- 1.背景
- 2.总体概述
- 3. BatteryService
- 4.android.hardware.health@2.0-service
- 附录
- 参考文献
1.背景
由于前段时间负责的项目涉及到电源管理方面的内容,如电源的充放电状态,电源百分比等信息,由此萌发想学习相关方面的念头,而这又需要学习BatteryService,Healthd的源码。 为了查看Andorid最新源码地址https://cs.android.com/,本文基于Android 10.0基础上学习。
2.总体概述
2.1 源码结构
电源框架源码包括如下:
-
system/core/healthd/
-
hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/
BatteryService,BatteryManager在源码解析时会标明其文件位置。
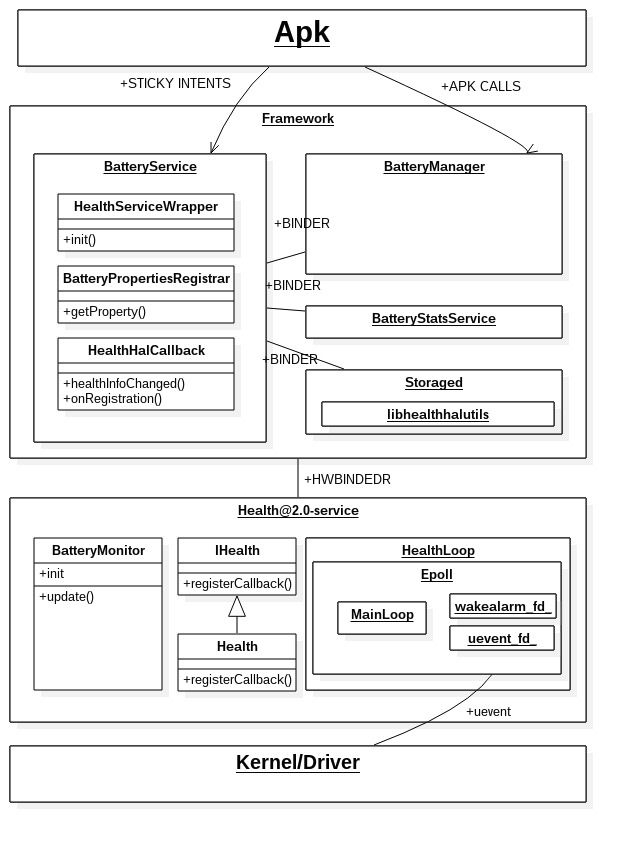
2.2 系统框架
Android 10.0 电源的系统框架如下图所示,接下来的学习就按照这个框架从上往下学习,主要将学习计划分为如下几点:
- BatteryService
- Healthd
如果对之前的电源框架感兴趣,可以参考链接:
链接清晰的讲述了Android 8.0/9.0的框架变化,本文也是基于这个框架去从源码角度去分析电源框架的内容。
3. BatteryService
首先从BatteryService着手分析,BatteryService即为电池服务,是在SystemServer中启动的一个服务, 负责监听充电状态,电量的变化等等.
3.1 BatteryService的启动
3.1.1 SystemServer启动BatteryService
SystemServer启动的服务,首先都会通过SystemServiceManager通过startService启动服务,其中又会调用服务的构造方法以及调用方法onStart.紧接着,SystemServiceManager又会通过startBootPhase对已经启动的服务进行启动后的处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
//SystemServer在开启核心服务时,第一个就是开启BatteryService
private void startCoreServices() {
...
//startService的实现可以参考附录5,将会调用BatteryService构造方法以及onStart
mSystemServiceManager.startServicde(BatteryService.class);
....
}
3.1.2 BatteryService的构造方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
public BatteryService(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
mHandler = new Handler(true /*async*/);
//获取Led服务(本地服务,通过getLocalService获取的),用于改变灯的状态。
mLed = new Led(context, getLocalService(LightsManager.class));
//获取BatteryStatsService服务,用于电量统计。
mBatteryStats = BatteryStatsService.getService();
//获取ActivityManager
mActivityManagerInternal = LocalServices.getService(ActivityManagerInternal.class);
/*
mCriticalBatteryLevel==5,低于该电量将强制关机。
mLowBatteryWarningLevel==15,低于该电量将会提示报警,同时将会发送广播ACTION_BATTERY_LOW。
mLowBatteryCloseWarningLevel==10,高于该值时,将结束低电量提示,同时发送广播ACTION_BATTER_OKAY。
mShutdownBatteryTemperature==680,即68°,高于该温度将自动关机。
*/
mCriticalBatteryLevel = mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_criticalBatteryWarningLevel);
mLowBatteryWarningLevel = mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_lowBatteryWarningLevel);
mLowBatteryCloseWarningLevel = mLowBatteryWarningLevel + mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_lowBatteryCloseWarningBump);
mShutdownBatteryTemperature = mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_shutdownBatteryTemperature);
mBatteryLevelsEventQueue = new ArrayDeque<>();
mMetricsLogger = new MetricsLogger();
//检测是否有不匹配的充电器,通过uevent发送。
if (new File("/sys/devices/virtual/switch/invalid_charger/state").exists()) {
UEventObserver invalidChargerObserver = new UEventObserver() {
@Override
public void onUEvent(UEvent event) {
final int invalidCharger = "1".equals(event.get("SWITCH_STATE")) ? 1 : 0;
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mInvalidCharger != invalidCharger) {
mInvalidCharger = invalidCharger;
}
}
}
};
invalidChargerObserver.startObserving(
"DEVPATH=/devices/virtual/switch/invalid_charger");
}
}
3.1.3 onStart
当BatteryService服务构建完后,SystemServiceManager紧接着调用onStart:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
@Override
public void onStart() {
//重要的方法,详细分析跳转到3.1.3.1
registerHealthCallback();
/*
创建BinderService,并注册到ServiceManger中。
dumpsys battery可以与服务交互并查看电池信息。
详细分析跳转到3.1.3.2
*/
mBinderService = new BinderService();
publishBinderService("battery", mBinderService);
/*
BatteryPropertiesRegistrar电池属性登记者
注册到ServiceManager中,BatteryManager可以通过binder通信获取电池属性
*/
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar = new BatteryPropertiesRegistrar();
publishBinderService("batteryproperties", mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar);
//注册本地服务,详细分析跳转到
publishLocalService(BatteryManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
}
3.1.3.1 registerHealthCallback
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private void registerHealthCallback() {
/*
新建了HealthServiceWrapper对象.
HealthServiceWrapper提供了init方法用于初始化IHealth服务.
HealthServiceWrapper中定义了一个Callback的接口类,其接口为onRegistration.
当接收到一个IServiceNotification时,就会调用onRegistration。
*/
mHealthServiceWrapper = new HealthServiceWrapper();
/*
HealthHalCallback实现了HealthServiceWrapper的Callback(实现onRegistration),
但同时也继承了IHealthInfoCallback.Stub(说明该类用于binder通信,且为服务端。
IHealthInfoCallback.Stub必须实现方法healthInfoChanged,当HealthInfo更新后将会调用该方法。)
*/
mHealthHalCallback = new HealthHalCallback();
try {
/*
调用HealthServiceWrapper的init方法,将callback对象传入
并又创建了两个新类IServiceManagerSupplier以及IHealthSupplier
1.IServiceMangerSupplier意为IServiceManager的提供者,是用来获取hidl的ServiceManager服务的。
2.IHealthSupplier意为IHealth的提供者,是用来获取IHealth服务的。
上述两者IServiceManager以及IHealth都是通过hal文件编译而成,默认带有getService获取hidl的ServiceManager。通常查看hal文件就能够看出该文件的功能。
*/
mHealthServiceWrapper.init(mHealthHalCallback,
new HealthServiceWrapper.IServiceManagerSupplier() {},
new HealthServiceWrapper.IHealthSupplier() {});
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
...
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
} catch (NoSuchElementException ex) {
...
throw ex;
} finally {
...
}
...
}
//再来看下HealthServiceWrapper.init的实现
...
private Callback mCallback;
...
void init(Callback callback,
IServiceManagerSupplier managerSupplier,
IHealthSupplier healthSupplier)
throws RemoteException, NoSuchElementException, NullPointerException {
if (callback == null || managerSupplier == null || healthSupplier == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
IServiceManager是通过编译system/libhidl/transport/manager/1.0/仓库下的IServiceManager.hal,
在对应的out目录下生成IServiceManager.java文件。
*/
IServiceManager manager;
mCallback = callback;
mHealthSupplier = healthSupplier;
IHealth newService = null;
for (String name : sAllInstances) {
try {
//获取IHealth服务,为Native进程,通过hwbinder通信。
newService = healthSupplier.get(name);
} catch (NoSuchElementException ex) {
/* ignored, handled below */
} finally {
...
}
if (newService != null) {
mInstanceName = name;
//将mLastService变量设置为newService
mLastService.set(newService);
break;
}
}
if (mInstanceName == null || newService == null) {....}
/*
此处调用HealthHalCallback的onRegistration,将newService作为初始服务注册,由于是第一次注册,
oldService为null.
