder");
continue;
}
// (1.1.1.2.1) 解析配置文件并返回MediaCodecListWriter对象
// buildMediaCodecList会在MediaCodecListWriter中创建MediaCodecInfos集合
auto currentCheck = builder->buildMediaCodecList(&writer);
if (currentCheck != OK) {
ALOGD("ignored failed builder");
continue;
} else {
mInitCheck = currentCheck;
}
}
writer.writeGlobalSettings(mGlobalSettings);
// (1.1.1.2.2) 将MediaCodecListWriter中的MediaCodecInfos集合传到MediaCodecList中。
writer.writeCodecInfos(&mCodecInfos);
std::stable_sort(
mCodecInfos.begin(),
mCodecInfos.end(),
[](const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &info1, const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &info2) {
// null is lowest
return info1 == nullptr
|| (info2 != nullptr && info1->getRank() < info2->getRank());
});
// remove duplicate entries
bool dedupe = property_get_bool("debug.stagefright.dedupe-codecs", true);
if (dedupe) {
std::set<std::string> codecsSeen;
for (auto it = mCodecInfos.begin(); it != mCodecInfos.end(); ) {
std::string codecName = (*it)->getCodecName();
if (codecsSeen.count(codecName) == 0) {
codecsSeen.emplace(codecName);
it++;
} else {
it = mCodecInfos.erase(it);
}
}
}
}
(1.1.1.2.1) Codec2InfoBuilder::buildMediaCodecList
buildMediaCodecList的流程比较长,精简的流程如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
// frameworks/av/media/codec2/sfplugin/Codec2InfoBuilder.cpp
status_t Codec2InfoBuilder::buildMediaCodecList(MediaCodecListWriter* writer) {
// 1.1.1.2.1.1获取HAL层Codec2服务的组件属性vector
std::vector<Traits> traits = Codec2Client::ListComponents();
// A. 对media_codecs.xml,media_codecs_performance.xml以及apex目录下的配置进行解析
MediaCodecsXmlParser parser;
parser.parseXmlFilesInSearchDirs(
{ "media_codecs.xml", "media_codecs_performance.xml" },
{ "/apex/com.android.media.swcodec/etc" });
// B. 对media_codecs_c2.xml,media_codecs_performance_c2.xml进行解析
parser.parseXmlFilesInSearchDirs(
{ "media_codecs_c2.xml", "media_codecs_performance_c2.xml" });
// C. 对默认目录进行解析,其中包括:
// /product/etc, /odm/etc, /vendor/etc, /system/etc,可想而知,都是支持硬解的配置
parser.parseXmlFilesInSearchDirs();
if (parser.getParsingStatus() != OK) {
ALOGD("XML parser no good");
return OK;
}
MediaCodecsXmlParser::AttributeMap settings = parser.getServiceAttributeMap();
for (const auto &v : settings) {
if (!hasPrefix(v.first, "media-type-")
&& !hasPrefix(v.first, "domain-")
&& !hasPrefix(v.first, "variant-")) {
writer->addGlobalSetting(v.first.c_str(), v.second.c_str());
}
}
for (const Traits& trait : traits) {
C2Component::rank_t rank = trait.rank;
std::vector<std::string> nameAndAliases = trait.aliases;
nameAndAliases.insert(nameAndAliases.begin(), trait.name);
for (const std::string &nameOrAlias : nameAndAliases) {
bool isAlias = trait.name != nameOrAlias;
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Interface> intf =
Codec2Client::CreateInterfaceByName(nameOrAlias.c_str());
if (!intf) {
ALOGD("could not create interface for %s'%s'",
isAlias ? "alias " : "",
nameOrAlias.c_str());
continue;
}
if (parser.getCodecMap().count(nameOrAlias) == 0) {
if (isAlias) {
std::unique_ptr<MediaCodecInfoWriter> baseCodecInfo =
writer->findMediaCodecInfo(trait.name.c_str());
if (!baseCodecInfo) {
ALOGD("alias '%s' not found in xml but canonical codec info '%s' missing",
nameOrAlias.c_str(),
trait.name.c_str());
} else {
ALOGD("alias '%s' not found in xml; use an XML <Alias> tag for this",
nameOrAlias.c_str());
// merge alias into existing codec
baseCodecInfo->addAlias(nameOrAlias.c_str());
}
} else {
ALOGD("component '%s' not found in xml", trait.name.c_str());
}
continue;
}
std::string canonName = trait.name;
....
const MediaCodecsXmlParser::CodecProperties &codec =
parser.getCodecMap().at(nameOrAlias);
// verify that either the codec is explicitly enabled, or one of its domains is
bool codecEnabled = codec.quirkSet.find("attribute::disabled") == codec.quirkSet.end();
if (!codecEnabled) {
for (const std::string &domain : codec.domainSet) {
const Switch enabled = isDomainEnabled(domain, settings);
ALOGV("codec entry '%s' is in domain '%s' that is '%s'",
nameOrAlias.c_str(), domain.c_str(), asString(enabled));
if (enabled) {
codecEnabled = true;
break;
}
}
}
// if codec has variants, also check that at least one of them is enabled
bool variantEnabled = codec.variantSet.empty();
for (const std::string &variant : codec.variantSet) {
const Switch enabled = isVariantExpressionEnabled(variant, settings);
ALOGV("codec entry '%s' has a variant '%s' that is '%s'",
nameOrAlias.c_str(), variant.c_str(), asString(enabled));
if (enabled) {
variantEnabled = true;
break;
}
}
if (!codecEnabled || !variantEnabled) {
ALOGD("codec entry for '%s' is disabled", nameOrAlias.c_str());
continue;
}
ALOGV("adding codec entry for '%s'", nameOrAlias.c_str());
// D. 通过MediaCodecListWriter的addMediaCodecInfo方法,会新建一个MediaCodecInfo对象
// 并放入容器mCodecInfos中,下次要找的时候,就可以在mCodecInfos中寻找!!
std::unique_ptr<MediaCodecInfoWriter> codecInfo = writer->addMediaCodecInfo();
codecInfo->setName(nameOrAlias.c_str());
codecInfo->setOwner(("codec2::" + trait.owner).c_str());
bool encoder = trait.kind == C2Component::KIND_ENCODER;
typename std::underlying_type<MediaCodecInfo::Attributes>::type attrs = 0;
if (encoder) {
attrs |= MediaCodecInfo::kFlagIsEncoder;
}
if (trait.owner == "software") {
attrs |= MediaCodecInfo::kFlagIsSoftwareOnly;
} else {
attrs |= MediaCodecInfo::kFlagIsVendor;
if (trait.owner == "vendor-software") {
attrs |= MediaCodecInfo::kFlagIsSoftwareOnly;
} else if (codec.quirkSet.find("attribute::software-codec")
== codec.quirkSet.end()) {
attrs |= MediaCodecInfo::kFlagIsHardwareAccelerated;
}
}
codecInfo->setAttributes(attrs);
if (!codec.rank.empty()) {
uint32_t xmlRank;
char dummy;
if (sscanf(codec.rank.c_str(), "%u%c", &xmlRank, &dummy) == 1) {
rank = xmlRank;
}
}
ALOGV("rank: %u", (unsigned)rank);
codecInfo->setRank(rank);
for (const std::string &alias : codec.aliases) {
ALOGV("adding alias '%s'", alias.c_str());
codecInfo->addAlias(alias.c_str());
}
for (auto typeIt = codec.typeMap.begin(); typeIt != codec.typeMap.end(); ++typeIt) {
const std::string &mediaType = typeIt->first;
const Switch typeEnabled = isSettingEnabled(
"media-type-" + mediaType, settings, Switch::ENABLED_BY_DEFAULT());
const Switch domainTypeEnabled = isSettingEnabled(
"media-type-" + mediaType + (encoder ? "-encoder" : "-decoder"),
settings, Switch::ENABLED_BY_DEFAULT());
ALOGV("type '%s-%s' is '%s/%s'",
mediaType.c_str(), (encoder ? "encoder" : "decoder"),
asString(typeEnabled), asString(domainTypeEnabled));
if (!typeEnabled || !domainTypeEnabled) {
ALOGD("media type '%s' for codec entry '%s' is disabled", mediaType.c_str(),
nameOrAlias.c_str());
continue;
}
ALOGI("adding type '%s'", typeIt->first.c_str());
const MediaCodecsXmlParser::AttributeMap &attrMap = typeIt->second;
std::unique_ptr<MediaCodecInfo::CapabilitiesWriter> caps =
codecInfo->addMediaType(mediaType.c_str());
for (const auto &v : attrMap) {
std::string key = v.first;
std::string value = v.second;
size_t variantSep = key.find(":::");
if (variantSep != std::string::npos) {
std::string variant = key.substr(0, variantSep);
const Switch enabled = isVariantExpressionEnabled(variant, settings);
ALOGV("variant '%s' is '%s'", variant.c_str(), asString(enabled));
if (!enabled) {
continue;
}
key = key.substr(variantSep + 3);
}
if (key.find("feature-") == 0 && key.find("feature-bitrate-modes") != 0) {
int32_t intValue = 0;
// Ignore trailing bad characters and default to 0.
