- 1. 背景
- 2. init启动AudioServer进程
- 3. AudioFlinger::instantiate
- 4. AudioPolicyService::instantiate
- 5. 小结
1. 背景
为了系统学习Audio系统,首先从Audio的初始化流程开始学习,重点在分析通路的走向,如何加载音频策略,音频Hal库等方面展开,平台为Android P。 相关源码可以查看:https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/av/
整个通路如下图所示:

2. init启动AudioServer进程
当系统启动时,init进程会初始化Native的重要服务,包括java世界的入口zygote,显示方面的SurfaceFlinger,内存相关的管理lmkd,media相关的mediaserver,都是由init直接启动,而音频相关的AudioFlinger,AudioPolicyService也是由init启动的,只不过统一在AudioServer这个进程当中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//frameworks/av/media/audioserver/audioserver.rc
service audioserver /system/bin/audioserver
class core #audioserver为core类型的服务
user audioserver #user为audioserver,对应userid为1041
group audio camera drmrpc inet media mediadrm net_bt net_bt_admin net_bw_acct #group组
...
onrestart restart vendor.audio-hal-2-0 #重启audioserver时,需要重启vendor.audio-hal-2-0以及audio-hal-2-0
onrestart restart audio-hal-2-0
audioserver的入口在frameworks/av/media/audioserver/main_audioserver.cpp中,对比以往,audioFlinger/audioPolicyService被放入了mediaServer进程。
另外在看代码的过程,在启动AudioFlinger之前,还涉及到一个media.log的进程。当设置了ro.test_harness时,将会开启该进程。引入该进程的目的是由于在加入调试的android.util.Log(java),ALOGx(native)的调试打印可能会产生大量的垃圾打印,甚至会使关键日志因溢出而丢失。另一方面,还会影响依赖时效性(AudioFlinger中的FastMixer/FastCapture)。media.log则能够有效的解决该问题,并具有如下优势:
- 除非需要,否则它不会在主日志中产生垃圾内容。
- 即使在 mediaserver 崩溃或中断时,也可以对其进行检查。
- 在每个时间轴均是非阻塞的。
- 对性能的干扰较小(当然完全不会产生干扰的日志是不存在的)
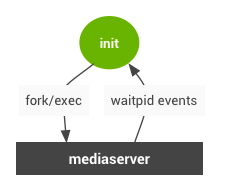
以往的旧架构如下:
添加了media.log的新架构:
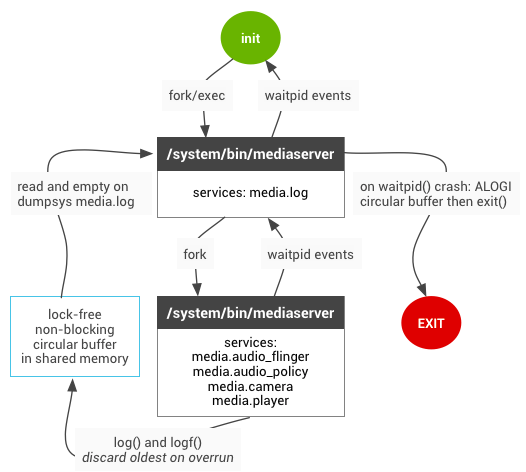
media.log会在共享内存中的环形缓存区保存日志,上层需要使用新的API(NBLOG)去代替以往的log。环形的缓存区能够保证任何内存损坏都不会导致media.log崩溃,并且media.log中的mediaLogService能够随时对其进行转储。
更多详情可以查看Android官网上的链接: https://source.android.google.cn/devices/audio/debugging#mediaLog
抛开media.log后,main_audioserver.cpp中会初始化音频的重要native服务:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
//frameworks/av/media/audioserver/main_audioserver.cpp
android::hardware::configureRpcThreadpool(4, false /*callerWillJoin*/);
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
//初始化AudioFlinger与AudioPolicyService
AudioFlinger::instantiate();
AudioPolicyService::instantiate();
//AAudioService是8.0推出的,通过mmap支持的HAL层和驱动结合,能够缩短延迟时间的服务。
aaudio_policy_t mmapPolicy = property_get_int32(AAUDIO_PROP_MMAP_POLICY,
AAUDIO_POLICY_NEVER);
if (mmapPolicy == AAUDIO_POLICY_AUTO || mmapPolicy == AAUDIO_POLICY_ALWAYS) {
AAudioService::instantiate();
}
//SoundTrigger是语音识别服务
SoundTriggerHwService::instantiate();
//监听Binder是否有服务与AudioServer通信
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
AAudio提供了一个低延迟数据路径。在“专有”模式下,该功能可让客户端应用代码直接写入到与 ALSA 驱动程序共享的内存映射缓冲区。在“共享”模式下,MMAP 缓冲区由在 AudioServer 中运行的混音器使用。在“专有”模式下,由于数据会绕过混音器,延迟时间会明显缩短。 关于AAudioService的内容可以查看:
https://source.android.google.cn/devices/audio/aaudio)
3. AudioFlinger::instantiate
AudioFlinger首先通过instantiate方法在audiosever中进行初始化。其继承了BinderService,可用于在Servicemanager中对服务AudioFlinger进行注册。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
//framworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/BinderService.h
template<typename SERVICE>
class BinderService
{
public:
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false,
int dumpFlags = IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
//新建服务SERVICE,并将服务加到ServiceManager中。
return sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()), new SERVICE(), allowIsolated,
dumpFlags);
}
static void instantiate() { publish(); }
...
};
getServiceName需要在服务(AudioFlinger)中实现,AudioFlinger的服务名为”media.audio_flinger”。也可以在adb中通过service list查询当前系统的服务包括哪些。也可以通过dumpsys media.audio_flinger将AudioFlinger的关键信息打印出来。
当instantiate将服务注册后,可转到服务的实现分析,由于AudioFlinger继承了RefBase类,所以能够被智能指针引用,在publish中的addService时,参数二实质是被sp引用,所以AudioFlinger会在构造方法之后调用onFirstRef方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
AudioFlinger::AudioFlinger()
: BnAudioFlinger(),
mMediaLogNotifier(new AudioFlinger::MediaLogNotifier()),
mPrimaryHardwareDev(NULL),
mAudioHwDevs(NULL),
mHardwareStatus(AUDIO_HW_IDLE),
mMasterVolume(1.0f),
mMasterMute(false),
mMode(AUDIO_MODE_INVALID),
mBtNrecIsOff(false),
mIsLowRamDevice(true),
mIsDeviceTypeKnown(false),
mTotalMemory(0),
mClientSharedHeapSize(kMinimumClientSharedHeapSizeBytes),
mGlobalEffectEnableTime(0),
mSystemReady(false)
{
for (unsigned use = AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_UNSPECIFIED; use < AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_MAX; use++) {
mNextUniqueIds[use] = AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_MAX;
}
getpid_cached = getpid();
//检查ro.test_harness属性,即之前说的media.log是否启用了
const bool doLog = property_get_bool("ro.test_harness", false);
if (doLog) {
//新建了大小为400K的MemoryDealer。本质是申请了匿名内存ashmem
mLogMemoryDealer = new MemoryDealer(kLogMemorySize, "LogWriters",
MemoryHeapBase::READ_ONLY);
//初始化sMediaLogInit,即获取media.log的引用sMediaLogService
(void) pthread_once(&sMediaLogOnce, sMediaLogInit);
}
//假如AudioFlinger崩溃,电池的状态可能会有问题,因此在初始化重设状态。
BatteryNotifier::getInstance().noteResetAudio();
//跟hidl通信相关的服务
mDevicesFactoryHal = DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create();
mEffectsFactoryHal = EffectsFactoryHalInterface::create();
//新建了一个MediaLogNotifier的线程,但是需要配合media.log服务运行,假如media.log没启动,该线程退出
mMediaLogNotifier->run("MediaLogNotifier");
//这部分代码和AudioFlinger调试相关,当打开了TEE_SINK时,系统播放音频时,会保留音频内容为pcm数据保存在/data/misc/audioserver目录里
#ifdef TEE_SINK
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
(void) property_get("ro.debuggable", value, "0");
int debuggable = atoi(value);
int teeEnabled = 0;
if (debuggable) {
(void) property_get("af.tee", value, "0");
teeEnabled = atoi(value);
}
if (teeEnabled & 1) {
mTeeSinkInputEnabled = true;
}
if (teeEnabled & 2) {
mTeeSinkOutputEnabled = true;
}
if (teeEnabled & 4) {
mTeeSinkTrackEnabled = true;
}
#endif
}
tee的调试功能还是相当有用,可以将播放的音频通过audioflinger转存为pcm数据,具体的操作也可以参照:
https://source.android.google.cn/devices/audio/debugging
此后,由于AudioFlinger被强引用指向,调用onFirstRef方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
void AudioFlinger::onFirstRef()
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
char val_str[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = { 0 };
if (property_get("ro.audio.flinger_standbytime_ms", val_str, NULL) >= 0) {
uint32_t int_val;
//设置了ro.audio.flinger_standbytime_ms时间
if (1 == sscanf(val_str, "%u", &int_val)) {
mStandbyTimeInNsecs = milliseconds(int_val);
} else {
//默认的standby时间为kDefaultStandbyTimeInNsecs,即3s。
mStandbyTimeInNsecs = kDefaultStandbyTimeInNsecs;
}
}
mPatchPanel = new PatchPanel(this);
mMode = AUDIO_MODE_NORMAL;
//将自身放在gAudioFlinger的全局变量中,方便客户端调用AudioFlinger服务
gAudioFlinger = this;
}
系统默认在播放完音频后,经过mStandbyTimeInNsecs后会进入StandBy状态。
至于hidl相关,需要在方案里配置,当AudioFlinger创建hidl对象时:
1
2
3
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
mDevicesFactoryHal = DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create();
mEffectsFactoryHal = EffectsFactoryHalInterface::create();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DevicesFactoryHalInterface.cpp
sp<DevicesFactoryHalInterface> DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create() {
//从高到低获取服务是否存在,来确定使用哪一套方案,本例使用的是2.0,需要在方案中配置。
if (hardware::audio::V4_0::IDevicesFactory::getService() != nullptr) {
return new V4_0::DevicesFactoryHalHybrid();
}
if (hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::getService() != nullptr) {
return new DevicesFactoryHalHybrid();
}
return nullptr;
}
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DevicesFactoryHalInterface.cpp
sp<EffectsFactoryHalInterface> EffectsFactoryHalInterface::create() {
if (hardware::audio::effect::V4_0::IEffectsFactory::getService() != nullptr) {
return new V4_0::EffectsFactoryHalHidl();
}
if (hardware::audio::effect::V2_0::IEffectsFactory::getService() != nullptr) {
return new EffectsFactoryHalHidl();
}
return nullptr;
}
方案中可以通过如下方式选择的方案选择编译:
1
2
3
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
android.hardware.audio@2.0-service \
...