HealthHalCallback的onRegistration会调用IHealth的方法registerCallback,将mCallback注册到
IHealth中,为后续IHealth通知到上层BatteryService做好准备
(IHealth通过回调方法healthInfoChanged通知BatteryService)。
*/
mCallback.onRegistration(null, newService, mInstanceName);
//运行HandlerThread线程。新开一个线程用于处理IHealth接收到的服务。
mHandlerThread.start();
try {
/*
为IHealth服务在ServiceManager中注册notification通知。当有IHealth的消息来临时,
就会调用mNotificaiton的onRegistration方法处理。
*/
managerSupplier.get().registerForNotifications(
IHealth.kInterfaceName, mInstanceName, mNotification);
} finally {
...
}
}
3.1.3.2 BinderService
BatteryService内部定义了一个BinderService服务,并继承了Binder父类。这样的目的是为了通过dumpsys,可以调用到BinderService服务的dump方法,从而获取到电池信息。(dumpsys通过和ServiceManager通信,将参数传给BinderService)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private final class BinderService extends Binder {
@Override protected void dump(FileDescriptor fd, PrintWriter pw, String[] args) {
if (!DumpUtils.checkDumpPermission(mContext, TAG, pw)) return;
if (args.length > 0 && "--proto".equals(args[0])) {
dumpProto(fd);
} else {
//输入dumpsys battery时打印电池信息
dumpInternal(fd, pw, args);
}
}
...
}
//所有电池信息来源于mHealthInfo。
private void dumpInternal(FileDescriptor fd, PrintWriter pw, String[] args) {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (args == null || args.length == 0 || "-a".equals(args[0])) {
pw.println("Current Battery Service state:");
if (mUpdatesStopped) {
pw.println(" (UPDATES STOPPED -- use 'reset' to restart)");
}
pw.println(" AC powered: " + mHealthInfo.chargerAcOnline);
pw.println(" USB powered: " + mHealthInfo.chargerUsbOnline);
pw.println(" Wireless powered: " + mHealthInfo.chargerWirelessOnline);
pw.println(" Max charging current: " + mHealthInfo.maxChargingCurrent);
pw.println(" Max charging voltage: " + mHealthInfo.maxChargingVoltage);
pw.println(" Charge counter: " + mHealthInfo.batteryChargeCounter);
pw.println(" status: " + mHealthInfo.batteryStatus);
pw.println(" health: " + mHealthInfo.batteryHealth);
pw.println(" present: " + mHealthInfo.batteryPresent);
pw.println(" level: " + mHealthInfo.batteryLevel);
pw.println(" scale: " + BATTERY_SCALE);
pw.println(" voltage: " + mHealthInfo.batteryVoltage);
pw.println(" temperature: " + mHealthInfo.batteryTemperature);
pw.println(" technology: " + mHealthInfo.batteryTechnology);
} else {
Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.exec(mBinderService, null, fd, null, args, null, new ResultReceiver(null));
}
}
}
3.1.3.3 BatteryPropertiesRegistrar
BatteryService新建了BatteryPropertiesRegistrar对象。以往BatteryPropertiesRegistrar使用C++实现的服务,进行重构后,以Java代码实现在了BatteryService中。
1
2
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar = new BatteryPropertiesRegistrar();
publishBinderService("batteryproperties", mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar);
新建BatteryPropertiesRegistrar(继承stub,为服务类),并将其注册到ServiceManger中,BatteryPropertiesRegistrar的形式如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private final class BatteryPropertiesRegistrar extends IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.Stub {
@Override
public int getProperty(int id, final BatteryProperty prop) throws RemoteException {
traceBegin("HealthGetProperty");
try {
//获取LastService,是IHealth服务
IHealth service = mHealthServiceWrapper.getLastService();
if (service == null) throw new RemoteException("no health service");
final MutableInt outResult = new MutableInt(Result.NOT_SUPPORTED);
switch(id) {
//遍历ID来判断是需要获取什么属性,从而通过IHealth服务获取,并返回到outResult中。
case BatteryManager.BATTERY_PROPERTY_CHARGE_COUNTER:
service.getChargeCounter((int result, int value) -> {
outResult.value = result;
if (result == Result.SUCCESS) prop.setLong(value);
});
break;
}
.....
return outResult.value;
}
finally {
....
}
}
BatteryManager可以通过Binder通信和BatteryPropertiesRegistrar通信。BatteryManger使用BatteryPropertiesRegistrar的方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/BatteryManager.java
public BatteryManager() {
mContext = null;
mBatteryStats = IBatteryStats.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(BatteryStats.SERVICE_NAME));
//通过以下方式就可以用到mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar,自然也可以调用getproperty方法了。
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar = IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService("batteryproperties"));
}
3.1.3.4 LocalService
1
publishLocalService(BatteryManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
publishLocalService一般用于注册本地服务,即用于在SystemServer同一个进程的服务可以通过getLocalService去获取其他服务的内容。如通过LocalService就可以获取如下信息:
- isPowered //是否正在充电
- getPlugType //充电类型,1为AC,2为USB,3为WIRELESS
- getBatteryLevel //充电百分比
- getBatteryChargeCounter //充电次数
- getBatteryFullCharge //是否完全充电
- getBatteryLevelLow //是否电池电量低
- getInvalidCharger //获取是否存在不匹配的充电器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private final class LocalService extends BatteryManagerInternal {
@Override
public boolean isPowered(int plugTypeSet) {
synchronized (mLock) {
return isPoweredLocked(plugTypeSet);
}
}
@Override
public int getPlugType() {
synchronized (mLock) {
return mPlugType;
}
}
@Override
public int getBatteryLevel() {
synchronized (mLock) {
return mHealthInfo.batteryLevel;
}
}
@Override
public int getBatteryChargeCounter() {
synchronized (mLock) {
return mHealthInfo.batteryChargeCounter;
}
}
@Override
public int getBatteryFullCharge() {
synchronized (mLock) {
return mHealthInfo.batteryFullCharge;
}
}
@Override
public boolean getBatteryLevelLow() {
synchronized (mLock) {
return mBatteryLevelLow;
}
}
@Override
public int getInvalidCharger() {
synchronized (mLock) {
return mInvalidCharger;
}
}
}
3.1.4 onBootPhase
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
@Override
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
//表明ActivityManagerService此时已处于准备状态
if (phase == PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY) {
// check our power situation now that it is safe to display the shutdown dialog.
synchronized (mLock) {
//新建一个ContentObserver(内容观察者),当监察的uri(LOW_POWER_MODE_TRIGGER_LEVEL)发生变化时(即检测到低电量了),就调用updateBatteryWarningLevelLocked方法进行处理。
ContentObserver obs = new ContentObserver(mHandler) {
@Override
public void onChange(boolean selfChange) {
synchronized (mLock) {
updateBatteryWarningLevelLocked();
}
}
};
final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Global.getUriFor(
Settings.Global.LOW_POWER_MODE_TRIGGER_LEVEL),
false, obs, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
//手动先调用了一次。
updateBatteryWarningLevelLocked();
}
}
}
3.2 BatteryService的电量管理
BatteryService当电量低时,或者接收到来自IHealth的通知时,都会调用到其中一个重要的方法processValuesLocked.以后者流程分析,其流程图如下:
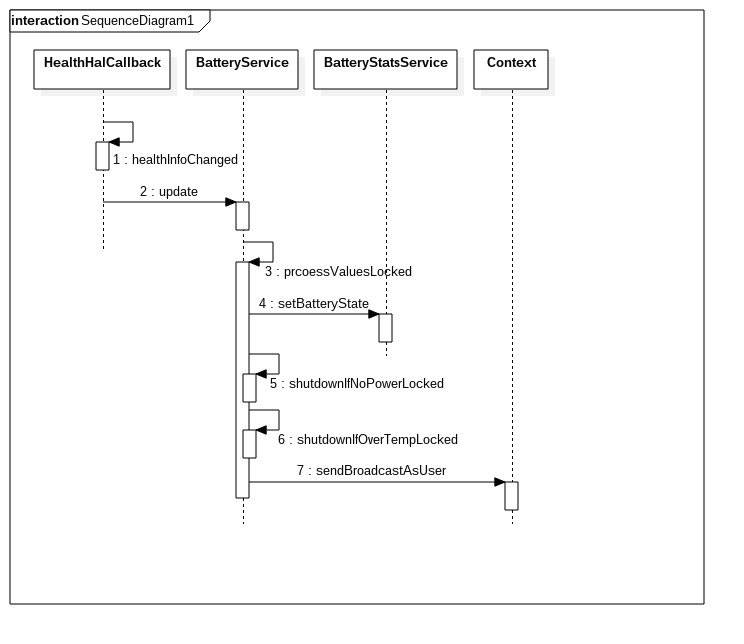
3.2.1 healthInfoChanged
之前提到将Notification注册到hwServiceManager中,指明监听IHealth服务的消息,并将HealthCallback注册到IHealth服务中。现在分析接收到IHealth服务的通知时,BatteryService的流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private final class HealthHalCallback extends IHealthInfoCallback.Stub
implements HealthServiceWrapper.Callback {
@Override public void healthInfoChanged(android.hardware.health.V2_0.HealthInfo props) {
//跳转到BatteryService的update方法,props是IHealth传递上来的
BatteryService.this.update(props);
SystemProperties.set("battery.present",props.legacy.batteryPresent+"");
}
...