(void)sscanf(value.c_str(), "%d", &intValue);
caps->addDetail(key.c_str(), intValue);
} else {
caps->addDetail(key.c_str(), value.c_str());
}
}
addSupportedProfileLevels(intf, caps.get(), trait, mediaType);
addSupportedColorFormats(intf, caps.get(), trait, mediaType);
}
}
}
return OK;
}
(1.1.1.2.1.1) Codec2Client::ListComponents
Codec2Client是与HAL层的Codec2服务进行交互的客户端,通过Binder/Hidl通信,获取编解码器的属性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
std::vector<C2Component::Traits> const& Codec2Client::ListComponents() {
static std::vector<C2Component::Traits> sList{[]() {
std::vector<C2Component::Traits> list;
// A. Cache这个类设计的目的,就是在client初次被创建的时候
// 获取component组件的属性(traits).
for (Cache& cache : Cache::List()) {
// B. getTraits
std::vector<C2Component::Traits> const& traits = cache.getTraits();
list.insert(list.end(), traits.begin(), traits.end());
}
return list;
}()};
return sList;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
// List() returns the list of all caches.
static std::vector<Cache>& List() {
static std::vector<Cache> sCaches{[]() {
size_t numServices = GetServiceNames().size();
std::vector<Cache> caches(numServices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < numServices; ++i) {
// Cache的init只是更新mIndex,用于记录
caches[i].init(i);
}
return caches;
}()};
return sCaches;
}
getTraits只需要在初次调用时读取即可,这里使用了std的call_once来保证这点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
std::vector<C2Component::Traits> const& getTraits() {
std::call_once(mTraitsInitializationFlag, [this]() {
bool success{false};
// Spin until _listComponents() is successful.
while (true) {
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client = getClient();
// 继续调用_listComponents
mTraits = client->_listComponents(&success);
if (success) {
break;
}
invalidate();
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
static constexpr auto kServiceRetryPeriod = 5s;
LOG(INFO) << "Failed to retrieve component traits from service "
"\"" << GetServiceNames()[mIndex] << "\". "
"Retrying...";
std::this_thread::sleep_for(kServiceRetryPeriod);
}
});
return mTraits;
}
std::vector<C2Component::Traits> Codec2Client::_listComponents(
bool* success) const {
std::vector<C2Component::Traits> traits;
std::string const& serviceName = getServiceName();
// 这里直接对接到HAL层服务,定义了匿名lambda方法给到HAL层初始化
// 通过objcpy拷贝到framework层
Return<void> transStatus = mBase1_0->listComponents(
[&traits, &serviceName](Status s,
const hidl_vec<IComponentStore::ComponentTraits>& t) {
if (s != Status::OK) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "_listComponents -- call failed: "
<< static_cast<c2_status_t>(s) << ".";
return;
}
traits.resize(t.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < t.size(); ++i) {
if (!objcpy(&traits[i], t[i])) {
LOG(ERROR) << "_listComponents -- corrupted output.";
return;
}
traits[i].owner = serviceName;
}
});
if (!transStatus.isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "_listComponents -- transaction failed.";
*success = false;
} else {
*success = true;
}
return traits;
}
以原生的软解为例子, 看下是如何获取这些编解码组件属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/1.0/utils/ComponentStore.cpp
// 如果是使用Codec2 hidl 1.0版本的话如下,具体store的初始化后续分析软解服务时分析
Return<void> ComponentStore::listComponents(listComponents_cb _hidl_cb) {
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits>> c2traits =
mStore->listComponents();
hidl_vec<IComponentStore::ComponentTraits> traits(c2traits.size());
size_t ix = 0;
for (const std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits> &c2trait : c2traits) {
if (c2trait) {
if (objcpy(&traits[ix], *c2trait)) {
++ix;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
traits.resize(ix);
_hidl_cb(Status::OK, traits);
return Void();
}
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/vndk/C2Store.cpp
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits>> C2PlatformComponentStore::listComponents() {
// This method SHALL return within 500ms.
visitComponents();
return mComponentList;
}
void C2PlatformComponentStore::visitComponents() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
if (mVisited) {
return;
}
for (auto &pathAndLoader : mComponents) {
const C2String &path = pathAndLoader.first;
ComponentLoader &loader = pathAndLoader.second;
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> module;
if (loader.fetchModule(&module) == C2_OK) {
//通过module的getTraits方法
std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits> traits = module->getTraits();
if (traits) {
mComponentList.push_back(traits);
mComponentNameToPath.emplace(traits->name, path);
for (const C2String &alias : traits->aliases) {
mComponentNameToPath.emplace(alias, path);
}
}
}
}
mVisited = true;
}
c2_status_t fetchModule(std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module) {
c2_status_t res = C2_OK;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> localModule = mModule.lock();
if (localModule == nullptr) {
if(mCreateFactory) {
// For testing only
localModule = std::make_shared<ComponentModule>(mCreateFactory,
mDestroyFactory);
} else {
localModule = std::make_shared<ComponentModule>();
}
res = localModule->init(mLibPath);
if (res == C2_OK) {
mModule = localModule;
}
}
*module = localModule;
return res;
}
C2PlatformComponentStore::C2PlatformComponentStore()
: mVisited(false),
mReflector(std::make_shared<C2ReflectorHelper>()),
mInterface(mReflector) {
auto emplace = [this](const char *libPath) {
mComponents.emplace(libPath, libPath);
};
// TODO: move this also into a .so so it can be updated
emplace("libcodec2_soft_aacdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_aacenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrnbdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrnbenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrwbdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_amrwbenc.so");
//emplace("libcodec2_soft_av1dec_aom.so"); // deprecated for the gav1 implementation
emplace("libcodec2_soft_av1dec_gav1.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_avcdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_avcenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_flacdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_flacenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_g711alawdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_g711mlawdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_gsmdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_h263dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_h263enc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_hevcdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_hevcenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mp3dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mpeg2dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mpeg4dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_mpeg4enc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_opusdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_opusenc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_rawdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vorbisdec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp8dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp8enc.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp9dec.so");
emplace("libcodec2_soft_vp9enc.so");
}
(1.1.1.2.2) MediaCodecListWriter::writeCodecInfos
writeCodecInfos的目的是将MediaCodecListWriter中的mCodecInfos传到外层的MediaCodecListWriter中,方便后续查找使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp
void MediaCodecListWriter::writeCodecInfos(
std::vector<sp<MediaCodecInfo>> *codecInfos) const {
for (const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &info : mCodecInfos) {
codecInfos->push_back(info);
}
}
(2) MediaCodecList::findCodecByType: 通过类型找到对应的Codec
既然上一步骤已经获取到了mCodecInfos,所以就可以在集合里进行查找了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp
ssize_t MediaCodecList::findCodecByType(
const char *type, bool encoder, size_t startIndex) const {
static const char *advancedFeatures[] = {
"feature-secure-playback",
"feature-tunneled-playback",
};
// mCodecInfos是一个Vector类型容器!