Hidl的工作将在后续继续分析。至此,AudioFlinger初始化完成。进入AudioPolicyService的初始化。
4. AudioPolicyService::instantiate
4.1 AudioPolicyService::onFirstRef
AudioPolicyService在服务中注册为“media.audio_policy”,其instantiate初始化与AudioFlinger如出一辙,因此可以直接到其构造函数进行分析:
1
2
3
4
5
6
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/service/AudioPolicyService.cpp
AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyService()
: BnAudioPolicyService(), mpAudioPolicyDev(NULL), mpAudioPolicy(NULL),
mAudioPolicyManager(NULL), mAudioPolicyClient(NULL), mPhoneState(AUDIO_MODE_INVALID)
{
}
可以看出其构造方法仅仅通过初始化列表对成员变量进行了初始化,因此直接到onFirstRef进行分析:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
./services/audiopolicy/service/AudioPolicyService.cpp
void AudioPolicyService::onFirstRef()
{
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
//AudioPolicyService创建了3个AudioCommandThread线程,
//用于铃声播放以及发送音频配置命令到AudioFlinger中(step 1)
mTonePlaybackThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmTone"), this);
mAudioCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmAudio"), this);
mOutputCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmOutput"), this);
//新建AudioPolicyClient对象,并传入到createAudioPolicyManger接口(step 2)
mAudioPolicyClient = new AudioPolicyClient(this);
//新建出AduioPolicyManager对象。(step 3)
mAudioPolicyManager = createAudioPolicyManager(mAudioPolicyClient);
}
sp<AudioPolicyEffects>audioPolicyEffects = new AudioPolicyEffects();
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
mAudioPolicyEffects = audioPolicyEffects;
}
mUidPolicy = new UidPolicy(this);
mUidPolicy->registerSelf();
}
step 1: AudioCommandThread在threadLoop循环处理消息,处理的消息类型包括:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
START_TONE,
STOP_TONE,
SET_VOLUME,
SET_PARAMETERS,
SET_VOICE_VOLUME,
STOP_OUTPUT,
RELEASE_OUTPUT,
CREATE_AUDIO_PATCH,
RELEASE_AUDIO_PATCH,
UPDATE_AUDIOPORT_LIST,
UPDATE_AUDIOPATCH_LIST,
SET_AUDIOPORT_CONFIG,
DYN_POLICY_MIX_STATE_UPDATE,
RECORDING_CONFIGURATION_UPDATE
为了让AudioCommandThread处理消息,通过sendCommmand将command填充到mAudioCommands中,并随后通过mWaitWorkCV.signal()唤醒线程,线程首先通过mWaitWorkCV.wait(mLock)进行等待,当被唤醒后,就会开始处理,最终将给到AudioFlinger处理.
step 2: AudioPolicyClient继承了AudioPolicyClientInterface,基类AudioPolicyClientInterface定义在/hardware/libhardware_legacy/include/hardware_legacy/AudioPolicyInterface.h文件中,定义了hal层的重要接口,如下是部分接口展示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
///hardware/libhardware_legacy/include/hardware_legacy/AudioPolicyInterface.h
//加载音频设备的描述文件audio_policy.conf
virtual audio_module_handle_t loadHwModule(const char *name) = 0;
//打开音频输出通道
virtual audio_io_handle_t openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask,
uint32_t *pLatencyMs,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo = NULL) = 0;
//关闭音频输出通道
virtual status_t closeOutput(audio_io_handle_t output) = 0;
...
//打开音频输入通道
virtual audio_io_handle_t openInput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask) = 0;
virtual status_t closeInput(audio_io_handle_t input) = 0;
//设置音频音量
virtual status_t setStreamVolume(AudioSystem::stream_type stream, float volume, audio_io_handle_t output, int delayMs = 0) = 0;
...
AudioPolicyClient作为子类,需要实现这些方法,但实际的操作不是它来完成,而是AudioFlinger,如loadHwModule的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/service/AudioPolicyService.cpp
audio_module_handle_t AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyClient::loadHwModule(const char *name)
{
//通过get_audio_flinger获取AudioFlinger
sp<IAudioFlinger> af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger();
if (af == 0) {
return AUDIO_MODULE_HANDLE_NONE;
}
//最终调用到AudioFlinger的loadHwModule完成
return af->loadHwModule(name);
}
step 3: 回到AudioPolicyService的流程,新建完AudioPolicyClient后作为参数,传到了方法createAudioPolicyManager中,其定义在frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/manager/AudioPolicyFactory.cpp中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/manager/AudioPolicyFactory.cpp
extern "C" AudioPolicyInterface* createAudioPolicyManager(
AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
{
//实质是新建了一个AudioPolicyManager对象。
return new AudioPolicyManager(clientInterface);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.cpp
AudioPolicyManager::AudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
: AudioPolicyManager(clientInterface, false /*forTesting*/)
{
loadConfig();
initialize();
}
4.2 AudioPolicyManager::loadConfig
于是问题变成了loadConfig以及initialize中做了什么操作, 先从loadConfig开始,实质通过ConfigParsingUtils的loadConfig分别读取了AUDIO_POLICY_VENDOR_CONFIG_FILE以及AUDIO_POLICY_CONFIG_FILE两个配置文件,即”/system/etc/audio_policy.conf” 以及”/vendor/etc/audio_policy.conf”。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.cpp
void AudioPolicyManager::loadConfig() {
if ((ConfigParsingUtils::loadConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_VENDOR_CONFIG_FILE, getConfig()) != NO_ERROR)
&& (ConfigParsingUtils::loadConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_CONFIG_FILE, getConfig()) != NO_ERROR)) {
getConfig().setDefault();
}
}
常规的audio_policy.conf格式如下, 其中配置了当前项目audio策略中支持的输入输出设备,采样率,采样精度,声道数等等:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
//audio_policy.conf
audio_hw_modules {
primary {
outputs {
primary {
sampling_rates 44100
channel_masks AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO
formats AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
devices AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE|AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER|AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET|AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE|AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_ALL_SCO|AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL|AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DGTL_DOCK_HEADSET
flags AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY
}
}
inputs{
....
}
}
a2dp{
...
}
usb{
...
}
...
}
再来看ConfigParsingUtils的loadConfig的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/common/managerdefinitions/src/ConfigParsingUtils.cpp
status_t ConfigParsingUtils::loadConfig(const char *path, AudioPolicyConfig &config)
{
cnode *root;
char *data;
//step1. 读取audio_policy.conf的内容,load_file是libcutils的方法.
//将会申请一段内存并将文件内容读取到该内存中.
data = (char *)load_file(path, NULL);
if (data == NULL) {
return -ENODEV;
}
//step2. 创建了根节点cnode类型的root,name与value均设置为空
root = config_node("", "");
//step3. 解析data内容,config_utils实现了一套十分有趣的词法分析器解析配置文件,后续实现配置文件的时候也可以参照audio_policy这段逻辑.
//每个节点都有key/value键值对,每个节点都有指向孩子节点的指针,能够获取下一层的节点内容,也具有next指针可以获取同级的内容。
config_load(root, data);
HwModuleCollection hwModules;
//Step4.加载HwModules设备到HwModules集合中,如primary,a2dp,usb等
loadHwModules(root, hwModules, config);
//Step5.读取primary中的是否有global_configuration的部分
loadGlobalConfig(root, config, hwModules.getModuleFromName(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_PRIMARY));
//Step6.设置hwModules
config.setHwModules(hwModules);
config_free(root);
free(root);
free(data);
return NO_ERROR;
}
AudioPolicyService维护着一个如下形式的集合(HwModuleCollection),也可以通过dumpsys media.audio_policy获取细节.同级的子节点之间可以通过next获取到下一个兄弟节点.
再深入到Step4中的loadHwModules看其实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
void ConfigParsingUtils::loadHwModules(cnode *root, HwModuleCollection &hwModules,
AudioPolicyConfig &config)
{
//AUDIO_HW_MODULE_TAG即"audio_hw_modules",找到根节点
cnode *node = config_find(root, AUDIO_HW_MODULE_TAG);
if (node == NULL) {
return;
}
node = node->first_child;
//为audio_hw_modules下的子节点各创建一个HwModule对象,并加入hwModules集合中
//node包括如primary,a2dp,usb等设备
while (node) {
sp<HwModule> module = new HwModule(node->name);
//调用loadHwModule处理
if (loadHwModule(node, module, config) == NO_ERROR) {
hwModules.add(module);
}
node = node->next;
}
}
status_t ConfigParsingUtils::loadHwModule(cnode *root, sp<HwModule> &module,
AudioPolicyConfig &config)
{
status_t status = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
//DEVICES_TAG即devices字段,遍历找到设备root下的devices
cnode *node = config_find(root, DEVICES_TAG);
if (node != NULL) {
node = node->first_child;
//新建一个DeviceVector类型的deivces,用于保存设备
DeviceVector devices;
while (node) {
//A. 使用loadHWModuleDevice加载设备
status_t tmpStatus = loadHwModuleDevice(node, devices);
if (status == NAME_NOT_FOUND || status == NO_ERROR) {
status = tmpStatus;
}
node = node->next;
}
module->setDeclaredDevices(devices);
}
//OUTPUTS_TAG即outputs字段
node = config_find(root, OUTPUTS_TAG);
if (node != NULL) {
node = node->first_child;
while (node) {
//B. 调用loadHwModuleProfile
status_t tmpStatus = loadHwModuleProfile(node, module, AUDIO_PORT_ROLE_SOURCE);
if (status == NAME_NOT_FOUND || status == NO_ERROR) {
status = tmpStatus;
}
node = node->next;
}
}
//OUTPUTS_TAG即intputs字段
node = config_find(root, INPUTS_TAG);
if (node != NULL) {
node = node->first_child;
while (node) {
//C. 调用loadHwModuleProfile
status_t tmpStatus = loadHwModuleProfile(node, module, AUDIO_PORT_ROLE_SINK);
if (status == NAME_NOT_FOUND || status == NO_ERROR) {
status = tmpStatus;
}
node = node->next;
}
}
//D. 加载通用的属性
loadModuleGlobalConfig(root, module, config);
return status;
}
loadHwModule分别去找devices,outputs,inputs字段进行处理,分步进行分析:
A.devices
1
2
status_t tmpStatus = loadHwModuleDevice(node, devices);
module->setDeclaredDevices(devices);
首先展示常规的devices字段下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
//primary中devices配置
primary{
...
devices {
speaker {
type AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
gains {
gain_1 {
mode AUDIO_GAIN_MODE_JOINT
min_value_mB -8400
max_value_mB 4000
default_value_mB 0
step_value_mB 100
}
}
}
HDMI {
type AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL
}
SPDIF {
type AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPDIF
}
wired_headphone {
type AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE
}
wired_headset {
type AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET
}
BT_sco {
type AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO
}
BT_sco_headset {
type AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO_HEADSET
}
}
...
}
可以看到devices中都是设备的名称,且都设置了type类型,speaker较为特殊,还设置了gains增益.来看代码是如何解析这段配置的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
//static
status_t ConfigParsingUtils::loadHwModuleDevice(cnode *root, DeviceVector &devices)
{
cnode *node = root->first_child;
audio_devices_t type = AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE;
while (node) {
if (strcmp(node->name, APM_DEVICE_TYPE) == 0) {
//从这里获取type类型
deviceFromString(node->value, type);
break;
}
node = node->next;
}
if (type == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE ||
(!audio_is_input_device(type) && !audio_is_output_device(type))) {
//type读取有误则退出
return BAD_VALUE;
}
//DeviceDescriptor用于描述设备的信息
sp<DeviceDescriptor> deviceDesc = new DeviceDescriptor(type, String8(root->name));
node = root->first_child;
while (node) {
if (strcmp(node->name, APM_DEVICE_ADDRESS) == 0) {
//处理address字段,设置设备地址
deviceDesc->mAddress = String8((char *)node->value);
} else if (strcmp(node->name, CHANNELS_TAG) == 0) {
//处理channel_masks字段
//输入设备
if (audio_is_input_device(type)) {
//新建了一个AudioProfile对象到deviceDesc中,且将channel_mask的值读取出来
deviceDesc->addAudioProfile(
new AudioProfile(gDynamicFormat,
inputChannelMasksFromString(node->value),
SampleRateVector()));
} else {//输出设备
deviceDesc->addAudioProfile(
new AudioProfile(gDynamicFormat,
outputChannelMasksFromString(node->value),
SampleRateVector()));
}
} else if (strcmp(node->name, GAINS_TAG) == 0) {
//处理gains字段
loadDeviceDescriptorGains(node, deviceDesc);
}
node = node->next;
}
//将当前deviceDesc加入devices Vector中
devices.add(deviceDesc);
return NO_ERROR;
}
//将上述处理的devices加入到HwModule类的mPorts中.mPorts类型为AudioPortVector.
void HwModule::setDeclaredDevices(const DeviceVector &devices)
{
mDeclaredDevices = devices;
for (size_t i = 0; i < devices.size(); i++) {
mPorts.add(devices[i]);
}
}
假如HwModules中配置了devices,会通过type以及设备名创建DeviceDescriptor(继承了AudioPort以及AudioPortConfig),并会继续解析,假如设置了如地址,通道,增益等,DeviceDescriptor就会设置相应的属性.最终将DeviceDescriptor加入到mPorts(AudioPort类)中进行管理.