}
### 3.2.2 BatteryService.update
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private void update(android.hardware.health.V2_0.HealthInfo info) {
...
synchronized (mLock) {
if (!mUpdatesStopped) {
mHealthInfo = info.legacy;
//核心方法,处理电池信息
processValuesLocked(false);
mLock.notifyAll(); // for any waiters on new info
} else {
copy(mLastHealthInfo, info.legacy);
}
}
}
3.2.3 BatteryService.processValuesLocked
processValuesLocked的代码很长,如图可以简单归纳为以下几个步骤:
- mBatteryStats.setBatteryState设置电池统计数据
- BatteryService.shutdownIfNoPowerLocked检查是否因电池不足而关机
- BatteryService.shutdownIfNoPowerLocked检查是否因温度过高而关机
- 发送系统广播通知应用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private void processValuesLocked(boolean force) {
boolean logOutlier = false;
long dischargeDuration = 0;
//检查是否为电池已经严重不足
mBatteryLevelCritical =
mHealthInfo.batteryStatus != BatteryManager.BATTERY_STATUS_UNKNOWN
&& mHealthInfo.batteryLevel <= mCriticalBatteryLevel;
//检查充电类型
if (mHealthInfo.chargerAcOnline) {
mPlugType = BatteryManager.BATTERY_PLUGGED_AC;
} else if (mHealthInfo.chargerUsbOnline) {
mPlugType = BatteryManager.BATTERY_PLUGGED_USB;
} else if (mHealthInfo.chargerWirelessOnline) {
mPlugType = BatteryManager.BATTERY_PLUGGED_WIRELESS;
} else {
mPlugType = BATTERY_PLUGGED_NONE;
}
....
//Step A. 将最新的HealthInfo信息传入到BatteryStats中。
try {
mBatteryStats.setBatteryState(mHealthInfo.batteryStatus, mHealthInfo.batteryHealth,
mPlugType, mHealthInfo.batteryLevel, mHealthInfo.batteryTemperature,
mHealthInfo.batteryVoltage, mHealthInfo.batteryChargeCounter,
mHealthInfo.batteryFullCharge);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Should never happen.
}
//Step B. 电量低时关机
shutdownIfNoPowerLocked();
//Step C. 温度高时关机
shutdownIfOverTempLocked();
//如果force为true(强制的)或者电池信息与最近的状态发生变化了
if (force || (mHealthInfo.batteryStatus != mLastBatteryStatus ||
mHealthInfo.batteryHealth != mLastBatteryHealth ||
mHealthInfo.batteryPresent != mLastBatteryPresent ||
mHealthInfo.batteryLevel != mLastBatteryLevel ||
mPlugType != mLastPlugType ||
mHealthInfo.batteryVoltage != mLastBatteryVoltage ||
mHealthInfo.batteryTemperature != mLastBatteryTemperature ||
mHealthInfo.maxChargingCurrent != mLastMaxChargingCurrent ||
mHealthInfo.maxChargingVoltage != mLastMaxChargingVoltage ||
mHealthInfo.batteryChargeCounter != mLastChargeCounter ||
mInvalidCharger != mLastInvalidCharger)) {
...
}
....
}
mSequence++;
//当电源插入时,发送广播Intent.ACTION_POWER_CONNECTED
if (mPlugType != 0 && mLastPlugType == 0) {
final Intent statusIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_POWER_CONNECTED);
statusIntent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT);
statusIntent.putExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SEQUENCE, mSequence);
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(statusIntent, UserHandle.ALL);
}
});
}
//当电源断开时,发送广播Intent.ACTION_POWER_DISCONNECTED
else if (mPlugType == 0 && mLastPlugType != 0) {
final Intent statusIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_POWER_DISCONNECTED);
statusIntent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT);
statusIntent.putExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SEQUENCE, mSequence);
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(statusIntent, UserHandle.ALL);
}
});
}
//当电池电量低时,发送广播Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_LOW
if (shouldSendBatteryLowLocked()) {
mSentLowBatteryBroadcast = true;
final Intent statusIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_LOW);
statusIntent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT);
statusIntent.putExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SEQUENCE, mSequence);
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(statusIntent, UserHandle.ALL);
}
});
//当电池电量高于低等级时,发送广播Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_OKAY
} else if (mSentLowBatteryBroadcast &&
mHealthInfo.batteryLevel >= mLowBatteryCloseWarningLevel) {
mSentLowBatteryBroadcast = false;
final Intent statusIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_OKAY);
statusIntent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT);
statusIntent.putExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SEQUENCE, mSequence);
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(statusIntent, UserHandle.ALL);
}
});
}
//这里也是发广播,Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED。并带上非常详细的电池信息
sendBatteryChangedIntentLocked();
if (mLastBatteryLevel != mHealthInfo.batteryLevel || mLastPlugType != mPlugType) {
//电池百分比变化时还是发广播,Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_LEVEL_CHANGED
sendBatteryLevelChangedIntentLocked();
}
//更新Led灯状态
mLed.updateLightsLocked();
...
//将当前电池状态更新最近的电池状态中.
mLastBatteryStatus = mHealthInfo.batteryStatus;
mLastBatteryHealth = mHealthInfo.batteryHealth;
mLastBatteryPresent = mHealthInfo.batteryPresent;
mLastBatteryLevel = mHealthInfo.batteryLevel;
mLastPlugType = mPlugType;
mLastBatteryVoltage = mHealthInfo.batteryVoltage;
mLastBatteryTemperature = mHealthInfo.batteryTemperature;
mLastMaxChargingCurrent = mHealthInfo.maxChargingCurrent;
mLastMaxChargingVoltage = mHealthInfo.maxChargingVoltage;
mLastChargeCounter = mHealthInfo.batteryChargeCounter;
mLastBatteryLevelCritical = mBatteryLevelCritical;
mLastInvalidCharger = mInvalidCharger;
}
}
详细再分析下shutdownIfNoPowerLocked和shutdownIfOverTempLocked.
3.2.3.1 shutdownIfNoPowerLocked
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private void shutdownIfNoPowerLocked() {
//shouldShutdownLocked判断是否需要关机
if (shouldShutdownLocked()) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mActivityManagerInternal.isSystemReady()) {
//关机也是通过发送Intent.ACTION_REQUEST_SHUTDOWN
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_REQUEST_SHUTDOWN);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_KEY_CONFIRM, false);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REASON,
PowerManager.SHUTDOWN_LOW_BATTERY);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mContext.startActivityAsUser(intent, UserHandle.CURRENT);
}
}
});
}
}
private boolean shouldShutdownLocked() {
//电池百分大于0,不应该关机
if (mHealthInfo.batteryLevel > 0) {
return false;
}
//没有电池的设备不应该关机,比如盒子之类的
if (!mHealthInfo.batteryPresent) {
return false;
}
// If battery state is not CHARGING, shutdown.
// - If battery present and state == unknown, this is an unexpected error state.
// - If level <= 0 and state == full, this is also an unexpected state
// - All other states (NOT_CHARGING, DISCHARGING) means it is not charging.