size_t numCodecInfos = mCodecInfos.size();
for (; startIndex < numCodecInfos; ++startIndex) {
const MediaCodecInfo &info = *mCodecInfos[startIndex];
// 首先根据是否为编码进行对比,相同时才能继续往下匹配
if (info.isEncoder() != encoder) {
continue;
}
// 根据类型获取对应的特性Capabilities, 假如为空,即当前的组件不匹配
sp<MediaCodecInfo::Capabilities> capabilities = info.getCapabilitiesFor(type);
if (capabilities == nullptr) {
continue;
}
const sp<AMessage> &details = capabilities->getDetails();
int32_t required;
bool isAdvanced = false;
// 只要不满足"feature-secure-playback"和"feature-tunneled-playback",就可以返回该组件啦
for (size_t ix = 0; ix < ARRAY_SIZE(advancedFeatures); ix++) {
if (details->findInt32(advancedFeatures[ix], &required) &&
required != 0) {
isAdvanced = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isAdvanced) {
return startIndex;
}
}
return -ENOENT;
}
上一步已经获取到了对应的下标,此处只要从mCodecInfos中获取对应的MediaCodecInfo就好了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/include/media/stagefright/MediaCodecList.h
virtual sp<MediaCodecInfo> getCodecInfo(size_t index) const {
if (index >= mCodecInfos.size()) {
ALOGE("b/24445127");
return NULL;
}
return mCodecInfos[index];
}
至此,从findMatchingCodecs的流程梳理完毕,我们应当掌握了如何从配置文件中匹配到最为合适的编解码组件的过程, 那么下一步可以直接移步到Codec2组件的初始化流程了。
2.3 Codec2编解码组件的初始化
承接上一节的内容,当使用了CreateByType中选取了适合的编解码器后,会对其进行初始化,以CreateByType流程为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
sp<MediaCodec> MediaCodec::CreateByType(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, const AString &mime, bool encoder, status_t *err, pid_t pid,
uid_t uid) {
Vector<AString> matchingCodecs;
// 2.2内容, 返回的是编解码器的名字
MediaCodecList::findMatchingCodecs(
mime.c_str(),
encoder,
0,
&matchingCodecs);
if (err != NULL) {
*err = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
// 由于合适的解码器可能有多个, 对靠前的编解码器尝试进行初始化,直到有一个成功为止
for (size_t i = 0; i < matchingCodecs.size(); ++i) {
sp<MediaCodec> codec = new MediaCodec(looper, pid, uid);
AString componentName = matchingCodecs[i];
// 0. MediaCodec的init
status_t ret = codec->init(componentName);
if (err != NULL) {
*err = ret;
}
if (ret == OK) {
return codec;
}
ALOGD("Allocating component '%s' failed (%d), try next one.",
componentName.c_str(), ret);
}
return NULL;
}
在着手看MediaCodec的init流程前,先梳理下通路,如下图所示:
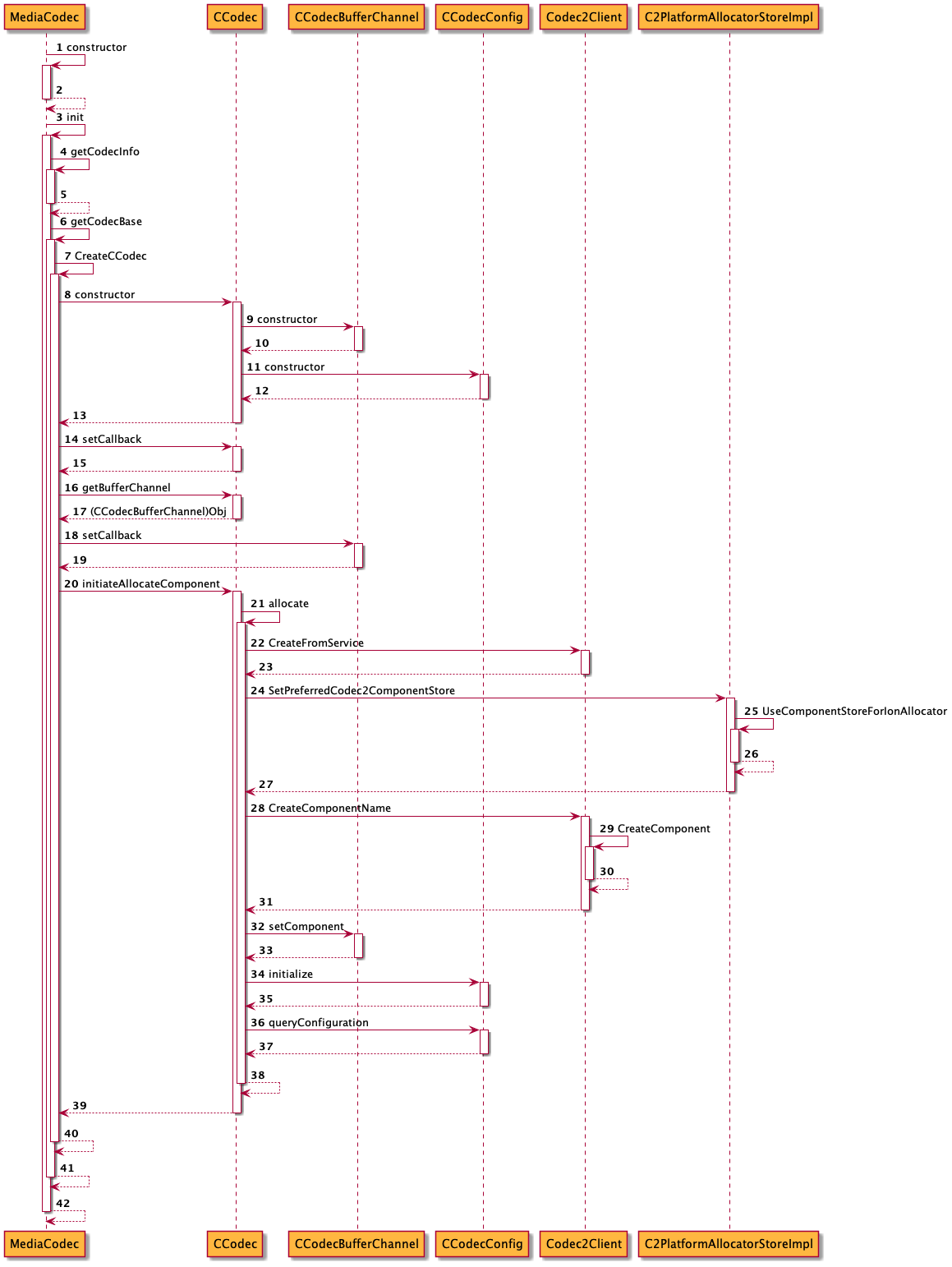
代码流程如下:
- (0) MediaCodec constructor
- (1) MediaCodec::init
- (1.1) MediaCodec::getCodecBase
- (1.2) registerHandler
- (1.3) MediaCodec::setCallback
- (1.4) CCodec::getBufferChannel
- (1.5) setCallback
- (1.6) CCodec::initiateAllocateComponent
MediaCodec的构造函数定义在头文件中定义如下,可以看到传参的getCodecBase和getCodecInfo均指向空指针,且调用时并没有 对这两个参数进行赋值,说明一开始时,调用该两个函数时为空。
1
2
3
4
5
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.h
MediaCodec(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, pid_t pid, uid_t uid,
std::function<sp<CodecBase>(const AString &, const char *)> getCodecBase = nullptr,
std::function<status_t(const AString &, sp<MediaCodecInfo> *)> getCodecInfo = nullptr);
再来看看构造函数的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
MediaCodec::MediaCodec(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, pid_t pid, uid_t uid,
std::function<sp<CodecBase>(const AString &, const char *)> getCodecBase,
std::function<status_t(const AString &, sp<MediaCodecInfo> *)> getCodecInfo)
: mState(UNINITIALIZED),
mReleasedByResourceManager(false),
mLooper(looper),
mCodec(NULL),
mReplyID(0),
mFlags(0),
mStickyError(OK),
mSoftRenderer(NULL),
mIsVideo(false),
mVideoWidth(0),
mVideoHeight(0),
mRotationDegrees(0),
mDequeueInputTimeoutGeneration(0),
mDequeueInputReplyID(0),
mDequeueOutputTimeoutGeneration(0),
mDequeueOutputReplyID(0),
mTunneledInputWidth(0),
mTunneledInputHeight(0),
mTunneled(false),
mHaveInputSurface(false),
mHavePendingInputBuffers(false),
mCpuBoostRequested(false),
mLatencyUnknown(0),
mNumLowLatencyEnables(0),
mNumLowLatencyDisables(0),
mIsLowLatencyModeOn(false),
mIndexOfFirstFrameWhenLowLatencyOn(-1),
mInputBufferCounter(0),
mGetCodecBase(getCodecBase),
mGetCodecInfo(getCodecInfo) {
if (uid == kNoUid) {
mUid = AIBinder_getCallingUid();
} else {
mUid = uid;
}
mResourceManagerProxy = new ResourceManagerServiceProxy(pid, mUid,
::ndk::SharedRefBase::make<ResourceManagerClient>(this));
// 初始化时mCodecBase为空,就将mGetCodecBase指向了成员变量GetCodecBase。
if (!mGetCodecBase) {
mGetCodecBase = [](const AString &name, const char *owner) {
return GetCodecBase(name, owner);
};
}
// 初始化时mGetCodecInfo为空,但此处还进行了些操作
if (!mGetCodecInfo) {
mGetCodecInfo = [](const AString &name, sp<MediaCodecInfo> *info) -> status_t {
*info = nullptr;
// 继续通过MediaPlayerService获取MediaCodecList
const sp<IMediaCodecList> mcl = MediaCodecList::getInstance();
if (!mcl) {
return NO_INIT; // if called from Java should raise IOException
}
AString tmp = name;
if (tmp.endsWith(".secure")) {
tmp.erase(tmp.size() - 7, 7);
}
// 通过MediaCodecList中找到对应名字复合的下标,获取其MediaCodecInfo返回
for (const AString &codecName : { name, tmp }) {
ssize_t codecIdx = mcl->findCodecByName(codecName.c_str());
if (codecIdx < 0) {
continue;
}
*info = mcl->getCodecInfo(codecIdx);
return OK;
}
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
};
}
initMediametrics();
}
至此,构造函数对该两个方法进行了赋值,继续往下看init的流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
status_t MediaCodec::init(const AString &name) {
mResourceManagerProxy->init();
// save init parameters for reset
mInitName = name;
// Current video decoders do not return from OMX_FillThisBuffer
// quickly, violating the OpenMAX specs, until that is remedied
// we need to invest in an extra looper to free the main event
// queue.