B/C.Outputs and Inputs
1
2
3
4
//Outputs
status_t tmpStatus = loadHwModuleProfile(node, module, AUDIO_PORT_ROLE_SOURCE);
//Inputs
status_t tmpStatus = loadHwModuleProfile(node, module, AUDIO_PORT_ROLE_SINK);
再来看下Outputs是怎么配置的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
outputs {
primary {
sampling_rates 48000
channel_masks AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO
formats AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
devices speaker
flags AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
status_t ConfigParsingUtils::loadHwModuleProfile(cnode *root, sp<HwModule> &module,
audio_port_role_t role)
{
cnode *node = root->first_child;
sp<IOProfile> profile = new IOProfile(String8(root->name), role);
AudioProfileVector audioProfiles;
SampleRateVector sampleRates;
ChannelsVector channels;
FormatVector formats;
while (node) {
//解析formats(采样精度)
if (strcmp(node->name, FORMATS_TAG) == 0 &&
strcmp(node->value, DYNAMIC_VALUE_TAG) != 0) {
formats = formatsFromString(node->value);
//解析sampling_rates(采样率)
} else if (strcmp(node->name, SAMPLING_RATES_TAG) == 0 &&
strcmp(node->value, DYNAMIC_VALUE_TAG) != 0) {
collectionFromString<SampleRateTraits>(node->value, sampleRates);
//解析channel_mask(通道数)
} else if (strcmp(node->name, CHANNELS_TAG) == 0 &&
strcmp(node->value, DYNAMIC_VALUE_TAG) != 0) {
if (role == AUDIO_PORT_ROLE_SINK) {
channels = inputChannelMasksFromString(node->value);
} else {
channels = outputChannelMasksFromString(node->value);
}
//解析devices
} else if (strcmp(node->name, DEVICES_TAG) == 0) {
DeviceVector devices;
loadDevicesFromTag(node->value, devices, module->getDeclaredDevices());
profile->setSupportedDevices(devices);
//解析flags
} else if (strcmp(node->name, FLAGS_TAG) == 0) {
if (role == AUDIO_PORT_ROLE_SINK) {
profile->setFlags(InputFlagConverter::maskFromString(node->value));
} else {
profile->setFlags(OutputFlagConverter::maskFromString(node->value));
}
//解析gains
} else if (strcmp(node->name, GAINS_TAG) == 0) {
loadAudioPortGains(node, *profile);
}
node = node->next;
}
//当精度为空时,会创建一个新的默认值为gDynamicFormat的AudioProfile加入到audioProfiles中
if (formats.isEmpty()) {
sp<AudioProfile> profileToAdd = new AudioProfile(gDynamicFormat, channels, sampleRates);
profileToAdd->setDynamicFormat(true);
profileToAdd->setDynamicChannels(channels.isEmpty());
profileToAdd->setDynamicRate(sampleRates.isEmpty());
audioProfiles.add(profileToAdd);
} else {
for (size_t i = 0; i < formats.size(); i++) {
对于每一个采样精度,都会创建一个AudioProfile
sp<AudioProfile> profileToAdd = new AudioProfile(formats[i], channels, sampleRates);
profileToAdd->setDynamicFormat(formats[i] == gDynamicFormat);
profileToAdd->setDynamicChannels(channels.isEmpty());
profileToAdd->setDynamicRate(sampleRates.isEmpty());
audioProfiles.add(profileToAdd);
}
}
//将audioProfiles设置为mProfiles
profile->setAudioProfiles(audioProfiles);
if (profile->hasSupportedDevices()) {
//将输入输出AudioProfile分别加入到mInputProfiles和mOutputProfiles中.同时mPorts会加入输入以及输出的Profile.
return module->addProfile(profile);
}
return BAD_VALUE;
}
B/C步骤分别对HwModules中的inputs,outputs进行解析,首先每个HwModules新建一个IOProfile,接着针对audio_policy.conf的设备树,解析出HwModules的outputs/inputs的采样频率,通道数,采样精度,支持设备等信息,并遍历精度,每个精度创建一个AudioProfile,最后将同一个HwModules中所有的AudioProfile加入到IOProfile中.
D.loadModuleGlobalConfig
除了上述的配置外,audio_policy.conf还可以配置通用类的属性,这类属性既可以在audio_hw_modules平行的地方设置,也可以在HwModules中设置,如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
global_configuration {
attached_output_devices AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
default_output_device AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
attached_input_devices AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC|AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_REMOTE_SUBMIX
}
audio_hw_modules {
primary {
global_configuration {
attached_output_devices AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
default_output_device AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
attached_input_devices AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC
audio_hal_version 3.0
}
...
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
void ConfigParsingUtils::loadModuleGlobalConfig(cnode *root, const sp<HwModule> &module,
AudioPolicyConfig &config)
{
//GLOBAL_CONFIG_TAG表示global_configuration
cnode *node = config_find(root, GLOBAL_CONFIG_TAG);
if (node == NULL) {
return;
}
DeviceVector declaredDevices;
if (module != NULL) {
//获取A步骤的DeviceDescriptor
declaredDevices = module->getDeclaredDevices();
}
node = node->first_child;
while (node) {
//获取attached_output_devices
if (strcmp(ATTACHED_OUTPUT_DEVICES_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
DeviceVector availableOutputDevices;
//读取attached_output_devices的值
loadDevicesFromTag(node->value, availableOutputDevices, declaredDevices);
//增加到mAvailableOutputDevices中
config.addAvailableOutputDevices(availableOutputDevices);
//获取default_output_device
} else if (strcmp(DEFAULT_OUTPUT_DEVICE_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
audio_devices_t device = AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE;
deviceFromString(node->value, device);
if (device != AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {
//新建DeviceDescriptor类,并将default_output_device的值设置为mDefaultOutputDevices的值
sp<DeviceDescriptor> defaultOutputDevice = new DeviceDescriptor(device);
config.setDefaultOutputDevice(defaultOutputDevice);
} else {
ALOGW("loadGlobalConfig() default device not specified");
}
//获取attached_input_devices,与Output类同
} else if (strcmp(ATTACHED_INPUT_DEVICES_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
DeviceVector availableInputDevices;
loadDevicesFromTag(node->value, availableInputDevices, declaredDevices);
config.addAvailableInputDevices(availableInputDevices);
//获取audio_hal_version
} else if (strcmp(AUDIO_HAL_VERSION_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
uint32_t major, minor;
sscanf((char *)node->value, "%u.%u", &major, &minor);
//设置HAL版本
module->setHalVersion(major, minor);
ALOGV("loadGlobalConfig() mHalVersion = major %u minor %u", major, minor);
}
node = node->next;
}
}
通过通用的配置,可以看出,即使A中的devices中不设置,也可以通过通用配置去设置默认的DeviceDescriptor用以描述设备.如对audio_policy.conf感兴趣,可以参考如下链接:
4.3 AudioPolicyManager::initialize
4.3.1 initialize流程
initialize的初始化流程较长,后续将会分步分析,首先涉及到engine的概念,其类图如下:
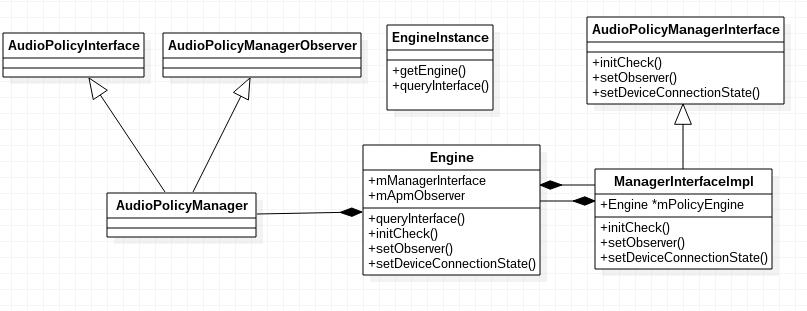
- 第一阶段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.cpp
status_t AudioPolicyManager::initialize() {
//初始化音量调节点
mVolumeCurves->initializeVolumeCurves(getConfig().isSpeakerDrcEnabled());
//获取engineInstance实例
audio_policy::EngineInstance *engineInstance = audio_policy::EngineInstance::getInstance();
if (!engineInstance) {
return NO_INIT;
}
//engineInstance调用queryInterface,实际会调用到Engine类的queryInterface方法,并最终返回了ManagerInterfaceImpl类型(继承于AudioPolicyManagerInterface类)的mEngine.由于ManagerInterfaceImpl中传入了Engine对象,实际执行工作的还是Engine.
mEngine = engineInstance->queryInterface<AudioPolicyManagerInterface>();
if (mEngine == NULL) {
return NO_INIT;
}
//将AudioPolicyManager设置到Engine中的mApmObserver
mEngine->setObserver(this);
//检查mApmObserver是否为空
status_t status = mEngine->initCheck();
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
return status;
}
...