/*
电池状态不等为BATTERY_STATUS_CHARGING应该要关机
*/
return mHealthInfo.batteryStatus != BatteryManager.BATTERY_STATUS_CHARGING;
}
3.2.3.2 shutdownIfOverTempLocked
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/BatteryService.java
private void shutdownIfOverTempLocked() {
//当温度比设定关机温度高时,确认关机
if (mHealthInfo.batteryTemperature > mShutdownBatteryTemperature) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mActivityManagerInternal.isSystemReady()) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_REQUEST_SHUTDOWN);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_KEY_CONFIRM, false);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REASON,
PowerManager.SHUTDOWN_BATTERY_THERMAL_STATE);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mContext.startActivityAsUser(intent, UserHandle.CURRENT);
}
}
});
}
}
4.android.hardware.health@2.0-service
分析了BatteryService后,正式开始分析health@2.0-service,在以往名为healthd。
4.1 Android.bp/mk
一般进入工程习惯先看Android.bp或者mk文件,确定这个模块中编译的输入和输出,以当前关心的先以binary文件着手分析:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# system/core/healthd/Android.bp
cc_binary {
# 编译出的binary名
name: "android.hardware.health@2.0-service",
# 默认依赖的库
defaults: ["android.hardware.health@2.0-service_defaults"],
vendor: true,
#编译binary路径为/vendor/bin/hw/路径下
relative_install_path: "hw",
# 服务对应的rc文件
init_rc: ["android.hardware.health@2.0-service.rc"],
# 编译源文件
srcs: [
"HealthServiceDefault.cpp",
],
# 将binary "healthd"覆盖
overrides: [
"healthd",
]
}
在以往的Android平台中,该服务名为Healthd,Android 10.0使用了”android.hardware.health@2.0-service”来代替了服务Healthd。但后续为了方便分析,还是将android.hardware.health@2.0-service简称为healthd
为了让大家了解编译文件所依赖的文件,可以参考下图:
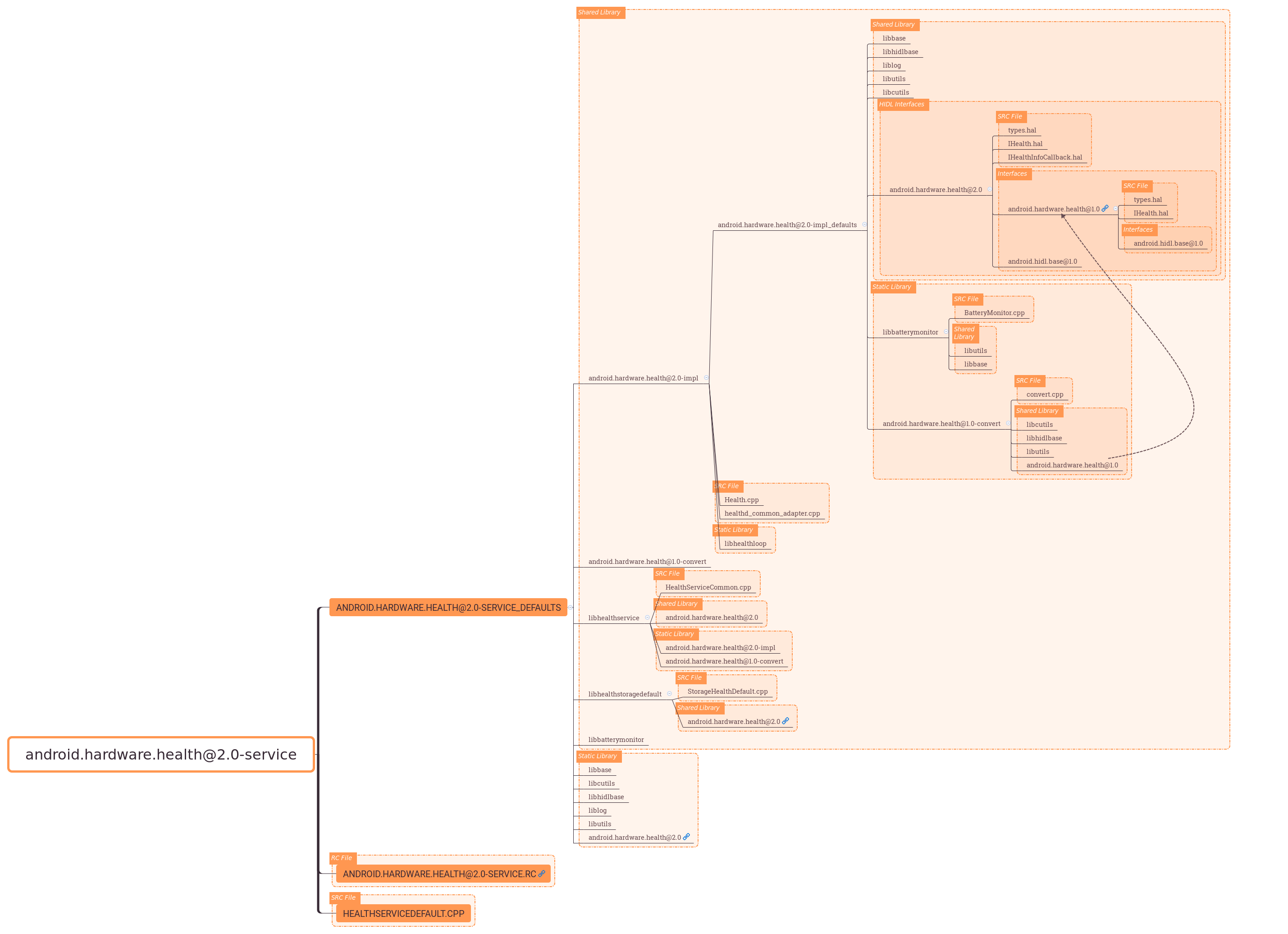
4.2 healthd入口
从Android.bp中的srcs字段即指定源文件,作为开始分析的入口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// system/core/healthd/HealthServiceDefault.cpp
#include <health2/service.h>
#include <healthd/healthd.h>
....
int main() {
return health_service_main();
}
HealthServiceDefault内容十分简洁,直接分析health_service_main,跳转到HAL目录中。
4.2.1 health_service_main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/utils/libhealthservice/HealthServiceCommon.cpp
/*
healthd的常用操作包括,init,preparetowait,heartbeat,battery_update后续将一一分析。
*/
static struct healthd_mode_ops healthd_mode_service_2_0_ops = {
.init = healthd_mode_service_2_0_init,
.preparetowait = healthd_mode_service_2_0_preparetowait,
.heartbeat = healthd_mode_service_2_0_heartbeat,
.battery_update = healthd_mode_service_2_0_battery_update,
};
//instance默认为空字符,因此gInstanceName为字符串"default"
int health_service_main(const char* instance) {
gInstanceName = instance;
if (gInstanceName.empty()) {
gInstanceName = "default";
}
//ops初始化
healthd_mode_ops = &healthd_mode_service_2_0_ops;
LOG(INFO) << LOG_TAG << gInstanceName << ": Hal starting main loop...";
//跳转到4.2.2小节healthd_main分析
return healthd_main();
}
4.2.2 healthd_main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/default/healthd_common_adapter.cpp
int healthd_main() {
//首先检查下healthd_mode_ops是否为空
if (!healthd_mode_ops) {
KLOG_ERROR("healthd ops not set, exiting\n");
exit(1);
}
//使用make系列的方式创建对象HealthLoopAdapter,参照4.3.2小节
health_loop = std::make_unique<HealthLoopAdapter>();
//循环处理,参照4.3.3.2小节
int ret = health_loop->StartLoop();
// Should not reach here. The following will exit().
health_loop.reset();
return ret;
}
值得一提的是,使用make函数代替new或者unique_ptr等智能指针,能够消除代码重复,提高异常安全的优势,具体可以查看下make_unique的实现方式。接下来看看HealthLooperAdapter的实现。
4.3.2 HealthLooperAdapter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/default/healthd_common_adapter.cpp
class HealthLoopAdapter : public HealthLoop {
public:
int RegisterEvent(int fd, BoundFunction func, EventWakeup wakeup) {
return HealthLoop::RegisterEvent(fd, func, wakeup);
}
void AdjustWakealarmPeriods(bool charger_online) {
return HealthLoop::AdjustWakealarmPeriods(charger_online);
}
protected:
//这边的接口和上文提到的接口一一对应,实际上调用的即healthd_mode_service_2_0_op的接口。
void Init(healthd_config* config) override { healthd_mode_ops->init(config); }
void Heartbeat() override { healthd_mode_ops->heartbeat(); }
int PrepareToWait() override { return healthd_mode_ops->preparetowait(); }
void ScheduleBatteryUpdate() override { Health::getImplementation()->update(); }
};
Adapter仅仅是适配的功能,还需要看HealthLoop以及healthd_mode_ops的实现。
4.3.3 HealthLoop
4.3.3.1 HealthLoop构造函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/HealthLoop.cpp
HealthLoop::HealthLoop() {
/*
healthd_config_类型为healthd_config
struct healthd_config healthd_config_;
*/
//初始化healthd_config
InitHealthdConfig(&healthd_config_);
awake_poll_interval_ = -1;
wakealarm_wake_interval_ = healthd_config_.periodic_chores_interval_fast;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
//system/core/healthd/include/healthd/healthd.h
struct healthd_config {
//间隔模式fast/slow,分别对应60s和600s
int periodic_chores_interval_fast;
int periodic_chores_interval_slow;
//电池的信息路径
android::String8 batteryStatusPath;
android::String8 batteryHealthPath;
android::String8 batteryPresentPath;
android::String8 batteryCapacityPath;
android::String8 batteryVoltagePath;
android::String8 batteryTemperaturePath;
android::String8 batteryTechnologyPath;
android::String8 batteryCurrentNowPath;
android::String8 batteryCurrentAvgPath;
android::String8 batteryChargeCounterPath;
android::String8 batteryFullChargePath;
android::String8 batteryCycleCountPath;
android::String8 batteryCapacityLevelPath;
android::String8 batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath;
int (*energyCounter)(int64_t *);
int boot_min_cap;
bool (*screen_on)(android::BatteryProperties *props);
std::vector<android::String8> ignorePowerSupplyNames;
};
enum EventWakeup {
EVENT_NO_WAKEUP_FD,
EVENT_WAKEUP_FD,
};
healthd_config定义了两种方式分别为periodic_chores_interval_fast以及periodic_chores_interval_slow。默认HealthLoop设置为前者,简单来说,interval指的是服务healthd从休眠到唤醒(wake up)后将health信息poll出来并处理周期性的任务之间的时间。其中periodic_chores_interval_fast适用于设备不在suspend状态,或者充着电的时候处于suspend状态。此时interval设置为60s.后者periodic_chores_interval_slow适用于设备处于suspend状态且没有充电。interval设置为10分钟。
电池的信息路径如batteryStatusPath等,后续会在BatteryMonitor中更新。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/utils.cpp
// Periodic chores fast interval in seconds
#define DEFAULT_PERIODIC_CHORES_INTERVAL_FAST (60 * 1)
// Periodic chores fast interval in seconds
#define DEFAULT_PERIODIC_CHORES_INTERVAL_SLOW (60 * 10)
void InitHealthdConfig(struct healthd_config* healthd_config) {
*healthd_config = {
.periodic_chores_interval_fast = DEFAULT_PERIODIC_CHORES_INTERVAL_FAST,
.periodic_chores_interval_slow = DEFAULT_PERIODIC_CHORES_INTERVAL_SLOW,
.batteryStatusPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryHealthPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryPresentPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryCapacityPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryVoltagePath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryTemperaturePath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryTechnologyPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryCurrentNowPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryCurrentAvgPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryChargeCounterPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryFullChargePath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryCycleCountPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryCapacityLevelPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath = String8(String8::kEmptyString),
.energyCounter = NULL,
.boot_min_cap = 0,
.screen_on = NULL,
};
}
InitHealthdConfig只是对healthd_config进行了简单初始化。
至此分析了基类HealthLoop()的构造方法逻辑,还需要看StartLoop的实现。
4.3.3.2 HealthLoop::StartLoop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/HealthLoop.cpp
#define KLOG_LEVEL 6
...