mCodecInfo.clear();
bool secureCodec = false;
const char *owner = "";
if (!name.startsWith("android.filter.")) {
// getCodecInfo,上小节得知,是从MediaCodecList中获取MediaCodecInfo对象,返回到mCodecInfo中
status_t err = mGetCodecInfo(name, &mCodecInfo);
if (err != OK) {
mCodec = NULL; // remove the codec.
return err;
}
if (mCodecInfo == nullptr) {
ALOGE("Getting codec info with name '%s' failed", name.c_str());
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
secureCodec = name.endsWith(".secure");
Vector<AString> mediaTypes;
mCodecInfo->getSupportedMediaTypes(&mediaTypes);
for (size_t i = 0; i < mediaTypes.size(); ++i) {
if (mediaTypes[i].startsWith("video/")) {
mIsVideo = true;
break;
}
}
owner = mCodecInfo->getOwnerName();
}
// (1.1) getCodecBase
mCodec = mGetCodecBase(name, owner);
if (mCodec == NULL) {
ALOGE("Getting codec base with name '%s' (owner='%s') failed", name.c_str(), owner);
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
// (1.2) 注册Handler
if (mIsVideo) {
// video codec needs dedicated looper
if (mCodecLooper == NULL) {
mCodecLooper = new ALooper;
mCodecLooper->setName("CodecLooper");
mCodecLooper->start(false, false, ANDROID_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
}
mCodecLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
} else {
mLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
}
mLooper->registerHandler(this);
// (1.3) MediaCodec设置回调方法
mCodec->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::CodecCallback>(
new CodecCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
// (1.4) 重要的类型:CCodecBufferChannel,送码流和获取解码数据都会经过它实现
mBufferChannel = mCodec->getBufferChannel();
// (1.5) CCodecBufferChannel设置回调方法
mBufferChannel->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback>(
new BufferCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
sp<AMessage> msg = new AMessage(kWhatInit, this);
if (mCodecInfo) {
msg->setObject("codecInfo", mCodecInfo);
// name may be different from mCodecInfo->getCodecName() if we stripped
// ".secure"
}
msg->setString("name", name);
if (mMetricsHandle != 0) {
mediametrics_setCString(mMetricsHandle, kCodecCodec, name.c_str());
mediametrics_setCString(mMetricsHandle, kCodecMode,
mIsVideo ? kCodecModeVideo : kCodecModeAudio);
}
if (mIsVideo) {
mBatteryChecker = new BatteryChecker(new AMessage(kWhatCheckBatteryStats, this));
}
status_t err;
std::vector<MediaResourceParcel> resources;
resources.push_back(MediaResource::CodecResource(secureCodec, mIsVideo));
for (int i = 0; i <= kMaxRetry; ++i) {
if (i > 0) {
// Don't try to reclaim resource for the first time.
if (!mResourceManagerProxy->reclaimResource(resources)) {
break;
}
}
sp<AMessage> response;
// (1.6) 发送消息到Looper初始化,调用到CCodec的initiateAllocateComponent
err = PostAndAwaitResponse(msg, &response);
if (!isResourceError(err)) {
break;
}
}
return err;
}
(1.1) MediaCodec::getCodecBase
从这里我们得知, 通过owner或者name可以确定需要创建的Codec类型:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
sp<CodecBase> MediaCodec::GetCodecBase(const AString &name, const char *owner) {
if (owner) {
// default时创建ACodec,即OMX
if (strcmp(owner, "default") == 0) {
return new ACodec;
// 与codec2匹配时,调用CreateCCodec创建CCodec
} else if (strncmp(owner, "codec2", 6) == 0) {
return CreateCCodec();
}
}
// owner为空时,通过“c2”开头的创建CCodec
if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("c2.")) {
return CreateCCodec();
// "omx"开头的创建ACodec
} else if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("omx.")) {
// at this time only ACodec specifies a mime type.
return new ACodec;
// "android.filter"开头的创建MediaFilter
} else if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("android.filter.")) {
return new MediaFilter;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
在MediaCodec中会经常看到这样的消息发送代码:
1
2
3
4
sp<AMessage> msg = new AMessage([消息类型], this);
msg->setMessage("[消息键值]", [结构体]);
sp<AMessage> response;
return PostAndAwaitResponse(msg, &response);
而处理的类需要继承AHandler,并且重新定义onMessageReceived。具体的代码可以参考Handler源码分析。回过头看,当MediaCodec需要处理繁杂的消息时,需要设定对应的Handler,如init代码的内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
...
if (mIsVideo) {
// video codec needs dedicated looper
// 当判断是视频时,会新建一个ALooper,并且调用registerHandler进行注册
if (mCodecLooper == NULL) {
mCodecLooper = new ALooper;
mCodecLooper->setName("CodecLooper");
mCodecLooper->start(false, false, ANDROID_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
}
// 使用mCodecLooper注册Handler,处理流程在CCodec中
mCodecLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
} else {
// 使用本地的mLooper注册Handler,处理流程在CCodec中
mLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
}
// 使用本地的mLooper注册Handler,处理流程在MediaCodec中
mLooper->registerHandler(this);
...
明白了这点后,在发送对应的消息类型后,就可以在MediaCodec或者CCodec中查看了。
1
2
3
4
5
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
mCodec->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::CodecCallback>(
new CodecCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
先来看下MediaCodec的setCallback做了什么:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
status_t MediaCodec::setCallback(const sp<AMessage> &callback) {
sp<AMessage> msg = new AMessage(kWhatSetCallback, this);
msg->setMessage("callback", callback);
sp<AMessage> response;
return PostAndAwaitResponse(msg, &response);
}
有了之前的基础,就可以通过查找kWhatSetCallback来找到对应的处理流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
void MediaCodec::onMessageReceived(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
switch (msg->what()) {
...
case kWhatSetCallback:
{
sp<AReplyToken> replyID;
// 通过senderAwaitsResponse获取replyID
CHECK(msg->senderAwaitsResponse(&replyID));
if (mState == UNINITIALIZED
|| mState == INITIALIZING
|| isExecuting()) {
// callback can't be set after codec is executing,
// or before it's initialized (as the callback
// will be cleared when it goes to INITIALIZED)
PostReplyWithError(replyID, INVALID_OPERATION);
break;
}
//获取MediaCodec设置的callback
sp<AMessage> callback;
CHECK(msg->findMessage("callback", &callback));
// 将callback设置到mCallback
mCallback = callback;
if (mCallback != NULL) {
ALOGI("MediaCodec will operate in async mode");
mFlags |= kFlagIsAsync;
} else {
mFlags &= ~kFlagIsAsync;
}
//发送回复
sp<AMessage> response = new AMessage;
response->postReply(replyID);
break;
}
MediaCodec将回调对象给到CCodec中,是想希望CCodec有消息时,通知到上层的MediaCodec中。
(1.4) CCodec::getBufferChannel
至此终于涉及到CCodecBufferChannel这个类了,getBufferChannel定义在CCodec类中,如下:
1
2
3
4
std::shared_ptr<BufferChannelBase> CCodec::getBufferChannel() {
// mChannel在CCodec初始化时已经创建了!
return mChannel;
}
这里的设置回调是从CCodecBufferChannel中调用,setCallback函数是定义在CCodecBufferChannel的基类BufferChannelBase中。其目的也是将回调设置给CCodecBufferChannel中,希望CCodecBufferChannel有相应的消息后,通知到MediaCodec这一层。
(1.6) CCodec::initiateAllocateComponent
当完成上述步骤后,MediaCodec就开始发送消息类型为kWhatInit的消息给到Looper处理了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
...