第一阶段engine首先进行了必要的初始化,还将AudioManager设为它的成员变量,最后检查是否为空。且engine实现了AudioPolicyInterface的必要接口,通过ManagerInterfaceImpl作为中转,但实际的实现仍然为engine。
- 第二阶段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.cpp
//status_t AudioPolicyManager::initialize() {
...
audio_devices_t outputDeviceTypes = mAvailableOutputDevices.types();
audio_devices_t inputDeviceTypes = mAvailableInputDevices.types() & ~AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN;
//mHwModulesAll在初始化时被传入了AudioPolicyConfig中,所以当loadConfig完毕时,mHwModulesAll中就保存了audio_policy.conf中的音频设备结构了。
for (const auto& hwModule : mHwModulesAll) {
//Step 1. 遍历并调用loadHwModule加载。
//loadHwModule返回的audio_module_handle_t,设置到hwModule的mHandle中。
hwModule->setHandle(mpClientInterface->loadHwModule(hwModule->getName()));
if (hwModule->getHandle() == AUDIO_MODULE_HANDLE_NONE) {
ALOGW("could not open HW module %s", hwModule->getName());
continue;
}
//AudioPolicyManager使用Vector类型的mHwModules重新将HwModule加入集合当中。
mHwModules.push_back(hwModule);
//OutputProfile即之前根据配置基于不同formats(精度)生成的AudioProfile
for (const auto& outProfile : hwModule->getOutputProfiles()) {
if (!outProfile->canOpenNewIo()) {
ALOGE("Invalid Output profile max open count %u for profile %s",
outProfile->maxOpenCount, outProfile->getTagName().c_str());
continue;
}
//Output中必须要有devices字段
if (!outProfile->hasSupportedDevices()) {
ALOGW("Output profile contains no device on module %s", hwModule->getName());
continue;
}
if ((outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_TTS) != 0) {
mTtsOutputAvailable = true;
}
if ((outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT) != 0) {
continue;
}
audio_devices_t profileType = outProfile->getSupportedDevicesType();
if ((profileType & mDefaultOutputDevice->type()) != AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {
profileType = mDefaultOutputDevice->type();
} else {
profileType = outProfile->getSupportedDeviceForType(outputDeviceTypes);
}
if ((profileType & outputDeviceTypes) == 0) {
continue;
}
//Step 2.每一个AudioProfile会新建一个SwAudioOutputDescriptor
sp<SwAudioOutputDescriptor> outputDesc = new SwAudioOutputDescriptor(outProfile,
mpClientInterface);
const DeviceVector &supportedDevices = outProfile->getSupportedDevices();
const DeviceVector &devicesForType = supportedDevices.getDevicesFromType(profileType);
String8 address = devicesForType.size() > 0 ? devicesForType.itemAt(0)->mAddress
: String8("");
audio_io_handle_t output = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
//Step 3.调用open打开设备
status_t status = outputDesc->open(nullptr, profileType, address,
AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT, AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NONE, &output);
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGW("Cannot open output stream for device %08x on hw module %s",
outputDesc->mDevice,
hwModule->getName());
} else {
for (const auto& dev : supportedDevices) {
ssize_t index = mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(dev);
if (index >= 0 && !mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->isAttached()) {
//调用了AudioPort的attach方法(将成员变量mModule设置为hwModule),并调用getNextUniqueId分配Id
mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->attach(hwModule);
}
}
if (mPrimaryOutput == 0 &&
outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY) {
mPrimaryOutput = outputDesc;
}
//Step 4. 将output(handle值)以及outputDesc作为一组键值对,加入到mOutputs中.
addOutput(output, outputDesc);
//Step 5. 设置输出设备
setOutputDevice(outputDesc,
profileType,
true,
0,
NULL,
address);
}
}
//输入设备的处理和output类同,暂不重复分析
....
}
// make sure all attached devices have been allocated a unique ID
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableOutputDevices.size();) {
if (!mAvailableOutputDevices[i]->isAttached()) {
ALOGW("Output device %08x unreachable", mAvailableOutputDevices[i]->type());
mAvailableOutputDevices.remove(mAvailableOutputDevices[i]);
continue;
}
//调用setDeviceConnectionState
mEngine->setDeviceConnectionState(mAvailableOutputDevices[i],
AUDIO_POLICY_DEVICE_STATE_AVAILABLE);
i++;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableInputDevices.size();) {
if (!mAvailableInputDevices[i]->isAttached()) {
mAvailableInputDevices.remove(mAvailableInputDevices[i]);
continue;
}
mEngine->setDeviceConnectionState(mAvailableInputDevices[i],
AUDIO_POLICY_DEVICE_STATE_AVAILABLE);
i++;
}
// make sure default device is reachable
if (mDefaultOutputDevice == 0 || mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(mDefaultOutputDevice) < 0) {
ALOGE("Default device %08x is unreachable", mDefaultOutputDevice->type());
status = NO_INIT;
}
// If microphones address is empty, set it according to device type
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableInputDevices.size(); i++) {
if (mAvailableInputDevices[i]->mAddress.isEmpty()) {
if (mAvailableInputDevices[i]->type() == AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC) {
mAvailableInputDevices[i]->mAddress = String8(AUDIO_BOTTOM_MICROPHONE_ADDRESS);
} else if (mAvailableInputDevices[i]->type() == AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BACK_MIC) {
mAvailableInputDevices[i]->mAddress = String8(AUDIO_BACK_MICROPHONE_ADDRESS);
}
}
}
if (mPrimaryOutput == 0) {
ALOGE("Failed to open primary output");
status = NO_INIT;
}
updateDevicesAndOutputs();
return status;
}
4.3.2 loadHwModule_l
mpClientInterface的loadHwModule最终使用到AudioFlinger的loadHwModule:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
audio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule(const char *name)
{
....
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
return loadHwModule_l(name);
}
audio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule_l(const char *name)
{
//检查mAudioHwDevs是否已经加载过这个设备了?有则从mAudioHwDevs这个DefaultKeyedVector
//中获取,其形式为key/value形式,key为audio_module_handle_t(handle),value为AudioHwDevice。
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAudioHwDevs.size(); i++) {
if (strncmp(mAudioHwDevs.valueAt(i)->moduleName(), name, strlen(name)) == 0) {
return mAudioHwDevs.keyAt(i);
}
}
sp<DeviceHalInterface> dev;
//mDevicesFactoryHal为DevicesFactoryHalHybrid,是之前调用DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create创建的.
//调用构造函数时会创建两个对象,分别为DevicesFactoryHalLocal以及DevicesFactoryHalHidl
//假如打开的设备不为a2dp或者hearing, 使用hidl经过binder形式去调用HAL,
//即使用DevicesFactoryHalHidl的openDevice接口;其余的以直通方式调用,调用的是DevicesFactoryHalLocal的openDevice接口。返回的dev为继承了DeviceHalInterface的对象。
int rc = mDevicesFactoryHal->openDevice(name, &dev);
if (rc) {
return AUDIO_MODULE_HANDLE_NONE;
}
//后面是一系列HAL初始化操作。
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_INIT;
//初始化audio Interface是否成功。
rc = dev->initCheck();
...
//获取下一个有效ID,保存为audio_module_handle_t类型
audio_module_handle_t handle = (audio_module_handle_t) nextUniqueId(AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_MODULE);
//新建一个AudioHwDevices,加入到mAudioHwdevs集合中管理。
mAudioHwDevs.add(handle, new AudioHwDevice(handle, name, dev, flags));
return handle;
}
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DevicesFactoryHalInterface.cpp
DevicesFactoryHalHybrid::DevicesFactoryHalHybrid()
: mLocalFactory(new DevicesFactoryHalLocal()),
mHidlFactory(new DevicesFactoryHalHidl()) {
}
status_t DevicesFactoryHalHybrid::openDevice(const char *name, sp<DeviceHalInterface> *device) {
if (mHidlFactory != 0 && strcmp(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_A2DP, name) != 0 &&
strcmp(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_HEARING_AID, name) != 0) {
return mHidlFactory->openDevice(name, device);
}
//a2dp,hearing使用直通,其余使用hidl
return mLocalFactory->openDevice(name, device);
}
mDevicesFactoryHal调用openDevice即最终是加载设备对应的库文件,而Android支持的音频设备包括(还有部分未展示):
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE | 听筒 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER | 喇叭 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET | 带麦克风的耳机 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE | 耳机 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO | SCO蓝牙 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO_HEADSET | SCO蓝牙带麦克风耳机 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO_CARKIT | SCO蓝牙车载套件 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP | A2DP蓝牙 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP_HEADPHONES | A2DP蓝牙耳机 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP_SPEAKER | A2DP喇叭 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL | AUX |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_HDMI | HDMI |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_ANLG_DOCK_HEADSET | 模拟DOCK耳机 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DGTL_DOCK_HEADSET | 数字DOCK耳机 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_USB_ACCESSORY | USB配件 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_USB_DEVICE | USB设备 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_REMOTE_SUBMIX | SubMix设备 |
| AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_TELEPHONY_TX | 电话 |
| … | … |
回到之前提及的loadHwModule_l,其中涉及到关键的hidl通信,从8.0开始,上层需要调用HAL层就需要借助hidl进行通信了。如下图所示, 在音频方面可见,使用了第一种Legacy Hal和第三种binderized模式。
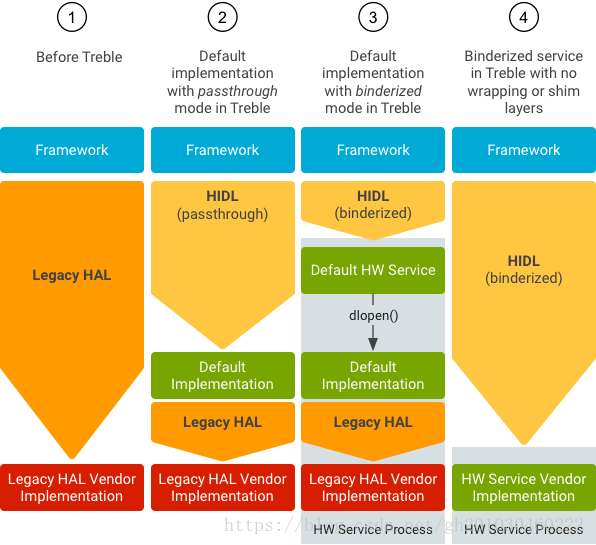
如需要了解hidl相关内容,可以参考如下链接: Android O HIDL的实现对接
1.LegacyHal模式
以openDevice为例,当为primary,usb时采用的是LegacyHal。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/2.0/DevicesFactoryHalLocal.cpp
status_t DevicesFactoryHalLocal::openDevice(const char *name, sp<DeviceHalInterface> *device) {
audio_hw_device_t *dev;
//加载指定的audio interface,即加载所需要的库文件,如audio.primary.xxx.so
status_t rc = load_audio_interface(name, &dev);
if (rc == OK) {
//DeviceHalLocal封装了一层,是audio_hw_device_t的proxy端
*device = new DeviceHalLocal(dev);
}
return rc;
}
static status_t load_audio_interface(const char *if_name, audio_hw_device_t **dev)
{
const hw_module_t *mod;
int rc;
//hw_getmodule_by_class通过if_name参数在/system/lib/hw,/vendor/lib/hw,/odm/lib/hw找相关的库文件。
rc = hw_get_module_by_class(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, &mod);
...
//对接到HAL层open接口
rc = audio_hw_device_open(mod, dev);
...
//失败时关闭设备
...
audio_hw_device_close(*dev);
return OK;
out:
*dev = NULL;
return rc;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/audio.h
static inline int audio_hw_device_open(const struct hw_module_t* module,
struct audio_hw_device** device)
{
//这里即调用到HAL层的真正实现,至此与HAL层正式对接上。
return module->methods->open(module, AUDIO_HARDWARE_INTERFACE,
TO_HW_DEVICE_T_OPEN(device));
}
//编译为audio.primary.$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM).so
static struct hw_module_methods_t hal_module_methods = {
//最终调用到HAL层的adev_open接口,具体实现与厂商实现相关。
.open = adev_open,
};
2.Binderized模式
介绍binderized模式时,首先介绍相关的接口: IDevicesFactory在IDevicesFactory.hal文件定义了openDevice接口。编译时会通过hidl-gen生成对应的头文件IDevicesFactory.h和实现文件DevicesFactoryAll.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//hardware/interfaces/audio/2.0/IDevicesFactory.hal
interface IDevicesFactory {
typedef android.hardware.audio@2.0::Result Result;
enum Device : int32_t {
PRIMARY,
A2DP,
USB,
R_SUBMIX,
STUB
};
//定义的接口
openDevice(Device device) generates (Result retval, IDevice result);
};
经过hidl-gen生成的IDevicesFactory.h头文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
//out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/audio/2.0/android.hardware.audio@2.0_genc++_headers/gen/android/hardware/audio/2.0/IDevicesFactory.h
//hal文件经过hidl转换后,都会继承IBase类,IBase继承了RefBase,可以经过智能指针管理生命周期。
struct IDevicesFactory : public ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase {
...
enum class Device : int32_t {
PRIMARY = 0,
A2DP = 1, // (::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device.PRIMARY implicitly + 1)
USB = 2, // (::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device.A2DP implicitly + 1)
R_SUBMIX = 3, // (::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device.USB implicitly + 1)
STUB = 4, // (::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device.R_SUBMIX implicitly + 1)
};
//定义了getservice
...