int HealthLoop::StartLoop() {
int ret;
//设置内核打印等级,此处为6
klog_set_level(KLOG_LEVEL);
//Step 1. 参照4.3.3.2.1
ret = InitInternal();
if (ret) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "Initialization failed, exiting\n");
return 2;
}
//Step 2. 参照4.3.3.2.2
MainLoop();
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "Main loop terminated, exiting\n");
return 3;
}
StartLoop分两个步骤,InitInternal以及MainLoop.
4.3.3.2.1 InitInternal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/HealthLoop.cpp
int HealthLoop::InitInternal() {
/*
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/include/health/HealthLoop.h
android::base::unique_fd epollfd_;
*/
epollfd_.reset(epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC));
if (epollfd_ == -1) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "epoll_create1 failed; errno=%d\n", errno);
return -1;
}
// Call subclass's init for any additional init steps.
// Note that healthd_config_ is initialized before wakealarm_fd_; see
// AdjustUeventWakealarmPeriods().
//此处是调用healthd_mode_service_2_0_init,参考Step A
Init(&healthd_config_);
//参考Step B
WakeAlarmInit();
//参考Step C
UeventInit();
return 0;
}
A. healthd_mode_service_2_0_init
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/utils/libhealthservice/HealthServiceCommon.cpp
void healthd_mode_service_2_0_init(struct healthd_config* config) {
LOG(INFO) << LOG_TAG << gInstanceName << " Hal is starting up...";
/*
setupTransportPolling实际将用于hidl通信的binder线程设置数量为1(只需要一个用于polling)
并将BC_ENTER_LOOPER写进parcel中,表明上层服务应当是准备好了,能够和hwbinder进行通信了。
gBinderFd即hwbinder驱动fd
*/
gBinderFd = setupTransportPolling();
if (gBinderFd >= 0) {
if (healthd_register_event(gBinderFd, binder_event))
LOG(ERROR) << LOG_TAG << gInstanceName << ": Register for binder events failed";
}
//初始化Health服务,即新建一个Health对象。
android::sp<IHealth> service = Health::initInstance(config);
//注册名为gInstanceName的服务到HAL,检查其返回值。
CHECK_EQ(service->registerAsService(gInstanceName), android::OK)
<< LOG_TAG << gInstanceName << ": Failed to register HAL";
LOG(INFO) << LOG_TAG << gInstanceName << ": Hal init done";
}
马上再看Health这个类以及initInstance的实现,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
//hidl_death_recipeient是一个回调的接口类能够与linkToDeath()/unlinktoDeath一起使用。
struct Health : public IHealth, hidl_death_recipient {
public:
static sp<IHealth> initInstance(struct healthd_config* c);
...
}
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/default/Health.cpp
Health::Health(struct healthd_config* c) {
healthd_board_init(c);
//此处终于新建了BatteryMonitor对象了,定义在/system/core中。
battery_monitor_ = std::make_unique<BatteryMonitor>();
//battery_monitor初始化,传入参数healthd_config
battery_monitor_->init(c);
}
sp<IHealth> Health::initInstance(struct healthd_config* c) {
if (instance_ == nullptr) {
//新建了Health对象
instance_ = new Health(c);
}
return instance_;
}
BatteryMonitor从接口而言,大多是获取类型的,如getChargeStatus,getProperty,getHealthInfo**等等,是上层能够获取到电池信息的重要一环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
//system/core/healthd/BatteryMonitor.cpp
BatteryMonitor::BatteryMonitor()
: mHealthdConfig(nullptr),
mBatteryDevicePresent(false),
mBatteryFixedCapacity(0),
mBatteryFixedTemperature(0),
mHealthInfo(std::make_unique<HealthInfo_2_1>()) {
//初始化电池信息
initHealthInfo(mHealthInfo.get());
}
static void initHealthInfo(HealthInfo_2_1* health_info_2_1) {
*health_info_2_1 = HealthInfo_2_1{};
// HIDL enum values are zero initialized, so they need to be initialized
// properly.
health_info_2_1->batteryCapacityLevel = BatteryCapacityLevel::UNKNOWN;
auto* props = &health_info_2_1->legacy.legacy;
props->batteryStatus = BatteryStatus::UNKNOWN;
props->batteryHealth = BatteryHealth::UNKNOWN;
}
再来看BatteryMonitor的init方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
//system/core/healthd/BatteryMonitor.cpp
#define POWER_SUPPLY_SUBSYSTEM "power_supply"
#define POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH "/sys/class/" POWER_SUPPLY_SUBSYSTEM
...
void BatteryMonitor::init(struct healthd_config *hc) {
String8 path;
char pval[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
mHealthdConfig = hc;
//读取目录/sys/class/power_supply
std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)> dir(opendir(POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH), closedir);
if (dir == NULL) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "Could not open %s\n", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH);
} else {
struct dirent* entry;
//遍历读取该目录下的文件
while ((entry = readdir(dir.get()))) {
const char* name = entry->d_name;
std::vector<String8>::iterator itIgnoreName;
if (!strcmp(name, ".") || !strcmp(name, ".."))
continue;
itIgnoreName = find(hc->ignorePowerSupplyNames.begin(),
hc->ignorePowerSupplyNames.end(), String8(name));
if (itIgnoreName != hc->ignorePowerSupplyNames.end())
continue;
// Look for "type" file in each subdirectory
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/type", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
//类型共分为AC,USB,WIRELESS,BATTERY
switch(readPowerSupplyType(path)) {
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_AC:
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_USB:
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_WIRELESS:
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/online", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
//online即表明当前设备是否有该类型的电源供给。如AC的/sys/class/power_supply/ac/online为1时,即插入了AC电源。
//如果能够访问,就用一个Vector变量mChargerNames将其加入方便管理
if (access(path.string(), R_OK) == 0)
mChargerNames.add(String8(name));
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_BATTERY:
mBatteryDevicePresent = true;
//如果是电池类型,那么就检查路径/sys/class/power_supply/battery/status是否能够访问,如果能够就对mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath赋值。
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/status", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath = path;
}
//下面是对电池的路径一一赋值
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/health", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath = path;
}
//设备是否有电池
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/present", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath = path;
}
//电池容量
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/capacity", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/voltage_now",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) {
mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath = path;
}
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/charge_full",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath = path;
}
//电池当前电流
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/current_now",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/cycle_count",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath = path;
}
//该路径即电源的百分比
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityLevelPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/capacity_level", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityLevelPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/time_to_full_now", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargeDesignCapacityUahPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/charge_full_design", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargeDesignCapacityUahPath = path;
}
//电池平均电流
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentAvgPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/current_avg",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentAvgPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/charge_counter",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath = path;
}
//电池温度
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/temp", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) {
mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath = path;
}
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/technology",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath = path;
}
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_UNKNOWN:
break;
}
}
}
//如下逻辑一般指的是那些没有电池的设备,则periodic_chores_interval_fast/slow都会置为-1
if (!mBatteryDevicePresent) {
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "No battery devices found\n");
hc->periodic_chores_interval_fast = -1;
hc->periodic_chores_interval_slow = -1;
} else {
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryStatusPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryHealthPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryPresentPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryCapacityPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryVoltagePath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryTemperaturePath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryTechnologyPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryCurrentNowPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryFullChargePath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryCycleCountPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityLevelPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "batteryCapacityLevelPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath. not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargeDesignCapacityUahPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "batteryFullChargeDesignCapacityUahPath. not found\n");
}
if (property_get("ro.boot.fake_battery", pval, NULL) > 0
&& strtol(pval, NULL, 10) != 0) {
mBatteryFixedCapacity = FAKE_BATTERY_CAPACITY;
mBatteryFixedTemperature = FAKE_BATTERY_TEMPERATURE;
}
}
从上面代码可以得出,BatteryMonitor::int做的工作是初始化,并将之前的config的电池信息进行初始化,将具体的节点路径复制到config中,以后在BatteryMonitor就可以获取电池信息了。
B. WakeAlarmInit
WakeAlarmInit用于监听Alarm,假如收到信息,会调用WakeAlarmEvent唤醒系统。常用的场景应当是休眠时闹钟到时间时,唤醒系统。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/HealthLoop.cpp
void HealthLoop::WakeAlarmInit(void) {
//创建了一个定时器fd,类型为CLOCK_BOOTTIME_ALARM,具体timerfd_create用法可以参考附录1。
wakealarm_fd_.reset(timerfd_create(CLOCK_BOOTTIME_ALARM, TFD_NONBLOCK));
if (wakealarm_fd_ == -1) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "wakealarm_init: timerfd_create failed\n");
return;
}
//注册fd,回调函数为WakeAlarmEvent,即定时去调用回调函数更新数据。
//RegisterEvent与Epoll的用法相关,详情可以查看附录
if (RegisterEvent(wakealarm_fd_, &HealthLoop::WakeAlarmEvent, EVENT_WAKEUP_FD))
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "Registration of wakealarm event failed\n");
设置interval为fast即60s
WakeAlarmSetInterval(healthd_config_.periodic_chores_interval_fast);
}
void HealthLoop::WakeAlarmEvent(uint32_t /*epevents*/) {
unsigned long long wakeups;
if (read(wakealarm_fd_, &wakeups, sizeof(wakeups)) == -1) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "wakealarm_event: read wakealarm fd failed\n");
return;
}
//重点在这
PeriodicChores();
}
void HealthLoop::PeriodicChores() {
//参考小节D
ScheduleBatteryUpdate();
}
暂且不往下分析,先看下UeventInit做了什么。
C. UeventInit
Uevent的原理不在这里多解释,具体可以看参考文献3.可以看做是用户一种内核空间和用户空间之间的通信机制,广泛用于热插拔,电量通知等,这里即为了监听电池信息的变化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/HealthLoop.cpp
void HealthLoop::UeventInit(void) {
//创建了uevent fd,打开的socket的buffer size为64K
uevent_fd_.reset(uevent_open_socket(64 * 1024, true));
if (uevent_fd_ < 0) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "uevent_init: uevent_open_socket failed\n");
return;
}
//设置为非阻塞通信
fcntl(uevent_fd_, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
//注册uevent的fd,回调函数为UeventEvent
if (RegisterEvent(uevent_fd_, &HealthLoop::UeventEvent, EVENT_WAKEUP_FD))
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "register for uevent events failed\n");
}
...