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
void MediaCodec::onMessageReceived(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
...
case kWhatInit:
{
if (mState != UNINITIALIZED) {
PostReplyWithError(msg, INVALID_OPERATION);
break;
}
if (mReplyID) {
// 如果已经有mReplayID的话,将msg缓存起来
mDeferredMessages.push_back(msg);
break;
}
// 获取对应的replyID
sp<AReplyToken> replyID;
CHECK(msg->senderAwaitsResponse(&replyID));
mReplyID = replyID;
setState(INITIALIZING);
//从msg中找到名为“codecInfo”的MediaCodecInfo,这是从MediaCodecList中创建得来的。
sp<RefBase> codecInfo;
(void)msg->findObject("codecInfo", &codecInfo);
AString name;
//获取编解码器名字
CHECK(msg->findString("name", &name));
sp<AMessage> format = new AMessage;
if (codecInfo) {
format->setObject("codecInfo", codecInfo);
}
format->setString("componentName", name);
//(1.6.1)将message发送给CCodec中的initiateAllocateComponent进行初始化
mCodec->initiateAllocateComponent(format);
break;
}
(1.6.1) initiateallocatecomponent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
frameworks/av/media/codec2/sfplugin/CCodec.cpp
void CCodec::initiateAllocateComponent(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
auto setAllocating = [this] {
Mutexed<State>::Locked state(mState);
if (state->get() != RELEASED) {
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
state->set(ALLOCATING);
return OK;
};
if (tryAndReportOnError(setAllocating) != OK) {
return;
}
sp<RefBase> codecInfo;
CHECK(msg->findObject("codecInfo", &codecInfo));
// For Codec 2.0 components, componentName == codecInfo->getCodecName().
// (1.6.1.1)又发送kWhatAllocate消息,这次是CCodec处理,将MediaCodecInfo传入
sp<AMessage> allocMsg(new AMessage(kWhatAllocate, this));
allocMsg->setObject("codecInfo", codecInfo);
allocMsg->post();
}
void CCodec::onMessageReceived(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
TimePoint now = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
CCodecWatchdog::getInstance()->watch(this);
switch (msg->what()) {
case kWhatAllocate: {
// C2ComponentStore::createComponent() should return within 100ms.
setDeadline(now, 1500ms, "allocate");
sp<RefBase> obj;
CHECK(msg->findObject("codecInfo", &obj));
// (1.6.1.1) allocate
allocate((MediaCodecInfo *)obj.get());
break;
}
...
2.4 CCodec的初始化: allocate
从allocate再次理顺一下通路,如下图所示:
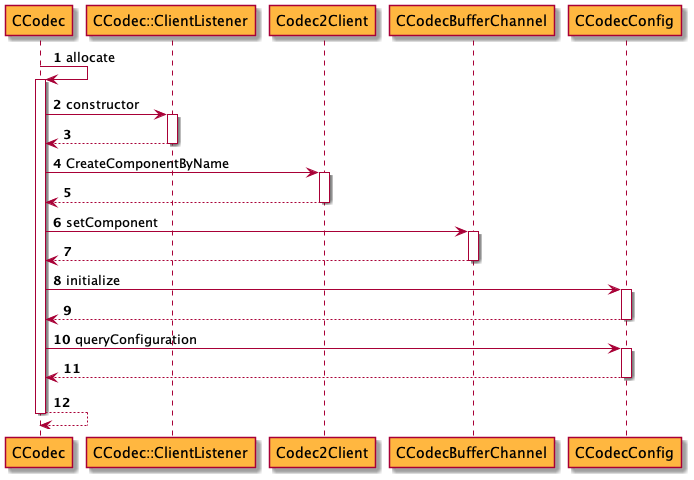
代码流程如下:
- (0) CCodec::allocate
- (A) CCodec::ClientListener的创建
- (B) CreateFromService
- (B.1) getServiceIndex
- (B.1.1) GetServiceNames
- (B.2) _CreateFromIndex创建Codec2Client
- (B.2.1) Base::getService
- (B.2.2) Codec2Client的创建
- (C) CreateComponentByName
- (C.1) createComponent
- (C.2) ForAllServices
- (D) CCodecBufferChannel::setComponent
- (B.1) getServiceIndex
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
frameworks/av/media/codec2/sfplugin/CCodec.cpp
void CCodec::allocate(const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &codecInfo) {
if (codecInfo == nullptr) {
mCallback->onError(UNKNOWN_ERROR, ACTION_CODE_FATAL);
return;
}
ALOGD("allocate(%s)", codecInfo->getCodecName());
// A. 新建ClientListener
mClientListener.reset(new ClientListener(this));
AString componentName = codecInfo->getCodecName();
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client;
// set up preferred component store to access vendor store parameters
// B. 创建服务,与软解或者硬解的服务交互
client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService("default");
if (client) {
ALOGI("setting up '%s' as default (vendor) store", client->getServiceName().c_str());
SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore(
std::make_shared<Codec2ClientInterfaceWrapper>(client));
}
// C. 创建服务组件
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component> comp =
Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
componentName.c_str(),
mClientListener,
&client);
if (!comp) {
ALOGE("Failed Create component: %s", componentName.c_str());
Mutexed<State>::Locked state(mState);
state->set(RELEASED);
state.unlock();
mCallback->onError(UNKNOWN_ERROR, ACTION_CODE_FATAL);
state.lock();
return;
}
ALOGI("Created component [%s]", componentName.c_str());
// D. 创建组件
mChannel->setComponent(comp);
auto setAllocated = [this, comp, client] {
Mutexed<State>::Locked state(mState);
if (state->get() != ALLOCATING) {
state->set(RELEASED);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
state->set(ALLOCATED);
state->comp = comp;
mClient = client;
return OK;
};
if (tryAndReportOnError(setAllocated) != OK) {
return;
}
// initialize config here in case setParameters is called prior to configure
Mutexed<std::unique_ptr<Config>>::Locked configLocked(mConfig);
const std::unique_ptr<Config> &config = *configLocked;
// CCodecConfig进行初始化
status_t err = config->initialize(mClient->getParamReflector(), comp);
if (err != OK) {
ALOGW("Failed to initialize configuration support");
// TODO: report error once we complete implementation.
}
// 查询组件的配置
config->queryConfiguration(comp);
mCallback->onComponentAllocated(componentName.c_str());
}
ClientListener继承了Codec2Client::Listener,实现了诸如:onWorkDone,onTripped,onError等多个回调函数,以onWorkDone为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
frameworks/av/media/codec2/sfplugin/CCodec.cpp
virtual void onWorkDone(
const std::weak_ptr<Codec2Client::Component>& component,
std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>>& workItems) override {
(void)component;
sp<CCodec> codec(mCodec.promote());
if (!codec) {
return;
}
// 回调函数onWorkDone调用时,实际上调用了CCodec的onWorkDone方法。
codec->onWorkDone(workItems);
}
如此看来,ClientListener如其名,也是当其底层调用回调时,负责调用到CCodec这一层的方法。后面在步骤C中的CreateComponentByName中,将会把ClientListener作为参数传给底层。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> Codec2Client::CreateFromService(
const char* name,
bool setAsPreferredCodec2ComponentStore) {
// (B.1)通过名字获得服务的下标
size_t index = getServiceIndex(name);
if (index == GetServiceNames().size()) {
if (setAsPreferredCodec2ComponentStore) {
LOG(WARNING) << "CreateFromService(" << name
<< ") -- preferred C2ComponentStore not set.";
}
return nullptr;
}
// (B.2) 通过下标获取对应的Codec2Client对象
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client = _CreateFromIndex(index);
if (setAsPreferredCodec2ComponentStore) {
// (B.3) 设置ComponentStore
SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore(
std::make_shared<Client2Store>(client));
LOG(INFO) << "CreateFromService(" << name
<< ") -- service set as preferred C2ComponentStore.";
}
return client;
}
获取服务下标,实际调用了Codec2Client的方法GetServiceNames获取vector集合,并遍历对比符合名字的返回对应下标。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
size_t getServiceIndex(char const* name) {
// B.1.1 GetServiceNames
std::vector<std::string> const& names = Codec2Client::GetServiceNames();
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < names.size(); ++i) {
if (name == names[i]) {
break;
}
}
return i;
}
在涉及如何获取服务时,先看下Manifest是如何定义的,以软解服务为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/services/manifest_media_c2_V1_0_default.xml
<manifest version="1.0" type="device">
<hal>
<name>android.hardware.media.c2</name>
<transport>hwbinder</transport>
<version>1.0</version>
<interface>
<name>IComponentStore</name>
<instance>default</instance>
</interface>
</hal>
</manifest>
可以看出,Manifest定义了HAL的名字”android.hardware.media.c2”, hidl传输方式”hwbinder”,interface的名字”IComponentStore”,instance的名字”default”。而GetServiceNames也是通过这些信息去定位到具体的HAL:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
std::vector<std::string> const& Codec2Client::GetServiceNames() {
static std::vector<std::string> sServiceNames{[]() {
using ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore;
using ::android::hidl::manager::V1_2::IServiceManager;
while (true) {
// 获取ServiceManager服务
sp<IServiceManager> serviceManager = IServiceManager::getService();
CHECK(serviceManager) << "Hardware service manager is not running.";
// There are three categories of services based on names.
std::vector<std::string> defaultNames; // Prefixed with "default"
std::vector<std::string> vendorNames; // Prefixed with "vendor"
std::vector<std::string> otherNames; // Others
Return<void> transResult;
// 通过Manifest中interface的名字"IComponentStore::descriptor"获取对应的服务
// lambda函数中,应当是指定了名字后,获取到了对应的所有instanceNames字符串集合
// 然后作为Lambada的输入进行遍历,从而将其进行分类(default开头的,vendor开头的,其余的)
transResult = serviceManager->listManifestByInterface(
IComponentStore::descriptor,
[&defaultNames, &vendorNames, &otherNames](
hidl_vec<hidl_string> const& instanceNames) {
for (hidl_string const& instanceName : instanceNames) {
char const* name = instanceName.c_str();
if (strncmp(name, "default", 7) == 0) {
defaultNames.emplace_back(name);
} else if (strncmp(name, "vendor", 6) == 0) {
vendorNames.emplace_back(name);
} else {
otherNames.emplace_back(name);
}
}
});
// hidl通信成功后,对三个集合进行排序
if (transResult.isOk()) {
// Sort service names in each category.
std::sort(defaultNames.begin(), defaultNames.end());
std::sort(vendorNames.begin(), vendorNames.end());
std::sort(otherNames.begin(), otherNames.end());
// Concatenate the three lists in this order: default, vendor,
// other.