//声明openDevice为虚函数
virtual ::android::hardware::Return<void> openDevice(::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device device, openDevice_cb _hidl_cb) = 0;
}
经过hidl-gen生成的DevicesFactoryAll.cpp实现文件,实现了getService,openDevice方法。回头看下AudioFlinger,当构造方法调用时,会调用DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create()时创建一个DevicesFactoryHalHidl对象.它的方式与Binder通信一致,先获取服务,返回对应的BpHwDevicesFactory对象,用以调用服务的接口(HAL接口),如openDevice。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/2.0/DevicesFactoryHalHidl.cpp
//构造函数
DevicesFactoryHalHidl::DevicesFactoryHalHidl() {
//mDevicesFactory即BpHwDevicesFactory,为proxy端
mDevicesFactory = IDevicesFactory::getService();
if (mDevicesFactory != 0) {
//注册死亡代理通知
mDevicesFactory->linkToDeath(HalDeathHandler::getInstance(), 0 /*cookie*/);
} else {
exit(1);
}
...
}
深入看getService的实现,最终会调用到ServiceManagement.cpp中的getRawServiceInternal方法,并判断是使用了hidl通信的binderized还是passthrough模式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
//out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/audio/2.0/android.hardware.audio@2.0_genc++/gen/android/hardware/audio/2.0/DevicesFactoryAll.cpp
::android::sp<IDevicesFactory> IDevicesFactory::getService(const std::string &serviceName, const bool getStub) {
//调用了getServiceInternal,泛型类别是BpHwDevicesFactory,应当是Proxy端
return ::android::hardware::details::getServiceInternal<BpHwDevicesFactory>(serviceName, true, getStub);
}
//system/libhidl/transport/include/hidl/HidlTransportSupport.h
template <typename BpType, typename IType = typename BpType::Pure,
typename = std::enable_if_t<std::is_same<i_tag, typename IType::_hidl_tag>::value>,
typename = std::enable_if_t<std::is_same<bphw_tag, typename BpType::_hidl_tag>::value>>
sp<IType> getServiceInternal(const std::string& instance, bool retry, bool getStub) {
using ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase;
//IBase与IBinder类似
sp<IBase> base = getRawServiceInternal(IType::descriptor, instance, retry, getStub);
if (base == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
//假如为远程服务,返回代理端
if (base->isRemote()) {
//从这里看,返回的是BpType泛型类别,即BpHwDevicesFactory。
//传入参数是IBinder类型。
return sp<IType>(new BpType(toBinder<IBase>(base)));
}
//与Binder的interfacecast类似
return IType::castFrom(base);
}
//system/libhidl/transport/ServiceManagement.cpp
sp<::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase> getRawServiceInternal(const std::string& descriptor,
const std::string& instance,
bool retry, bool getStub) {
...
sp<Waiter> waiter;
//获取hidl的ServiceManager,打开/dev/hwbinder节点
const sp<IServiceManager1_1> sm = defaultServiceManager1_1();
...
Return<Transport> transportRet = sm->getTransport(descriptor, instance);
...
Transport transport = transportRet;
//使用的传输模式是HWBINDER还是PASSTHROUGH?
const bool vintfHwbinder = (transport == Transport::HWBINDER);
const bool vintfPassthru = (transport == Transport::PASSTHROUGH);
...
//Legacy模式一般为false
const bool vintfLegacy = false;
...
//尝试一定次数去获得IBase对象,仅限于HwBinder以及Legacy模式
for (int tries = 0; !getStub && (vintfHwbinder || vintfLegacy); tries++) {
if (waiter == nullptr && tries > 0) {
//创建了Waiter对象,用于等待
waiter = new Waiter(descriptor, instance, sm);
}
if (waiter != nullptr) {
waiter->reset();
}
//根据descriptor获取IBase对象。IBase通过封装能转化成Bp类。
Return<sp<IBase>> ret = sm->get(descriptor, instance);
//假如返回结果不为ok,则跳出循环,走PASSTHROUGH逻辑
if (!ret.isOk()) {
break;
}
sp<IBase> base = ret;
if (base != nullptr) {
//检验是否可以进行转换
Return<bool> canCastRet =
details::canCastInterface(base.get(), descriptor.c_str(), true /* emitError */);
//可以转换,则waiter调用done完成工作,返回base对象
if (canCastRet.isOk() && canCastRet) {
if (waiter != nullptr) {
waiter->done();
}
return base; // still needs to be wrapped by Bp class.
}
if (!handleCastError(canCastRet, descriptor, instance)) break;
}
if (vintfLegacy || !retry) break;
//base为空,waiter不为空时,等待
if (waiter != nullptr) {
waiter->wait();
}
}
if (waiter != nullptr) {
waiter->done();
}
if (getStub || vintfPassthru || vintfLegacy) {
//假如是直通模式,获取直通模式的ServiceManager
const sp<IServiceManager> pm = getPassthroughServiceManager();
if (pm != nullptr) {
sp<IBase> base = pm->get(descriptor, instance).withDefault(nullptr);
if (!getStub || trebleTestingOverride) {
base = wrapPassthrough(base);
}
return base;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
当获取到了serviceManager后,即可通过binder方式去调用服务,最后通过binderized调用openDevice:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
status_t DevicesFactoryHalHidl::openDevice(const char *name, sp<DeviceHalInterface> *device) {
if (mDevicesFactory == 0) return NO_INIT;
IDevicesFactory::Device hidlDevice;
//通过name,如primary,a2dp调用相应的静态hidlDevice对象。
status_t status = nameFromHal(name, &hidlDevice);
if (status != OK) return status;
Result retval = Result::NOT_INITIALIZED;
//此处使用了c++ lambda,mDevicesFactory为BpHwDevicesFactory。
//参数2为回调方法,当openDevice动作成功时,会新建一个DeviceHalHidl的对象,由device指向。
Return<void> ret = mDevicesFactory->openDevice(
hidlDevice,
[&](Result r, const sp<IDevice>& result) {
retval = r;
if (retval == Result::OK) {
*device = new DeviceHalHidl(result);
}
});
//错误处理
....
}
//out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/audio/2.0/android.hardware.audio@2.0_genc++/gen/android/hardware/audio/2.0/DevicesFactoryAll.cpp
::android::hardware::Return<void> BpHwDevicesFactory::openDevice(::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device device, openDevice_cb _hidl_cb){
//调用代理端的BpHwDevicesFactory::_hidl_openDevice方法,经过Binder进行通信。
::android::hardware::Return<void> _hidl_out = ::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::BpHwDevicesFactory::_hidl_openDevice(this, this, device, _hidl_cb);
return _hidl_out;
}
Binderized运行openDevice会创建DeviceHalHidl,Local时则会创建DeviceHalLocal。接下来看_hidl_openDevice的实现:
BpHwDevicesFactory::_hidl_openDevice为代理端实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
//out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/audio/2.0/android.hardware.audio@2.0_genc++/gen/android/hardware/audio/2.0/DevicesFactoryAll.cpp
::android::hardware::Return<void> BpHwDevicesFactory::_hidl_openDevice(::android::hardware::IInterface *_hidl_this, ::android::hardware::details::HidlInstrumentor *_hidl_this_instrumentor, ::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device device, openDevice_cb _hidl_cb) {
...
(void) _hidl_this_instrumentor;
if (_hidl_cb == nullptr) {
return ::android::hardware::Status::fromExceptionCode(
::android::hardware::Status::EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT,
"Null synchronous callback passed.");
}
::android::hardware::Parcel _hidl_data;
::android::hardware::Parcel _hidl_reply;
::android::status_t _hidl_err;
::android::hardware::Status _hidl_status;
::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::Result _hidl_out_retval;
::android::sp<::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevice> _hidl_out_result;
//writeInterface,descriptor为"android.hardware.audio@2.0::IDevicesFactory"
_hidl_err = _hidl_data.writeInterfaceToken(BpHwDevicesFactory::descriptor);
if (_hidl_err != ::android::OK) { goto _hidl_error; }
_hidl_err = _hidl_data.writeInt32((int32_t)device);
if (_hidl_err != ::android::OK) { goto _hidl_error; }
//通过_hidl_this发起transact通信,1为openDevice协议,_hidl_reply为返回的信息
_hidl_err = ::android::hardware::IInterface::asBinder(_hidl_this)->transact(1 /* openDevice */, _hidl_data, &_hidl_reply);
if (_hidl_err != ::android::OK) { goto _hidl_error; }
//读取_hidl_reply的信息包括_hidl_status,_hidl_out_retrval
_hidl_err = ::android::hardware::readFromParcel(&_hidl_status, _hidl_reply);
if (_hidl_err != ::android::OK) { goto _hidl_error; }
if (!_hidl_status.isOk()) { return _hidl_status; }
_hidl_err = _hidl_reply.readInt32((int32_t *)&_hidl_out_retval);
if (_hidl_err != ::android::OK) { goto _hidl_error; }
{
::android::sp<::android::hardware::IBinder> _hidl_binder;
_hidl_err = _hidl_reply.readNullableStrongBinder(&_hidl_binder);
if (_hidl_err != ::android::OK) { goto _hidl_error; }
_hidl_out_result = ::android::hardware::fromBinder<::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevice,::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::BpHwDevice,::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::BnHwDevice>(_hidl_binder);
}
//调用回调函数,假如值_hidl_out_result为Result::OK,则新建DeviceHalHidl
_hidl_cb(_hidl_out_retval, _hidl_out_result);
_hidl_status.setFromStatusT(_hidl_err);
return ::android::hardware::Return<void>();
_hidl_error:
_hidl_status.setFromStatusT(_hidl_err);
return ::android::hardware::Return<void>(_hidl_status);
}
BnHwDevicesFactory::_hidl_openDevice为对应的服务端实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
//out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/audio/2.0/android.hardware.audio@2.0_genc++/gen/android/hardware/audio/2.0/DevicesFactoryAll.cpp
::android::status_t BnHwDevicesFactory::_hidl_openDevice(
::android::hidl::base::V1_0::BnHwBase* _hidl_this,
const ::android::hardware::Parcel &_hidl_data,
::android::hardware::Parcel *_hidl_reply,
TransactCallback _hidl_cb) {
::android::status_t _hidl_err = ::android::OK;
//校验descriptor
if (!_hidl_data.enforceInterface(BnHwDevicesFactory::Pure::descriptor)) {
_hidl_err = ::android::BAD_TYPE;
return _hidl_err;
}
::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::Device device;
//从请求服务的进程的_hidl_data Parcel包中读取device
_hidl_err = _hidl_data.readInt32((int32_t *)&device);
if (_hidl_err != ::android::OK) { return _hidl_err; }
bool _hidl_callbackCalled = false;
//调用HAL层openDevice
static_cast<IDevicesFactory*>(_hidl_this->getImpl().get())->openDevice(device, [&](const auto &_hidl_out_retval, const auto &_hidl_out_result) {
if (_hidl_callbackCalled) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("openDevice: _hidl_cb called a second time, but must be called once.");
}
_hidl_callbackCalled = true;
//将状态返回到_hidl_reply,使得上层得到回复
::android::hardware::writeToParcel(::android::hardware::Status::ok(), _hidl_reply);
_hidl_err = _hidl_reply->writeInt32((int32_t)_hidl_out_retval);
/* _hidl_err ignored! */
if (_hidl_out_result == nullptr) {
_hidl_err = _hidl_reply->writeStrongBinder(nullptr);
} else {
::android::sp<::android::hardware::IBinder> _hidl_binder = ::android::hardware::toBinder<
::android::hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevice>(_hidl_out_result);
if (_hidl_binder.get() != nullptr) {
//返回了_hidl_binder
_hidl_err = _hidl_reply->writeStrongBinder(_hidl_binder);
} else {
_hidl_err = ::android::UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
}
//回调方法
_hidl_cb(*_hidl_reply);
});
if (!_hidl_callbackCalled) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("openDevice: _hidl_cb not called, but must be called once.");
}
return _hidl_err;
}
至此,研究了上层是如何调用到HAL层的adev_open接口.