#define UEVENT_MSG_LEN 2048
void HealthLoop::UeventEvent(uint32_t /*epevents*/) {
char msg[UEVENT_MSG_LEN + 2];
char* cp;
int n;
//通过uevent_fd_读取信息到msg中,uevent_kernel_multicast_recv的实现感兴趣可以查看附录
n = uevent_kernel_multicast_recv(uevent_fd_, msg, UEVENT_MSG_LEN);
//检查数据长度
if (n <= 0) return;
if (n >= UEVENT_MSG_LEN) /* overflow -- discard */
return;
msg[n] = '\0';
msg[n + 1] = '\0';
cp = msg;
//检查信息中是否存在"SUBSYSTEM= power_supply"的信息,如果有,调用ScheduleBatteryUpdate,
//这方法在之前的回调方法中也有调用过。
while (*cp) {
if (!strcmp(cp, "SUBSYSTEM=" POWER_SUPPLY_SUBSYSTEM)) {
//参考后续小节SchedulBatteryUpdate
ScheduleBatteryUpdate();
break;
}
/* advance to after the next \0 */
while (*cp++)
;
}
}
在这里可以看出uevent事件是通过socket去读取信息的,当电池电量,温度,电压,电流等发起变化时,就会更新power_supply节点,并通过PMU驱动将发送Uevent到上层Healthd中,此时就会调用ScheduleBatteryUpdate进行信息的更新。
D. ScheduleBatteryUpdate
ScheduleBatteryUpdate最终会调用到BatteryMonitor中的update方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/default/healthd_common_adapter.cpp
class HealthLoopAdapter : public HealthLoop {
...
//调用了getImplementation的update方法,暂时跳过,后续分析。
void ScheduleBatteryUpdate() override { Health::getImplementation()->update(); }
...
}
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/default/Health.cpp
sp<Health> Health::instance_;
....
sp<Health> Health::getImplementation() {
CHECK(instance_ != nullptr);
//instance_即Health
return instance_;
}
Return<Result> Health::update() {
if (!healthd_mode_ops || !healthd_mode_ops->battery_update) {
LOG(WARNING) << "health@2.0: update: not initialized. "
<< "update() should not be called in charger";
return Result::UNKNOWN;
}
// Retrieve all information and call healthd_mode_ops->battery_update, which calls
// notifyListeners.
//参考步骤I updateValues 更新电池信息
battery_monitor_->updateValues();
//步骤II 类型转换
const HealthInfo_1_0& health_info = battery_monitor_->getHealthInfo_1_0();
struct BatteryProperties props;
convertFromHealthInfo(health_info, &props);
//默认healthd_board_battery_update返回0,即log为true
bool log = (healthd_board_battery_update(&props) == 0);
if (log) {
//步骤III 打印电池信息
battery_monitor_->logValues();
}
//即调用healthd_mode_service_2_0_battery_update,参考步骤IV 通知上层服务电池信息变化
healthd_mode_ops->battery_update(&props);
//充电状态一般而言会判断AC,USB,以及Wireless。
bool chargerOnline = battery_monitor_->isChargerOnline();
// adjust uevent / wakealarm periods
// 步骤 V 调整uevent/wakealarm的周期
healthd_battery_update_internal(chargerOnline);
return Result::SUCCESS;
}
至此,Health::update涉及的都是关于BatteryMonitor的操作,下面对这些步骤逐一详细分析。
Step I BatteryMonitor::updateValues
如果还记得之前BatteryMonitor::init,该方法打开了节点/sys/class/power_supply目录,并将节点的信息,包括AC,USB,Battery等记录在结构体mHealthConfig中。updateValues新建了props,并用于保存mHealthConfig中的信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
//system/core/healthd/include/healthd/BatteryMonitor.h
..
std::unique_ptr<android::hardware::health::V2_1::HealthInfo> mHealthInfo;
...
//system/core/healthd/BatteryMonitor.cpp
void BatteryMonitor::updateValues(void) {
//初始化HealthInfo,当前master分支上是初始化HealthInfo_2_1
initHealthInfo(mHealthInfo.get());
HealthInfo_1_0& props = mHealthInfo->legacy.legacy;
//更新props的属性
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryPresent = getBooleanField(mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath);
else
props.batteryPresent = mBatteryDevicePresent;
props.batteryLevel = mBatteryFixedCapacity ?
mBatteryFixedCapacity :
getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath);
props.batteryVoltage = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath) / 1000;
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryCurrent = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath) / 1000;
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty())
props.batteryFullCharge = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryCycleCount = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryChargeCounter = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentAvgPath.isEmpty())
mHealthInfo->legacy.batteryCurrentAverage =
getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentAvgPath);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath.isEmpty())
mHealthInfo->batteryChargeTimeToFullNowSeconds =
getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeTimeToFullNowPath);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargeDesignCapacityUahPath.isEmpty())
mHealthInfo->batteryFullChargeDesignCapacityUah =
getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargeDesignCapacityUahPath);
props.batteryTemperature = mBatteryFixedTemperature ?