// 三个集合合并为一个,以default,vendor,other排序
std::vector<std::string>& names = defaultNames;
names.reserve(names.size() + vendorNames.size() + otherNames.size());
names.insert(names.end(),
std::make_move_iterator(vendorNames.begin()),
std::make_move_iterator(vendorNames.end()));
names.insert(names.end(),
std::make_move_iterator(otherNames.begin()),
std::make_move_iterator(otherNames.end()));
// Summarize to logcat.
if (names.empty()) {
LOG(INFO) << "No Codec2 services declared in the manifest.";
} else {
//当names集合不为空时,返回该集合
std::stringstream stringOutput;
stringOutput << "Available Codec2 services:";
for (std::string const& name : names) {
stringOutput << " \"" << name << "\"";
}
LOG(INFO) << stringOutput.str();
}
return names;
}
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not retrieve the list of service instances of "
<< IComponentStore::descriptor
<< ". Retrying...";
}
}()};
return sServiceNames;
}
(B.2) _CreateFromIndex创建Codec2Client
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> Codec2Client::_CreateFromIndex(size_t index) {
std::string const& name = GetServiceNames()[index];
LOG(VERBOSE) << "Creating a Codec2 client to service \"" << name << "\"";
// (B.2.1)根据获取的名字,获取服务
sp<Base> baseStore = Base::getService(name);
CHECK(baseStore) << "Codec2 service \"" << name << "\""
" inaccessible for unknown reasons.";
LOG(VERBOSE) << "Client to Codec2 service \"" << name << "\" created";
// (B.2.2)根据baseStore和index创建Codec2Client
return std::make_shared<Codec2Client>(baseStore, index);
}
Codec2Client有一个类型为android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore的Base变量,getService正是通过IComponentStore中获取的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/include/codec2/hidl/client.h
struct Codec2Client : public Codec2ConfigurableClient {
typedef ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore Base1_0;
typedef ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_1::IComponentStore Base1_1;
typedef ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_2::IComponentStore Base1_2;
typedef Base1_0 Base;
...
}
IComponentStore的hal层接口文件定义在hardware/interfaces/media/c2/1.0/IComponentStore.hal, getService也是由于继承了HIDL的基类所以能够获取到服务。毫无疑问,这里将是与HAL层服务交互的一层。
1
2
3
4
out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/media/c2/1.0/android.hardware.media.c2@1.0_genc++/gen/android/hardware/media/c2/1.0/ComponentStoreAll.cpp
::android::sp<IComponentStore> IComponentStore::getService(const std::string &serviceName, const bool getStub) {
return ::android::hardware::details::getServiceInternal<BpHwComponentStore>(serviceName, true, getStub);
}
再深层次的代码就不再看了,属于hidl的系统代码,但是我们还是希望指导getService到底是获取了哪里的服务,以软解为例,这里和服务android.hardware.media.c2@1.2-default-service进行了交互, 并返回了类型为StoreImpl(继承了C2ComponentStore)的对象,后续我们会继续分析该知识点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
// Codec2Client
Codec2Client::Codec2Client(sp<Base> const& base,
size_t serviceIndex)
: Configurable{
// 匿名的Lambda方法,主要通过StoreImpl获取配置数据
[base]() -> sp<IConfigurable> {
Return<sp<IConfigurable>> transResult =
base->getConfigurable();
return transResult.isOk() ?
static_cast<sp<IConfigurable>>(transResult) :
nullptr;
}()
},
// mBase1_0,1_1,1_2分别指的是1.0,1.1,1.2的HAL版本,新版本都是基于前一版本的继承,所以直接cast就完了
mBase1_0{base},
mBase1_1{Base1_1::castFrom(base)},
mBase1_2{Base1_2::castFrom(base)},
mServiceIndex{serviceIndex} {
// 获取BuffferPool目录下的ClientManger服务,这部分放在后续分析
Return<sp<IClientManager>> transResult = base->getPoolClientManager();
if (!transResult.isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "getPoolClientManager -- transaction failed.";
} else {
mHostPoolManager = static_cast<sp<IClientManager>>(transResult);
}
}
回头再看,终于要创建对应的编解码组件了, 代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
//frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
c2_status_t Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
const char* componentName,
const std::shared_ptr<Listener>& listener,
std::shared_ptr<Component>* component,
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client>* owner,
size_t numberOfAttempts) {
std::string key{"create:"};
key.append(componentName);
// (C.2) ForAllServices
c2_status_t status = ForAllServices(
key,
numberOfAttempts,
[owner, component, componentName, &listener](
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> &client)
-> c2_status_t {
// (C.1) createComponent
c2_status_t status = client->createComponent(componentName,
listener,
component);
if (status == C2_OK) {
if (owner) {
*owner = client;
}
} else if (status != C2_NOT_FOUND) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "IComponentStore("
<< client->getServiceName()
<< ")::createComponent(\"" << componentName
<< "\") returned status = "
<< status << ".";
}
return status;
});
if (status != C2_OK) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Failed to create component \"" << componentName
<< "\" from all known services. "
"Last returned status = " << status << ".";
}
return status;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
//frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
c2_status_t Codec2Client::createComponent(
const C2String& name,
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Listener>& listener,
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component>* const component) {
c2_status_t status;
sp<Component::HidlListener> hidlListener = new Component::HidlListener{};
hidlListener->base = listener;
Return<void> transStatus;
// 判断HAL版本,使用对应的版本进行处理,并将hidlListener传下去,一旦下层有消息,就调用这个回调类型
if (mBase1_2) {
transStatus = mBase1_2->createComponent_1_2(
name,
hidlListener,
ClientManager::getInstance(),
[&status, component, hidlListener](
Status s,
const sp<IComponent>& c) {
status = static_cast<c2_status_t>(s);
if (status != C2_OK) {
return;
}
*component = std::make_shared<Codec2Client::Component>(c);
hidlListener->component = *component;
});
}
else if (mBase1_1) {
transStatus = mBase1_1->createComponent_1_1(
name,
hidlListener,
ClientManager::getInstance(),
[&status, component, hidlListener](
Status s,
const sp<IComponent>& c) {
status = static_cast<c2_status_t>(s);
if (status != C2_OK) {
return;
}
*component = std::make_shared<Codec2Client::Component>(c);
hidlListener->component = *component;
});
} else if (mBase1_0) { // ver1_0
// 以1.0版本为例子,调用到HAL层编解码组件的createComponent
transStatus = mBase1_0->createComponent(
name,
hidlListener,
ClientManager::getInstance(),
// 回调函数, component指向了底层创建的编解码组件,如果是软解H264,component就指向了C2SoftAvcDec(基类是C2Component)
[&status, component, hidlListener](
Status s,
const sp<hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponent>& c) {
status = static_cast<c2_status_t>(s);
if (status != C2_OK) {
return;
}
*component = std::make_shared<Codec2Client::Component>(c);
// 这里就将hidlListener和编解码组件联系起来了
hidlListener->component = *component;
});
} else {
status = C2_CORRUPTED;
}
if (!transStatus.isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "createComponent(" << name.c_str()
<< ") -- transaction failed.";
return C2_TRANSACTION_FAILED;
} else if (status != C2_OK) {
if (status == C2_NOT_FOUND) {
LOG(VERBOSE) << "createComponent(" << name.c_str()
<< ") -- component not found.";
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "createComponent(" << name.c_str()
<< ") -- call failed: " << status << ".";
}
return status;
} else if (!*component) {
LOG(ERROR) << "createComponent(" << name.c_str()
<< ") -- null component.";
return C2_CORRUPTED;
}
// 设置死亡通知,假如底层的编解码组件挂了,也会通知到Listenr中
status = (*component)->setDeathListener(*component, listener);
if (status != C2_OK) {
LOG(ERROR) << "createComponent(" << name.c_str()
<< ") -- failed to set up death listener: "
<< status << ".";
}
// mBufferPoolSender设置对应的接收者??