4.3.3 SwAudioOutputDescriptor && open
从initialize的流程可得,遍历AudioProfile并对每一个新建一个相应的SwAudioOutputDescriptor(继承于AudioOutputDescriptor).当调用open时:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
status_t SwAudioOutputDescriptor::open(const audio_config_t *config,
audio_devices_t device,
const String8& address,
audio_stream_type_t stream,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
audio_io_handle_t *output)
{
//本例中config为空,会新建一个lConfig,同时为采样率.通道数,采样精度赋值
audio_config_t lConfig;
if (config == nullptr) {
lConfig = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
lConfig.sample_rate = mSamplingRate;
lConfig.channel_mask = mChannelMask;
lConfig.format = mFormat;
} else {
lConfig = *config;
}
mDevice = device;
//假如选定的AudioProfile是offload模式,且没有指定offload info,则会创建一个默认的offload_info
if ((mProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD) &&
lConfig.offload_info.format == AUDIO_FORMAT_DEFAULT) {
flags = (audio_output_flags_t)(flags | AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD);
lConfig.offload_info = AUDIO_INFO_INITIALIZER;
lConfig.offload_info.sample_rate = lConfig.sample_rate;
lConfig.offload_info.channel_mask = lConfig.channel_mask;
lConfig.offload_info.format = lConfig.format;
lConfig.offload_info.stream_type = stream;
lConfig.offload_info.duration_us = -1;
lConfig.offload_info.has_video = true; // conservative
lConfig.offload_info.is_streaming = true; // likely
}
//mFlags置位
mFlags = (audio_output_flags_t)(mFlags | flags);
//调用AudioFlinger的openOutput
status_t status = mClientInterface->openOutput(mProfile->getModuleHandle(),
output,
&lConfig,
&mDevice,
address,
&mLatency,
mFlags);
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
mSamplingRate = lConfig.sample_rate;
mChannelMask = lConfig.channel_mask;
mFormat = lConfig.format;
mId = AudioPort::getNextUniqueId();
mIoHandle = *output;
mProfile->curOpenCount++;
}
return status;
}
mClientInterface的类型为AudioPolicyClient,其实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
status_t AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyClient::openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_io_handle_t *output,
audio_config_t *config,
audio_devices_t *devices,
const String8& address,
uint32_t *latencyMs,
audio_output_flags_t flags)
{
//获取audioFlinger的proxy端
sp<IAudioFlinger> af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger();
if (af == 0) {
return PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
return af->openOutput(module, output, config, devices, address, latencyMs, flags);
}
暂且忽略AudioFlinger的Binder通信过程,直接看AudioFlinger的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
status_t AudioFlinger::openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_io_handle_t *output,
audio_config_t *config,
audio_devices_t *devices,
const String8& address,
uint32_t *latencyMs,
audio_output_flags_t flags)
{
if (devices == NULL || *devices == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
//openOutput_l
sp<ThreadBase> thread = openOutput_l(module, output, config, *devices, address, flags);
if (thread != 0) {
if ((flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_MMAP_NOIRQ) == 0) {
PlaybackThread *playbackThread = (PlaybackThread *)thread.get();
*latencyMs = playbackThread->latency();
//通知clients进程output已经创建完毕了
playbackThread->ioConfigChanged(AUDIO_OUTPUT_OPENED);
if ((mPrimaryHardwareDev == NULL) && (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY)) {
mPrimaryHardwareDev = playbackThread->getOutput()->audioHwDev;
AutoMutex lock(mHardwareLock);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_SET_MODE;
mPrimaryHardwareDev->hwDevice()->setMode(mMode);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;
}
} else {
MmapThread *mmapThread = (MmapThread *)thread.get();
mmapThread->ioConfigChanged(AUDIO_OUTPUT_OPENED);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
return NO_INIT;
}
sp<AudioFlinger::ThreadBase> AudioFlinger::openOutput_l(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_io_handle_t *output,
audio_config_t *config,
audio_devices_t devices,
const String8& address,
audio_output_flags_t flags)
{
//Step 1.查找对应的audio interface
AudioHwDevice *outHwDev = findSuitableHwDev_l(module, devices);
if (outHwDev == NULL) {
return 0;
}
if (*output == AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE) {
*output = nextUniqueId(AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_OUTPUT);
} else {
ALOGE("openOutput_l requested output handle %d is not AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE", *output);
return 0;
}
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_OUTPUT_OPEN;
//.....
AudioStreamOut *outputStream = NULL;
//Step 2.为设备打开一个输出流,
status_t status = outHwDev->openOutputStream(
&outputStream,
*output,
devices,
flags,
config,
address.string());
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;
//Step 3.创建播放线程
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
if (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_MMAP_NOIRQ) {
sp<MmapPlaybackThread> thread =
new MmapPlaybackThread(this, *output, outHwDev, outputStream,
devices, AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE, mSystemReady);
mMmapThreads.add(*output, thread);
return thread;
} else {
sp<PlaybackThread> thread;
if (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD) {
thread = new OffloadThread(this, outputStream, *output, devices, mSystemReady);
} else if ((flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT)
|| !isValidPcmSinkFormat(config->format)
|| !isValidPcmSinkChannelMask(config->channel_mask)) {
//直接输出,不需要混音
thread = new DirectOutputThread(this, outputStream, *output, devices, mSystemReady);
} else {
//需要混音线程
thread = new MixerThread(this, outputStream, *output, devices, mSystemReady);
}
//加入到mPlaybackThreads播放线程中
mPlaybackThreads.add(*output, thread);
return thread;
}
}
return 0;
}
4.3.3.1 findSuitableHwDev_l
findSuitableHwDev_l是为了找到适合的audio interface:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
AudioHwDevice* AudioFlinger::findSuitableHwDev_l(
audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t devices)
{
if (module == 0) {
//假如module为0,会对所有audio interfaces调用loadHwModule_l
for (size_t i = 0; i < arraysize(audio_interfaces); i++) {
loadHwModule_l(audio_interfaces[i]);
}
//遍历所有设备,并尝试找可支持的设备
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAudioHwDevs.size(); i++) {
AudioHwDevice *audioHwDevice = mAudioHwDevs.valueAt(i);
sp<DeviceHalInterface> dev = audioHwDevice->hwDevice();
uint32_t supportedDevices;
//找到了可支持的设备
if (dev->getSupportedDevices(&supportedDevices) == OK &&
(supportedDevices & devices) == devices) {
return audioHwDevice;
}
}
} else {
//一般会提供不为0的module,直接通过键值对获取
//在之前AudioPolicyMananger中的initialize时,就会调用loadHwModule并对mAudioHwDevs赋值
AudioHwDevice *audioHwDevice = mAudioHwDevs.valueFor(module);
if (audioHwDevice != NULL) {
return audioHwDevice;
}
}
return NULL;
}
4.3.3.2 openOutputStream
openOutputStream是为了给设备打开输出流:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
status_t AudioHwDevice::openOutputStream(
AudioStreamOut **ppStreamOut,
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
struct audio_config *config,
const char *address)
{
struct audio_config originalConfig = *config;
AudioStreamOut *outputStream = new AudioStreamOut(this, flags);
status_t status = outputStream->open(handle, devices, config, address);
//....
*ppStreamOut = outputStream;
return status;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioStreamOut.cpp
status_t AudioStreamOut::open(
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
struct audio_config *config,
const char *address)
{
sp<StreamOutHalInterface> outStream;
audio_output_flags_t customFlags = (config->format == AUDIO_FORMAT_IEC61937)
? (audio_output_flags_t)(flags | AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_IEC958_NONAUDIO)
: flags;
int status = hwDev()->openOutputStream(
handle,
devices,
customFlags,
config,
address,
&outStream);
if (status != NO_ERROR && config->format == AUDIO_FORMAT_IEC61937) {
struct audio_config customConfig = *config;
customConfig.format = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT;
status = hwDev()->openOutputStream(
handle,
devices,
customFlags,
&customConfig,
address,
&outStream);
}
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
stream = outStream;
mHalFormatHasProportionalFrames = audio_has_proportional_frames(config->format);
status = stream->getFrameSize(&mHalFrameSize);
}
return status;
}
至于openOutputStream的实现,会根据设备类型,选择调用的是hidl还是LegacyHal,最终会到厂商HAL层的adev_open_output_stream方法.主要目的即创建了音频输出流,并返回了outputStream
4.3.3.3 PlayBackThread
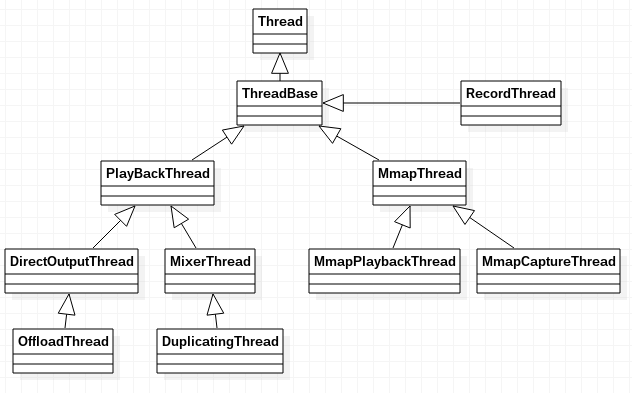
PlayBackThread是基类,这里暂且只分析DirectOutputThread以及MixerThread,给出线程的类图:
A. PlayBackThread
为了更好的了解DirectOutputThread以及MixerThread,先要了解PlayBackThread的实现,首先自然好奇其命名,可以查看AudioFlinger的线程,可输入如下命令:
1
ps -T | grep -i audioserver
此时展示出所有与audioserver相关的进程与线程:
1
2
#由于audioserver关键字的进程有两个,首先剔除第一行,只显示进程名的进程,再获取进程号,并赋值到ps -T显示其下所有线程
ps -T `ps -A |awk -F " " '{for(i=2;i<=NF;i++)printf("%s ",$i);printf "\n"}'| grep -i audioserver| awk '{print $1}'`
显示的结果如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
USER PID TID PPID VSZ RSS WCHAN ADDR S CMD
audioserver 1783 1783 1 54100 16856 binder_thread_read 0 S audioserver
audioserver 1783 1895 1 54100 16856 binder_thread_read 0 S HwBinder:1783_1
audioserver 1783 1899 1 54100 16856 futex_wait_queue_me 0 S ApmTone
audioserver 1783 1900 1 54100 16856 futex_wait_queue_me 0 S ApmAudio
audioserver 1783 1901 1 54100 16856 futex_wait_queue_me 0 S ApmOutput
audioserver 1783 1903 1 54100 16856 binder_thread_read 0 S HwBinder:1783_2
audioserver 1783 1906 1 54100 16856 binder_thread_read 0 S Binder:1783_1
audioserver 1783 1907 1 54100 16856 binder_thread_read 0 S Binder:1783_2
audioserver 1783 1947 1 54100 16856 futex_wait_queue_me 0 S AudioOut_D
audioserver 1783 2062 1 54100 16856 futex_wait_queue_me 0 S soundTrigger cb
audioserver 1783 2092 1 54100 16856 futex_wait_queue_me 0 S TimeCheckThread
audioserver 1783 14919 1 54100 16856 binder_thread_read 0 S Binder:1783_3
audioserver 1783 17914 1 54100 16856 binder_thread_read 0 S Binder:1783_4
可以快速剔除三个Apm相关线程,audioserver主线程,Binder线程,以及HW相关的线程.十分怀疑AudioOut_D就是指PlayBackThread线程了.结合到代码看PlayBackThread的构造方法,有如下逻辑,就更证实了之前的猜想.