mBatteryFixedTemperature :
getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath);
std::string buf;
if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityLevelPath, &buf) > 0)
mHealthInfo->batteryCapacityLevel = getBatteryCapacityLevel(buf.c_str());
if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath, &buf) > 0)
props.batteryStatus = getBatteryStatus(buf.c_str());
if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath, &buf) > 0)
props.batteryHealth = getBatteryHealth(buf.c_str());
if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath, &buf) > 0)
props.batteryTechnology = String8(buf.c_str());
double MaxPower = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < mChargerNames.size(); i++) {
String8 path;
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/online", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
mChargerNames[i].string());
if (getIntField(path)) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/type", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
mChargerNames[i].string());
switch(readPowerSupplyType(path)) {
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_AC:
props.chargerAcOnline = true;
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_USB:
props.chargerUsbOnline = true;
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_WIRELESS:
props.chargerWirelessOnline = true;
break;
default:
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "%s: Unknown power supply type\n",
mChargerNames[i].string());
}
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/current_max", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
mChargerNames[i].string());
int ChargingCurrent =
(access(path.string(), R_OK) == 0) ? getIntField(path) : 0;
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/voltage_max", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
mChargerNames[i].string());
int ChargingVoltage =
(access(path.string(), R_OK) == 0) ? getIntField(path) :
DEFAULT_VBUS_VOLTAGE;
double power = ((double)ChargingCurrent / MILLION) *
((double)ChargingVoltage / MILLION);
if (MaxPower < power) {
props.maxChargingCurrent = ChargingCurrent;
props.maxChargingVoltage = ChargingVoltage;
MaxPower = power;
}
}
}
}
至此,我们只需知道信息都已经同步到 mHealthInfo中即可,后续整理字段的含义。
Step II convertFromHealthInfo
上一个步骤将信息更新到mHealthInfo中,步骤II中的getHealthInfo_1_0即返回的是mHealthInfo对象,并通过convertFromHealthInfo,将mHealthInfo转化为类型为BatteryProperties的对象,其定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
//frameworks/native/services/batteryservice/include/batteryservice/BatteryService.h
struct BatteryProperties {
bool chargerAcOnline;
bool chargerUsbOnline;
bool chargerWirelessOnline;
int maxChargingCurrent;
int maxChargingVoltage;
int batteryStatus;
int batteryHealth;
bool batteryPresent;
int batteryLevel;
int batteryVoltage;
int batteryTemperature;
int batteryCurrent;
int batteryCycleCount;
int batteryFullCharge;
int batteryChargeCounter;
String8 batteryTechnology;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
//hardware/interfaces/health/1.0/default/convert.cpp
void convertFromHealthInfo(const HealthInfo& info,
struct android::BatteryProperties *p) {
p->chargerAcOnline = info.chargerAcOnline; //AC或者USB是否插入电源
p->chargerUsbOnline = info.chargerUsbOnline;//USB是否插入电源
p->chargerWirelessOnline = info.chargerWirelessOnline;//Wireless是否有充电
p->maxChargingCurrent = info.maxChargingCurrent;//电池最大充电电流
p->maxChargingVoltage = info.maxChargingVoltage;//电池最大充电电压
p->batteryStatus = static_cast<int>(info.batteryStatus);//电池状态
p->batteryHealth = static_cast<int>(info.batteryHealth);//电池是否健康
p->batteryPresent = info.batteryPresent;//电池是否有在用
p->batteryLevel = info.batteryLevel;//电池百分比
p->batteryVoltage = info.batteryVoltage;//当前电池电压
p->batteryTemperature = info.batteryTemperature;//电池温度
p->batteryCurrent = info.batteryCurrent;//电池电流
p->batteryCycleCount = info.batteryCycleCount;//循环充电次数
p->batteryFullCharge = info.batteryFullCharge;//电池是否完成充电了
p->batteryChargeCounter = info.batteryChargeCounter;//充电次数
p->batteryTechnology = android::String8(info.batteryTechnology.c_str());//电池类型
}
Step III logValues
这个方法在串口时观察内核打印可以经常看到这个方法被调用,如下:
1
healthd battery l=72 v=3994 t=3.0 h=2 st=2 c=1040 fc=5066880 chg=au
也许以前看到这个打印的时候还不太清楚其中的字段的含义,先看看logValues的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
//system/core/healthd/BatteryMonitor.cpp
void BatteryMonitor::logValues(void) {
char dmesgline[256];
size_t len;
const HealthInfo_1_0& props = mHealthInfo->legacy.legacy;
if (props.batteryPresent) {
/*
l为充电百分比,v为电池电压,t为电池温度,h为电池健康,st为电池状态
*/
snprintf(dmesgline, sizeof(dmesgline), "battery l=%d v=%d t=%s%d.%d h=%d st=%d",
props.batteryLevel, props.batteryVoltage, props.batteryTemperature < 0 ? "-" : "",
abs(props.batteryTemperature / 10), abs(props.batteryTemperature % 10),
props.batteryHealth, props.batteryStatus);
len = strlen(dmesgline);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty()) {
//c为电池电流
len += snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len, " c=%d",
props.batteryCurrent);
}
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty()) {
//fc为电池完全充电容量
len += snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len, " fc=%d",
props.batteryFullCharge);
}
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty()) {
//cc为完全充电次数
len += snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len, " cc=%d",
props.batteryCycleCount);
}
} else {
len = snprintf(dmesgline, sizeof(dmesgline), "battery none");
}
//chg字段中,a表示AC正在充电,u表示USB正在充电,w表示无线正在充电
snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len, " chg=%s%s%s",
props.chargerAcOnline ? "a" : "", props.chargerUsbOnline ? "u" : "",
props.chargerWirelessOnline ? "w" : "");
//最终内核打印出来
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "%s\n", dmesgline);
}
Step IV battery_update
battery_update之前说过最终会调用到healthd_mode_service_2_0_battery_update,其实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/utils/libhealthservice/HealthServiceCommon.cpp
void healthd_mode_service_2_0_battery_update(struct android::BatteryProperties* prop) {
HealthInfo info;
//将BatteryProperties转为HealthInfo
convertToHealthInfo(prop, info.legacy);
//通知Listeners,还将HealthInfo作为参数传入?
Health::getImplementation()->notifyListeners(&info);
}
看到这里就有点疑惑,到底是谁在监听?继续看代码Health:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/default/Health.cpp
void Health::notifyListeners(HealthInfo* healthInfo) {
std::vector<StorageInfo> info;
get_storage_info(info);
std::vector<DiskStats> stats;
get_disk_stats(stats);
int32_t currentAvg = 0;
struct BatteryProperty prop;
status_t ret = battery_monitor_->getProperty(BATTERY_PROP_CURRENT_AVG, &prop);
if (ret == OK) {
currentAvg = static_cast<int32_t>(prop.valueInt64);
}
//重新更新了如电池平均电流信息,diskStats,stoargeInfos等信息。
healthInfo->batteryCurrentAverage = currentAvg;
healthInfo->diskStats = stats;
healthInfo->storageInfos = info;
//加了锁
std::lock_guard<decltype(callbacks_lock_)> lock(callbacks_lock_);
//遍历callbacks_,并调用其接口healthInfoChanged.
for (auto it = callbacks_.begin(); it != callbacks_.end();) {
auto ret = (*it)->healthInfoChanged(*healthInfo);
if (!ret.isOk() && ret.isDeadObject()) {
it = callbacks_.erase(it);
} else {
++it;
}
}
}
看到这里大概明白,假如有服务对于电池的信息感兴趣,可以通过实现一个healthInfoChanged接口,并进行注册,当update时,信息就会同步刅该服务中。以其中一个storaged为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
//system/core/storaged/storaged.cpp
void storaged_t::init() {
init_health_service();
mDsm = std::make_unique<disk_stats_monitor>(health);
storage_info.reset(storage_info_t::get_storage_info(health));
}
void storaged_t::init_health_service() {
if (!mUidm.enabled())
return;
health = get_health_service();
if (health == NULL) {
LOG(WARNING) << "health: failed to find IHealth service";
return;
}
BatteryStatus status = BatteryStatus::UNKNOWN;
auto ret = health->getChargeStatus([&](Result r, BatteryStatus v) {
if (r != Result::SUCCESS) {
LOG(WARNING) << "health: cannot get battery status " << toString(r);
return;
}
if (v == BatteryStatus::UNKNOWN) {
LOG(WARNING) << "health: invalid battery status";
}
status = v;
});
if (!ret.isOk()) {
LOG(WARNING) << "health: get charge status transaction error " << ret.description();
}
mUidm.init(is_charger_on(status));
//注册回调函数
health->registerCallback(this);
health->linkToDeath(this, 0 /* cookie */);
}
//回调方法,当电池的信息更新时,storaged也会同步去更新状态
Return<void> storaged_t::healthInfoChanged(const HealthInfo& props) {
mUidm.set_charger_state(is_charger_on(props.legacy.batteryStatus));
return android::hardware::Void();
}
Step V healthd_battery_update_internal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
//hardware/interfaces/health/2.0/default/healthd_common_adapter.cpp
void healthd_battery_update_internal(bool charger_online) {
if (!health_loop) return;
health_loop->AdjustWakealarmPeriods(charger_online);
}
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/HealthLoop.cpp
void HealthLoop::AdjustWakealarmPeriods(bool charger_online) {
// Fast wake interval when on charger (watch for overheat);
// slow wake interval when on battery (watch for drained battery).