(*component)->mBufferPoolSender->setReceiver(mHostPoolManager);
return status;
}
从C1步骤看,我们确定了会通过createComponent创建组件,那么ForAllServices的意义呢?看起来有多个Service的样子?继续分析代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
// frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
c2_status_t Codec2Client::ForAllServices(
const std::string &key,
size_t numberOfAttempts,
std::function<c2_status_t(const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client>&)> predicate) {
c2_status_t status = C2_NO_INIT; // no IComponentStores present
// Cache the mapping key -> index of Codec2Client in Cache::List().
static std::mutex key2IndexMutex;
static std::map<std::string, size_t> key2Index;
// By default try all stores. However, try the last known client first. If
// the last known client fails, retry once. We do this by pushing the last
// known client in front of the list of all clients.
std::deque<size_t> indices;
for (size_t index = Cache::List().size(); index > 0; ) {
indices.push_front(--index);
}
bool wasMapped = false;
{
std::scoped_lock lock{key2IndexMutex};
auto it = key2Index.find(key);
if (it != key2Index.end()) {
indices.push_front(it->second);
wasMapped = true;
}
}
// Cache::List中保存有多个Service列表, 并对首先能够执行predicate,即CreateComponent成功的组件进行返回。
// 这里的顺序是与之前说的default,vendor,other来执行的。
for (size_t index : indices) {
Cache& cache = Cache::List()[index];
for (size_t tries = numberOfAttempts; tries > 0; --tries) {
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client{cache.getClient()};
status = predicate(client);
if (status == C2_OK) {
std::scoped_lock lock{key2IndexMutex};
key2Index[key] = index; // update last known client index
return C2_OK;
} else if (status == C2_NO_MEMORY) {
return C2_NO_MEMORY;
} else if (status == C2_TRANSACTION_FAILED) {
LOG(WARNING) << "\"" << key << "\" failed for service \""
<< client->getName()
<< "\" due to transaction failure. "
<< "(Service may have crashed.)"
<< (tries > 1 ? " Retrying..." : "");
cache.invalidate();
continue;
}
if (wasMapped) {
LOG(INFO) << "\"" << key << "\" became invalid in service \""
<< client->getName() << "\". Retrying...";
wasMapped = false;
}
break;
}
}
return status; // return the last status from a valid client
}
(D) CCodecBufferChannel::setComponent
当组件创建完毕后,CCodecBufferChannel会用mComponent指向它,后续将会利用component进行操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
void CCodecBufferChannel::setComponent(
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component> &component) {
mComponent = component;
mComponentName = component->getName() + StringPrintf("#%d", int(uintptr_t(component.get()) % 997));
mName = mComponentName.c_str();
}
CCodecConfig是关于Codec2的配置相关类型,后续将会专门研究。
2.6 Codec2的数据传输流程
在MediaCodec这一层,在解码方面直接就已经是拿到码流数据了,解封装流程在MediaExtractor这一层就已经完成了,不在本文的讨论范围内。所以可以认为解码时,输入码流数据(如h264,h265等等),然后经过层层传入,最终到达HAL层服务, 经过解码后,最终得到解码数据, 再层层返回。编码流程与该流程类似,只是输入输出反过来。
数据传输的流程如下所示:
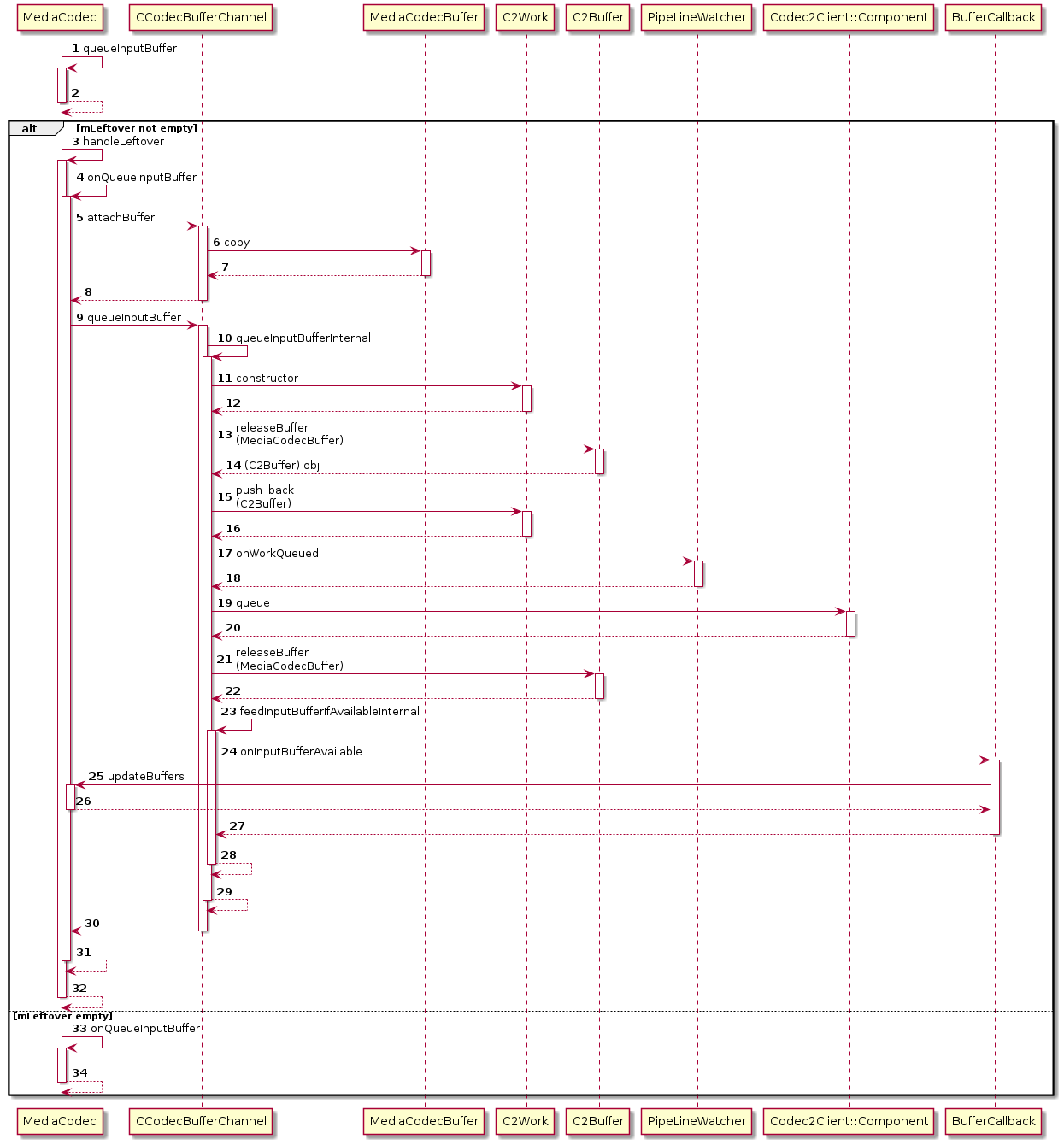
代码流程如下:
从MediaCodec的queueInputBuffer开始分析:
(A) MediaCodec::queueInputBuffer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
status_t MediaCodec::queueInputBuffer(
size_t index,
size_t offset,
size_t size,
int64_t presentationTimeUs,
uint32_t flags,
AString *errorDetailMsg) {
if (errorDetailMsg != NULL) {
errorDetailMsg->clear();
}
// 发送类型为kWhatQueueInpuBuffer给处理线程
sp<AMessage> msg = new AMessage(kWhatQueueInputBuffer, this);
msg->setSize("index", index);
msg->setSize("offset", offset);
msg->setSize("size", size);
msg->setInt64("timeUs", presentationTimeUs);
msg->setInt32("flags", flags);
msg->setPointer("errorDetailMsg", errorDetailMsg);
sp<AMessage> response;
return PostAndAwaitResponse(msg, &response);
}
// 处理流程
void MediaCodec::onMessageReceived(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
switch (msg->what()) {
...
case kWhatQueueInputBuffer:
{
sp<AReplyToken> replyID;
CHECK(msg->senderAwaitsResponse(&replyID));
if (!isExecuting()) {
PostReplyWithError(replyID, INVALID_OPERATION);
break;
} else if (mFlags & kFlagStickyError) {
PostReplyWithError(replyID, getStickyError());
break;
}
status_t err = UNKNOWN_ERROR;
// 当送输入数据时,假如申请的Buffer大小比实际数据要大时,
// 会将多出的数据转成C2Buffer放入到mLeftOver中, 那么下次就会优先处理这部分多出的数据
if (!mLeftover.empty()) {
mLeftover.push_back(msg);
size_t index;
msg->findSize("index", &index);
// handleLeftover实质也是调用下方的onQueueInputBuffer方法
err = handleLeftover(index);
} else {
// B. onQueueInputBuffer
err = onQueueInputBuffer(msg);
}
PostReplyWithError(replyID, err);
break;
}
...