1
snprintf(mThreadName, kThreadNameLength, "AudioOut_%X", id);
其threadLoop的内容十分冗长,为了方便分析,可以简化其流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp
bool AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::threadLoop()
{
....
acquireWakeLock();
//判断线程循环条件
while (!exitPending())
{
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
//Step 1. 循环处理config
processConfigEvents_l();
saveOutputTracks();
...
if ((!mActiveTracks.size() && systemTime() > mStandbyTimeNs) ||
isSuspended()) {
if (shouldStandby_l()) {
//step 2. threadLoop_standby
threadLoop_standby();
mStandby = true;
}
}
//step 3.准备音频数据
mMixerStatus = prepareTracks_l(&tracksToRemove);
...
} // mLock scope ends
if (mBytesRemaining == 0) {
...
if (mMixerStatus == MIXER_TRACKS_READY) {
//step 4. 开始混音
threadLoop_mix();
} else if ((mMixerStatus != MIXER_DRAIN_TRACK)
&& (mMixerStatus != MIXER_DRAIN_ALL)) {
//休眠
threadLoop_sleepTime();
...
}
}
...
if (!waitingAsyncCallback()) {
if (mSleepTimeUs == 0) {
ssize_t ret = 0;
nsecs_t previousLastWriteFinished = lastWriteFinished;
nsecs_t delta = 0;
if (mBytesRemaining) {
...
//step 5. 将数据写入音频硬件设备
ret = threadLoop_write();
...
} else if ((mMixerStatus == MIXER_DRAIN_TRACK) ||
(mMixerStatus == MIXER_DRAIN_ALL)) {
threadLoop_drain();
}
...
} else {
...
}
}
//step 6. 移除Tracks
threadLoop_removeTracks(tracksToRemove);
tracksToRemove.clear();
clearOutputTracks();
}
//step 7.退出线程
threadLoop_exit();
if (!mStandby) {
threadLoop_standby();
mStandby = true;
}
releaseWakeLock();
return false;
}
至此,可以总结PlaybackThread的循环流程为:
processConfigEvents_l循环处理configthreadLoop_standby进入休眠?prepareTracks_l准备音频数据threadLoop_mix开始混音threadLoop_write写入音频硬件threadLoop_removeTracks移除相关TracksthreadLoop_exit跳出循环后,结束线程
A.1 processConfigEvents_l
ThreadBase(PlayBackThread的父类)中实现了几个方法将events加入到mConfigEvents中,如下方法均可以变更配置:
- sendPrioConfigEvent 设置优先级
- sendIoConfigEvent 发送IO配置
- setParameters 设置参数
- sendCreateAudioPatchConfigEvent 发送创建AudioPatch配置
- sendReleaseAudioPatchConfigEvent 发送释放AudioPatch配置
关于AudioPatch的资料可以参考链接: 在Android5.0上Audio Patch和Patch Panel的一些分析
现在可以分析processConfigEvents_l了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp
void AudioFlinger::ThreadBase::processConfigEvents_l()
{
bool configChanged = false;
//当mConfigEvents不为空时
while (!mConfigEvents.isEmpty()) {
//每次从头部处理event
sp<ConfigEvent> event = mConfigEvents[0];
mConfigEvents.removeAt(0);
switch (event->mType) {
case CFG_EVENT_PRIO: {
PrioConfigEventData *data = (PrioConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
//调用libmediautils库的方法修改优先级
int err = requestPriority(data->mPid, data->mTid, data->mPrio, data->mForApp,
true /*asynchronous*/);
...
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_IO: {
IoConfigEventData *data = (IoConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
//最终调用到AudioSystem的ioConfigChanged,ioConfig类型包括:
//enum audio_io_config_event {
// AUDIO_OUTPUT_REGISTERED, //Output注册
// AUDIO_OUTPUT_OPENED, //Output打开
// AUDIO_OUTPUT_CLOSED, //Output关闭
// AUDIO_OUTPUT_CONFIG_CHANGED,//Output配置改变
// AUDIO_INPUT_REGISTERED, //INPUT注册
// AUDIO_INPUT_OPENED, //INPUT打开
// AUDIO_INPUT_CLOSED, //INPUT关闭
// AUDIO_INPUT_CONFIG_CHANGED, //INPUT配置改变
//};
ioConfigChanged(data->mEvent, data->mPid);
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_SET_PARAMETER: {
SetParameterConfigEventData *data = (SetParameterConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
//检查并设置属性,具体线程有自己的实现方式
if (checkForNewParameter_l(data->mKeyValuePairs, event->mStatus)) {
configChanged = true;
}
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_CREATE_AUDIO_PATCH: {
const audio_devices_t oldDevice = getDevice();
CreateAudioPatchConfigEventData *data =
(CreateAudioPatchConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
//创建AudioPatch,具体线程需要实现createAudioPatch_l
event->mStatus = createAudioPatch_l(&data->mPatch, &data->mHandle);
const audio_devices_t newDevice = getDevice();
...
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_RELEASE_AUDIO_PATCH: {
const audio_devices_t oldDevice = getDevice();
ReleaseAudioPatchConfigEventData *data =
(ReleaseAudioPatchConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
//释放AudioPatch,具体线程需要实现releaseAudioPatch_l
event->mStatus = releaseAudioPatch_l(data->mHandle);
const audio_devices_t newDevice = getDevice();
} break;
default:
break;
}
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(event->mLock);
if (event->mWaitStatus) {
event->mWaitStatus = false;
event->mCond.signal();
}
}
}
if (configChanged) {
cacheParameters_l();
}
}
A.2 threadLoop_standby
threadLoop_standby最终调用到HAL层的output_standby方法.
A.3 prepareTracks_l && threadLoop_mix
prepareTracks_l和threadLoop_mix会在具体线程实现,将放在后续进行分析.
A.4 threadLoop_write
threadLoop_write这里展示的是PlaybackThread的实现,一般DirectOutputThread以及OffloadThread会调用到这里.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
ssize_t AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::threadLoop_write()
{
mInWrite = true;
ssize_t bytesWritten;
const size_t offset = mCurrentWriteLength - mBytesRemaining;
//NBAIO模式
if (mNormalSink != 0) {
const size_t count = mBytesRemaining / mFrameSize;
uint32_t screenState = AudioFlinger::mScreenState;
if (screenState != mScreenState) {
mScreenState = screenState;
MonoPipe *pipe = (MonoPipe *)mPipeSink.get();
if (pipe != NULL) {
pipe->setAvgFrames((mScreenState & 1) ?
(pipe->maxFrames() * 7) / 8 : mNormalFrameCount * 2);
}
}
//也是将SinkBuffer写入
ssize_t framesWritten = mNormalSink->write((char *)mSinkBuffer + offset, count);
if (framesWritten > 0) {
bytesWritten = framesWritten * mFrameSize;
} else {
bytesWritten = framesWritten;
}
// otherwise use the HAL / AudioStreamOut directly
} else {
//Direct模式以及Offload模式
if (mUseAsyncWrite) {
mWriteAckSequence += 2;
mWriteAckSequence |= 1;
ALOG_ASSERT(mCallbackThread != 0);
mCallbackThread->setWriteBlocked(mWriteAckSequence);
}
//在这里将数据写入到音频硬件设备中,具体需要看HAL层接口,写的数据保存在了mSinkBuffer中
bytesWritten = mOutput->write((char *)mSinkBuffer + offset, mBytesRemaining);
if (mUseAsyncWrite &&
((bytesWritten < 0) || (bytesWritten == (ssize_t)mBytesRemaining))) {
mWriteAckSequence &= ~1;
mCallbackThread->setWriteBlocked(mWriteAckSequence);
}
}
mNumWrites++;
mInWrite = false;
mStandby = false;
return bytesWritten;
}
6. threadLoop_removeTracks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
void AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::threadLoop_removeTracks(
const Vector< sp<Track> >& tracksToRemove)
{
size_t count = tracksToRemove.size();
if (count > 0) {
//遍历tracksToRemove中的track进行移除
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < count ; i++) {
const sp<Track>& track = tracksToRemove.itemAt(i);
if (track->isExternalTrack()) {
//通过AudioSystem调用StopOutput停用
AudioSystem::stopOutput(mId, track->streamType(),
track->sessionId());
if (track->isTerminated()) {
AudioSystem::releaseOutput(mId, track->streamType(),
track->sessionId());
}
}
}
}
}
B. DirectOutputThread
至此具体到DirectOutputThread,即不需要进行混音即可输出.当满足flags置位了AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT,或采样精度,通道数不满足混音时,此时会新建DirectOutputThread.
1
2
3
4
5
else if ((flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT)
|| !isValidPcmSinkFormat(config->format)
|| !isValidPcmSinkChannelMask(config->channel_mask)) {
thread = new DirectOutputThread(this, outputStream, *output, devices, mSystemReady);
}
首先来看其构造函数,type类型定义为DIRECT.
1
2
3
4
5
AudioFlinger::DirectOutputThread::DirectOutputThread(const sp<AudioFlinger>& audioFlinger,
AudioStreamOut* output, audio_io_handle_t id, audio_devices_t device, bool systemReady)
: PlaybackThread(audioFlinger, output, id, device, DIRECT, systemReady)
{
}
DirectOutThread并没有实现自己的ThreadLoop,而是使用了父类PlaybackThread的,但对关键的步骤进行了覆盖,先再展示ThreadLoop的关键步骤:
processConfigEvents_l循环处理configthreadLoop_standby进入休眠?prepareTracks_l准备音频数据threadLoop_mix开始混音threadLoop_write写入音频硬件threadLoop_removeTracks移除相关TracksthreadLoop_exit跳出循环后,结束线程
DirectOutThread在上述方法进行重写的方法包括prepareTracks_l以及threadLoop_mix,其余步骤都是使用了父类PlaybackThread或者ThreadBase的方法.
prepareTracks_l进行准备性的工作,并处理了许多underrun的情景.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::mixer_state AudioFlinger::DirectOutputThread::prepareTracks_l(
Vector< sp<Track> > *tracksToRemove
)
{
size_t count = mActiveTracks.size();
mixer_state mixerStatus = MIXER_IDLE;
bool doHwPause = false;
bool doHwResume = false;
//当AudioTrack自上层创建后,会通过PlaybackThread的createTrack_l创建Track.