//如果充电的话,默认间隔为periodic_chores_interval_fast即60S
int new_wake_interval = charger_online ? healthd_config_.periodic_chores_interval_fast
: healthd_config_.periodic_chores_interval_slow;
//假如当前wakealam_wake_interval_和new_wake_interval不同,则重新设置。
if (new_wake_interval != wakealarm_wake_interval_) WakeAlarmSetInterval(new_wake_interval);
// During awake periods poll at fast rate. If wake alarm is set at fast
// rate then just use the alarm; if wake alarm is set at slow rate then
// poll at fast rate while awake and let alarm wake up at slow rate when
// asleep.
if (healthd_config_.periodic_chores_interval_fast == -1)
awake_poll_interval_ = -1;
else
awake_poll_interval_ = new_wake_interval == healthd_config_.periodic_chores_interval_fast
? -1
: healthd_config_.periodic_chores_interval_fast * 1000;
}
void HealthLoop::WakeAlarmSetInterval(int interval) {
struct itimerspec itval;
if (wakealarm_fd_ == -1) return;
wakealarm_wake_interval_ = interval;
if (interval == -1) interval = 0;
itval.it_interval.tv_sec = interval;
itval.it_interval.tv_nsec = 0;
itval.it_value.tv_sec = interval;
itval.it_value.tv_nsec = 0;
//重新设定定时器间隔
if (timerfd_settime(wakealarm_fd_, 0, &itval, NULL) == -1)
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "wakealarm_set_interval: timerfd_settime failed\n");
}
至此,分析完HealthLoop的InitInternal逻辑,接下来分析Step2. MainLoop流程。
4.3.3.3.2 Step2. MainLoop
MainLoop主要实现epoll的监听多路IO的功能,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
void HealthLoop::MainLoop(void) {
int nevents = 0;
while (1) {
reject_event_register_ = true;
size_t eventct = event_handlers_.size();
struct epoll_event events[eventct];
int timeout = awake_poll_interval_;
int mode_timeout;
/* Don't wait for first timer timeout to run periodic chores */
if (!nevents) PeriodicChores();
Heartbeat();
//PrepareToWait预留接口给子类去做准备工作。
mode_timeout = PrepareToWait();
if (timeout < 0 || (mode_timeout > 0 && mode_timeout < timeout)) timeout = mode_timeout;
//阻塞等待输入事件
nevents = epoll_wait(epollfd_, events, eventct, timeout);
//此时阻塞解除,说明接收到了事件,但是要遍历看是哪个事件有输入
if (nevents == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR) continue;
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "healthd_mainloop: epoll_wait failed\n");
break;
}
for (int n = 0; n < nevents; ++n) {
if (events[n].data.ptr) {
//找到后调用相应的回调函数
auto* event_handler = reinterpret_cast<EventHandler*>(events[n].data.ptr);
event_handler->func(event_handler->object, events[n].events);
}
}
}
return;
}
至此将HealthLoop::StartLoop()中的逻辑分析完了,总体来说Healthd关心的是AlarmTimer以及Uevent上的事件,通过epoll模型去监听这些节点,并在事件上报时调用ScheduleBatteryUpdate()更新信息,通知上层服务信息发生了变动。
附录
附录1.timerfd_create用法例子(来源于man timerfd_create)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
EXAMPLE
The following program creates a timer and then monitors its progress. The program accepts up to three command-line arguments. The first
argument specifies the number of seconds for the initial expiration of the timer. The second argument specifies the interval for the
timer, in seconds. The third argument specifies the number of times the program should allow the timer to expire before terminating. The
second and third command-line arguments are optional.
//该程序创建了一个timer并监听其过程,参数分别为定时器定时时间,间隔以及最大次数,通过///这个例子可以清晰看到
The following shell session demonstrates the use of the program:
$ a.out 3 1 100
0.000: timer started
3.000: read: 1; total=1
4.000: read: 1; total=2
^Z # type control-Z to suspend the program
[1]+ Stopped ./timerfd3_demo 3 1 100
$ fg # Resume execution after a few seconds
a.out 3 1 100
9.660: read: 5; total=7
10.000: read: 1; total=8
11.000: read: 1; total=9
^C # type control-C to suspend the program
Program source
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h> /* Definition of uint64_t */
#define handle_error(msg) \
do { perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while (0)
static void
print_elapsed_time(void)
{
static struct timespec start;
struct timespec curr;
static int first_call = 1;
int secs, nsecs;
if (first_call) {
first_call = 0;
if (clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start) == -1)
handle_error("clock_gettime");
}
if (clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &curr) == -1)
handle_error("clock_gettime");
secs = curr.tv_sec - start.tv_sec;
nsecs = curr.tv_nsec - start.tv_nsec;
if (nsecs < 0) {
secs--;
nsecs += 1000000000;
}
printf("%d.%03d: ", secs, (nsecs + 500000) / 1000000);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct itimerspec new_value;
int max_exp, fd;
struct timespec now;
uint64_t exp, tot_exp;
ssize_t s;
if ((argc != 2) && (argc != 4)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s init-secs [interval-secs max-exp]\n",
argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &now) == -1)
handle_error("clock_gettime");
/* Create a CLOCK_REALTIME absolute timer with initial
expiration and interval as specified in command line */
new_value.it_value.tv_sec = now.tv_sec + atoi(argv[1]);
new_value.it_value.tv_nsec = now.tv_nsec;
if (argc == 2) {
new_value.it_interval.tv_sec = 0;
max_exp = 1;
} else {
new_value.it_interval.tv_sec = atoi(argv[2]);
max_exp = atoi(argv[3]);
}
new_value.it_interval.tv_nsec = 0;
//创建定时器
fd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_REALTIME, 0);
if (fd == -1)
handle_error("timerfd_create");
//设定定时器超时时间以及间隔
if (timerfd_settime(fd, TFD_TIMER_ABSTIME, &new_value, NULL) == -1)
handle_error("timerfd_settime");
print_elapsed_time();
printf("timer started\n");
//循环最大定时次数
for (tot_exp = 0; tot_exp < max_exp;) {
//read将阻塞,直到定时时间到后,返回。
s = read(fd, &exp, sizeof(uint64_t));
if (s != sizeof(uint64_t))
handle_error("read");
tot_exp += exp;
print_elapsed_time();
printf("read: %llu; total=%llu\n",
(unsigned long long) exp,
(unsigned long long) tot_exp);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
附录2 RegisterEvent
如对epoll细节想深入了解,可继续看下RegisterEvent的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
//hardware/interfaces/health/utils/libhealthloop/HealthLoop.cpp
int HealthLoop::RegisterEvent(int fd, BoundFunction func, EventWakeup wakeup) {
CHECK(!reject_event_register_);
/*
* 1.event_handler类型为EventHandler,定义在HealthLoop.h,定义如下:
* struct EventHandler {
* HealthLoop* object = nullptr;
* int fd;
* BoundFunction func;
* };
* using BoundFunction = std::function<void(HealthLoop*, uint32_t /* epevents */)>;
* 当epollevent到来时,会主动去调用回调函数func.
* 2. event_handlers_为vector类型,定义如下:
* std::vector<std::unique_ptr<EventHandler>> event_handlers_;
*/
auto* event_handler =
event_handlers_
.emplace_back(std::make_unique<EventHandler>(EventHandler{this, fd, func}))
.get();
struct epoll_event ev;
//设定监听的事件为可读事件
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
//能够保证设备驱动在时间完成之前都保持唤醒
if (wakeup == EVENT_WAKEUP_FD) ev.events |= EPOLLWAKEUP;
//设置回调方法
ev.data.ptr = reinterpret_cast<void*>(event_handler);
//将epoll_event加入到epollfd_中
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd_, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ev) == -1) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "epoll_ctl failed; errno=%d\n", errno);
return -1;
}
return 0;
附录3 uevent_kernel_multicast_recv
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
//system/core/libcutils/uevent.cpp
ssize_t uevent_kernel_multicast_recv(int socket, void* buffer, size_t length) {
uid_t uid = -1;
return uevent_kernel_multicast_uid_recv(socket, buffer, length, &uid);
}
ssize_t uevent_kernel_multicast_uid_recv(int socket, void* buffer, size_t length, uid_t* uid) {
return uevent_kernel_recv(socket, buffer, length, true, uid);
}
ssize_t uevent_kernel_recv(int socket, void* buffer, size_t length, bool require_group, uid_t* uid) {
struct iovec iov = {buffer, length};
struct sockaddr_nl addr;
char control[CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(struct ucred))];
struct msghdr hdr = {
&addr, sizeof(addr), &iov, 1, control, sizeof(control), 0,
};
struct ucred* cred;
*uid = -1;
ssize_t n = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(recvmsg(socket, &hdr, 0));
if (n <= 0) {
return n;
}
struct cmsghdr* cmsg = CMSG_FIRSTHDR(&hdr);
if (cmsg == NULL || cmsg->cmsg_type != SCM_CREDENTIALS) {
/* ignoring netlink message with no sender credentials */
goto out;
}
cred = (struct ucred*)CMSG_DATA(cmsg);
*uid = cred->uid;
if (addr.nl_pid != 0) {
/* ignore non-kernel */
goto out;
}
if (require_group && addr.nl_groups == 0) {
/* ignore unicast messages when requested */
goto out;
}
return n;
out:
/* clear residual potentially malicious data */
bzero(buffer, length);
errno = EIO;
return -1;
}
附录4. startService
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/SystemServiceManager.java
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public SystemService startService(String className) {
final Class<SystemService> serviceClass;
try {
serviceClass = (Class<SystemService>)Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + className
+ ": service class not found, usually indicates that the caller should "
+ "have called PackageManager.hasSystemFeature() to check whether the "
+ "feature is available on this device before trying to start the "
+ "services that implement it", ex);
}
return startService(serviceClass);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + name);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartService " + name);
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service could not be instantiated", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
mServices.add(service);
...
try {
//调用BatteryService的onStart方法
service.onStart();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
...
}
参考文献
- Android Health/Android 运行状态
- 比起直接使用new,更偏爱使用std::make_unique和std::make_shared
- C++ 智能指针 unique_ptr 详解与示例
- 嵌入式Linux——uevent机制:uevent原理分析
- 实现“运行状况”