}
- (B) MediaCodec::onQueueInputBuffer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
// frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/MediaCodec.cpp
status_t MediaCodec::onQueueInputBuffer(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
size_t index;
size_t offset;
size_t size;
int64_t timeUs;
uint32_t flags;
CHECK(msg->findSize("index", &index));
CHECK(msg->findInt64("timeUs", &timeUs));
CHECK(msg->findInt32("flags", (int32_t *)&flags));
std::shared_ptr<C2Buffer> c2Buffer;
sp<hardware::HidlMemory> memory;
sp<RefBase> obj;
// 从queueInputBuffer流程分析,此时c2buffer并没有传入到msg中, 所以前面的c2Buffer为空
if (msg->findObject("c2buffer", &obj)) {
CHECK(obj);
c2Buffer = static_cast<WrapperObject<std::shared_ptr<C2Buffer>> *>(obj.get())->value;
// 只要涉及安全的queueEncryptedBuffer才会去传入"memory"
} else if (msg->findObject("memory", &obj)) {
CHECK(obj);
memory = static_cast<WrapperObject<sp<hardware::HidlMemory>> *>(obj.get())->value;
CHECK(msg->findSize("offset", &offset));
} else {
CHECK(msg->findSize("offset", &offset));
}
const CryptoPlugin::SubSample *subSamples;
size_t numSubSamples;
const uint8_t *key;
const uint8_t *iv;
CryptoPlugin::Mode mode = CryptoPlugin::kMode_Unencrypted;
// We allow the simpler queueInputBuffer API to be used even in
// secure mode, by fabricating a single unencrypted subSample.
CryptoPlugin::SubSample ss;
CryptoPlugin::Pattern pattern;
// 普通的数据传输是会传入size
if (msg->findSize("size", &size)) {
if (hasCryptoOrDescrambler()) {
ss.mNumBytesOfClearData = size;
ss.mNumBytesOfEncryptedData = 0;
subSamples = &ss;
numSubSamples = 1;
key = NULL;
iv = NULL;
pattern.mEncryptBlocks = 0;
pattern.mSkipBlocks = 0;
}
// queueSecureInputBuffer不会传入size,所以此时检查到c2Buffer为空时,就会看是不是有异常了
} else if (!c2Buffer) {
if (!hasCryptoOrDescrambler()) {
ALOGE("[%s] queuing secure buffer without mCrypto or mDescrambler!",
mComponentName.c_str());
return -EINVAL;
}
CHECK(msg->findPointer("subSamples", (void **)&subSamples));
CHECK(msg->findSize("numSubSamples", &numSubSamples));
CHECK(msg->findPointer("key", (void **)&key));
CHECK(msg->findPointer("iv", (void **)&iv));
CHECK(msg->findInt32("encryptBlocks", (int32_t *)&pattern.mEncryptBlocks));
CHECK(msg->findInt32("skipBlocks", (int32_t *)&pattern.mSkipBlocks));
int32_t tmp;
CHECK(msg->findInt32("mode", &tmp));
mode = (CryptoPlugin::Mode)tmp;
size = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < numSubSamples; ++i) {
size += subSamples[i].mNumBytesOfClearData;
size += subSamples[i].mNumBytesOfEncryptedData;
}
}
// mPortBuffers[kPortIndexInput]表示的是输入的MediaCodecBuffer
if (index >= mPortBuffers[kPortIndexInput].size()) {
return -ERANGE;
}
BufferInfo *info = &mPortBuffers[kPortIndexInput][index];
// 从BufferInfo中获取到MediaCodecBuffer
sp<MediaCodecBuffer> buffer = info->mData;
// 这个条件不满足
if (c2Buffer || memory) {
sp<AMessage> tunings;
CHECK(msg->findMessage("tunings", &tunings));
onSetParameters(tunings);
status_t err = OK;
if (c2Buffer) {
err = mBufferChannel->attachBuffer(c2Buffer, buffer);
// 安全模式
} else if (memory) {
err = mBufferChannel->attachEncryptedBuffer(
memory, (mFlags & kFlagIsSecure), key, iv, mode, pattern,
offset, subSamples, numSubSamples, buffer);
} else {
err = UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
// 涉及到之前提到mLeftOver的操作,对多出数据放入mLeftOver
if (err == OK && !buffer->asC2Buffer()
&& c2Buffer && c2Buffer->data().type() == C2BufferData::LINEAR) {
C2ConstLinearBlock block{c2Buffer->data().linearBlocks().front()};
if (block.size() > buffer->size()) {
C2ConstLinearBlock leftover = block.subBlock(
block.offset() + buffer->size(), block.size() - buffer->size());
sp<WrapperObject<std::shared_ptr<C2Buffer>>> obj{
new WrapperObject<std::shared_ptr<C2Buffer>>{
C2Buffer::CreateLinearBuffer(leftover)}};
msg->setObject("c2buffer", obj);
mLeftover.push_front(msg);
// Not sending EOS if we have leftovers
flags &= ~BUFFER_FLAG_EOS;
}
}
offset = buffer->offset();
size = buffer->size();
if (err != OK) {
return err;
}
}
if (buffer == nullptr || !info->mOwnedByClient) {
return -EACCES;
}
if (offset + size > buffer->capacity()) {
return -EINVAL;
}
buffer->setRange(offset, size);
buffer->meta()->setInt64("timeUs", timeUs);
if (flags & BUFFER_FLAG_EOS) {
buffer->meta()->setInt32("eos", true);
}
// csd数据,一般为码流开始时携带
if (flags & BUFFER_FLAG_CODECCONFIG) {
buffer->meta()->setInt32("csd", true);
}
if (mTunneled) {
TunnelPeekState previousState = mTunnelPeekState;
switch(mTunnelPeekState){
case TunnelPeekState::kEnabledNoBuffer:
buffer->meta()->setInt32("tunnel-first-frame", 1);
mTunnelPeekState = TunnelPeekState::kEnabledQueued;
ALOGV("TunnelPeekState: %s -> %s",
asString(previousState),
asString(mTunnelPeekState));
break;
case TunnelPeekState::kDisabledNoBuffer:
buffer->meta()->setInt32("tunnel-first-frame", 1);
mTunnelPeekState = TunnelPeekState::kDisabledQueued;
ALOGV("TunnelPeekState: %s -> %s",
asString(previousState),
asString(mTunnelPeekState));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
status_t err = OK;
// 安全相关
if (hasCryptoOrDescrambler() && !c2Buffer && !memory) {
AString *errorDetailMsg;
CHECK(msg->findPointer("errorDetailMsg", (void **)&errorDetailMsg));
// Notify mCrypto of video resolution changes
if (mTunneled && mCrypto != NULL) {
int32_t width, height;
if (mInputFormat->findInt32("width", &width) &&
mInputFormat->findInt32("height", &height) && width > 0 && height > 0) {
if (width != mTunneledInputWidth || height != mTunneledInputHeight) {
mTunneledInputWidth = width;
mTunneledInputHeight = height;
mCrypto->notifyResolution(width, height);
}
}
}
err = mBufferChannel->queueSecureInputBuffer(
buffer,
(mFlags & kFlagIsSecure),
key,
iv,
mode,
pattern,
subSamples,
numSubSamples,
errorDetailMsg);
if (err != OK) {
mediametrics_setInt32(mMetricsHandle, kCodecQueueSecureInputBufferError, err);
ALOGW("Log queueSecureInputBuffer error: %d", err);
}
// (B.1) 普通模式下,使用CCodecBufferChannel的queueInputBuffer
} else {
err = mBufferChannel->queueInputBuffer(buffer);
if (err != OK) {
mediametrics_setInt32(mMetricsHandle, kCodecQueueInputBufferError, err);
ALOGW("Log queueInputBuffer error: %d", err);
}
}
if (err == OK) {
// synchronization boundary for getBufferAndFormat
Mutex::Autolock al(mBufferLock);
info->mOwnedByClient = false;
info->mData.clear();
statsBufferSent(timeUs, buffer);
}
return err;
}
- (B.1) CCodecBufferChannel::queueInputBuffer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// frameworks/av/media/codec2/sfplugin/CCodecBufferChannel.cpp
status_t CCodecBufferChannel::queueInputBuffer(const sp<MediaCodecBuffer> &buffer) {
QueueGuard guard(mSync);
if (!guard.isRunning()) {
ALOGD("[%s] No more buffers should be queued at current state.", mName);
return -ENOSYS;
}
return queueInputBufferInternal(buffer);
}