//假如将Track加入到了mActiveTracks中,表明这个Track是Active(活跃的).这里就是希望从ActiveTracks中找到需要处理的Track
for (const sp<Track> &t : mActiveTracks) {
if (t->isInvalid()) {
tracksToRemove->add(t);
continue;
}
Track* const track = t.get();
#ifdef VERY_VERY_VERBOSE_LOGGING
//准备音频数据块
audio_track_cblk_t* cblk = track->cblk();
#endif
//获取mLatestActiveTrack,即最近一次调用add时,会将add的Track赋值为mLatestActiveTrack.
sp<Track> l = mActiveTracks.getLatest();
//假如上次处理的Track与当前Track相同
bool last = l.get() == track;
if (track->isPausing()) {
track->setPaused();
//HAL层支持暂停并且mLatestActiveTrack不为空,会设置doHwPause,mHwPaused为true,后续将会调用到HAL层的暂停
if (mHwSupportsPause && last && !mHwPaused) {
doHwPause = true;
mHwPaused = true;
}
tracksToRemove->add(track);
} else if (track->isFlushPending()) {
track->flushAck();
if (last) {
mFlushPending = true;
}
} else if (track->isResumePending()) {
track->resumeAck();
if (last) {
mLeftVolFloat = mRightVolFloat = -1.0;
if (mHwPaused) {
doHwResume = true;
mHwPaused = false;
}
}
}
//计算最小帧数,在createTrack_l时,mNormalFrameCount在readOutputParameters_l时被更新
//sharedBuffer为0表明当前为stream模式.
uint32_t minFrames;
if ((track->sharedBuffer() == 0) && !track->isStopping_1() && !track->isPausing()
&& (track->mRetryCount > 1) && audio_has_proportional_frames(mFormat)) {
minFrames = mNormalFrameCount;
} else {
minFrames = 1;
}
//当前准备帧数大于最小帧数,track已经准备就绪,且不是暂停或停止状态.
if ((track->framesReady() >= minFrames) && track->isReady() && !track->isPaused() &&
!track->isStopping_2() && !track->isStopped())
{
if (track->mFillingUpStatus == Track::FS_FILLED) {
track->mFillingUpStatus = Track::FS_ACTIVE;
if (last) {
mLeftVolFloat = mRightVolFloat = -1.0;
}
if (!mHwSupportsPause) {
track->resumeAck();
}
}
//处理音量,该方法DirectOutThread也进行了重写
processVolume_l(track, last);
if (last) {//假如上次处理的Track为当前循环遍历的Track
sp<Track> previousTrack = mPreviousTrack.promote();
if (previousTrack != 0) {
if (track != previousTrack.get()) {
mBytesRemaining = 0;
previousTrack->invalidate();
}
}
//将当前track赋值到mPreviousTrack,表明这是最近处理的Track
mPreviousTrack = track;
//最大重试次数为2
track->mRetryCount = kMaxTrackRetriesDirect;
mActiveTrack = t;
mixerStatus = MIXER_TRACKS_READY;
//假如mHwPause当前为True,设置doHwResume为True,mHwPause改为false
if (mHwPaused) {
doHwResume = true;
mHwPaused = false;
}
}
} else {//数据未准备好
if (!mEffectChains.isEmpty() && last) {
mEffectChains[0]->clearInputBuffer();
}
//STOPPING_1即出现了第一次underrun,生产者速度不及消费
if (track->isStopping_1()) {
//STOPPING_2等待当前完成
track->mState = TrackBase::STOPPING_2;
//上次处理的Track跟当前处理的相同,且mHwPaused为true
if (last && mHwPaused) {
doHwResume = true;
mHwPaused = false;
}
}
//当前为stream模式或者track处于停止或者暂停状态
if ((track->sharedBuffer() != 0) || track->isStopped() ||
track->isStopping_2() || track->isPaused()) {
//此时表明已经消费完所有Track中的buffer了,需要将Track从activeTracks中移除
size_t audioHALFrames;
if (audio_has_proportional_frames(mFormat)) {
audioHALFrames = (latency_l() * mSampleRate) / 1000;
} else {
audioHALFrames = 0;
}
int64_t framesWritten = mBytesWritten / mFrameSize;
if (mStandby || !last ||
track->presentationComplete(framesWritten, audioHALFrames)) {
if (track->isStopping_2()) {
track->mState = TrackBase::STOPPED;
}
if (track->isStopped()) {
track->reset();
}
tracksToRemove->add(track);
}
} else {
//该Track没有buffer,给它机会去填充buffer,然后从ActiveTracks中移除
if (--(track->mRetryCount) <= 0) {
tracksToRemove->add(track);
//disable该track,当数据有效时,会自动重启
track->disable();
} else if (last) {
//因为underrun而暂停,将doHwPause,mHwPaused设置为true
mixerStatus = MIXER_TRACKS_ENABLED;
if (mHwSupportsPause && !mHwPaused && !mStandby) {
doHwPause = true;
mHwPaused = true;
}
}
}
}
}
// if an active track did not command a flush, check for pending flush on stopped tracks
if (!mFlushPending) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < mTracks.size(); i++) {
if (mTracks[i]->isFlushPending()) {
mTracks[i]->flushAck();
mFlushPending = true;
}
}
}
//保证pause/flush/resume的序列以正确的顺序执行.
//假如flush是待执行而且track是active的,但硬件并没有暂停,会强制使硬件先于flush执行暂停,再继续运行.
if (mHwSupportsPause && !mStandby &&
(doHwPause || (mFlushPending && !mHwPaused && (count != 0)))) {
//调用到HAL层的暂停.
status_t result = mOutput->stream->pause();
}
//同步数据
if (mFlushPending) {
flushHw_l();
}
if (mHwSupportsPause && !mStandby && doHwResume) {
//调用到HAL层的resume
status_t result = mOutput->stream->resume();
}
//移除所有需要移除的Track
removeTracks_l(*tracksToRemove);
return mixerStatus;
}
再来看一下当数据准备完成后,DirectOutputThread调用processVolume_l的流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
void AudioFlinger::DirectOutputThread::processVolume_l(Track *track, bool lastTrack)
{
float left, right;
//当mMasterMute为true或者流音量中的mute设置为true,左右声道音量都设置为0
if (mMasterMute || mStreamTypes[track->streamType()].mute) {
left = right = 0;
} else {
float typeVolume = mStreamTypes[track->streamType()].volume;
//mMasterVolume恒为1.0,上层AudioManager已经废弃相关接口不使用MasterVolume了
float v = mMasterVolume * typeVolume;
sp<AudioTrackServerProxy> proxy = track->mAudioTrackServerProxy;
// Get volumeshaper scaling
std::pair<float /* volume */, bool /* active */>
vh = track->getVolumeHandler()->getVolume(
track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->framesReleased());
v *= vh.first;
mVolumeShaperActive = vh.second;
//获取左右音量,并进行转换赋值到left,right中,最终值还需要与v进行相乘.
gain_minifloat_packed_t vlr = proxy->getVolumeLR();
left = float_from_gain(gain_minifloat_unpack_left(vlr));
if (left > GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY) {
left = GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY;
}
left *= v;
right = float_from_gain(gain_minifloat_unpack_right(vlr));
if (right > GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY) {
right = GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY;
}
right *= v;
}
if (lastTrack) {
track->setFinalVolume((left + right) / 2.f);
if (left != mLeftVolFloat || right != mRightVolFloat) {
mLeftVolFloat = left;
mRightVolFloat = right;
if (!mEffectChains.isEmpty()) {
uint32_t vl = (uint32_t)(left * (1 << 24));
uint32_t vr = (uint32_t)(right * (1 << 24));
(void)mEffectChains[0]->setVolume_l(&vl, &vr);
} else {
setVolumeForOutput_l(left, right);
}
}
}
}
DirectOutputThread中的threadLoop_mix将数据从Track中搬运到了SinkBuffer中.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
void AudioFlinger::DirectOutputThread::threadLoop_mix()
{
size_t frameCount = mFrameCount;
//mSinkBuffer是在readOutputParameters_l时申请的内存,其大小是帧数乘以帧大小
//const size_t sinkBufferSize = mNormalFrameCount * mFrameSize;
//(void)posix_memalign(&mSinkBuffer, 32, sinkBufferSize);
//在后续的threadLoop_write,会将mSinkBuffer的数据写入到硬件中
int8_t *curBuf = (int8_t *)mSinkBuffer;
//输出Audio到HAL
while (frameCount) {
AudioBufferProvider::Buffer buffer;
buffer.frameCount = frameCount;
//获取mActiveTrack的buffer
status_t status = mActiveTrack->getNextBuffer(&buffer);
if (status != NO_ERROR || buffer.raw == NULL) {
// no need to pad with 0 for compressed audio
if (audio_has_proportional_frames(mFormat)) {
memset(curBuf, 0, frameCount * mFrameSize);
}
break;
}
//拷贝数据到mSinkBuffer
memcpy(curBuf, buffer.raw, buffer.frameCount * mFrameSize);
frameCount -= buffer.frameCount;
curBuf += buffer.frameCount * mFrameSize;
mActiveTrack->releaseBuffer(&buffer);
}
mCurrentWriteLength = curBuf - (int8_t *)mSinkBuffer;
mSleepTimeUs = 0;
mStandbyTimeNs = systemTime() + mStandbyDelayNs;
mActiveTrack.clear();
}
C. MixerThread
MixerThread一般用的场景更多,先来看下其构造方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
AudioFlinger::MixerThread::MixerThread(const sp<AudioFlinger>& audioFlinger, AudioStreamOut* output,
audio_io_handle_t id, audio_devices_t device, bool systemReady, type_t type)
: PlaybackThread(audioFlinger, output, id, device, type, systemReady),
mFastMixerFutex(0),
mMasterMono(false)
{
//MixerThread中都会有唯一的AudioMixer用于混音
mAudioMixer = new AudioMixer(mNormalFrameCount, mSampleRate);
//DuplicatingThread也是MixerThread,但不需要执行后续的初始化工作
if (type == DUPLICATING) {
return;
}
//为HAL层的output stream创建NBAIO sink端
mOutputSink = new AudioStreamOutSink(output->stream);
size_t numCounterOffers = 0;
const NBAIO_Format offers[1] = {Format_from_SR_C(mSampleRate, mChannelCount, mFormat)};
#if !LOG_NDEBUG
ssize_t index =
#else
(void)
#endif
mOutputSink->negotiate(offers, 1, NULL, numCounterOffers);
ALOG_ASSERT(index == 0);
//初始化FastMixer,暂不分析
....
}
}
关于FastMixer的内容,可以查看:
再继续看MixerThread::prepareTracks_l
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::mixer_state AudioFlinger::MixerThread::prepareTracks_l(
Vector< sp<Track> > *tracksToRemove)
{
//在分配新Track前清理AudioMixer中的tracks
(void)mTracks.processDeletedTrackNames([this](int name) {
// for each name, destroy it in the AudioMixer
if (mAudioMixer->exists(name)) {
mAudioMixer->destroy(name);
}
});
mTracks.clearDeletedTrackNames();
mixer_state mixerStatus = MIXER_IDLE;
// find out which tracks need to be processed
size_t count = mActiveTracks.size();
size_t mixedTracks = 0;
size_t tracksWithEffect = 0;
// counts only _active_ fast tracks
size_t fastTracks = 0;
uint32_t resetMask = 0; // bit mask of fast tracks that need to be reset
float masterVolume = mMasterVolume;
bool masterMute = mMasterMute;
if (masterMute) {
masterVolume = 0;
}
// Delegate master volume control to effect in output mix effect chain if needed
sp<EffectChain> chain = getEffectChain_l(AUDIO_SESSION_OUTPUT_MIX);
if (chain != 0) {
uint32_t v = (uint32_t)(masterVolume * (1 << 24));
chain->setVolume_l(&v, &v);
masterVolume = (float)((v + (1 << 23)) >> 24);
chain.clear();
}
// prepare a new state to push
FastMixerStateQueue *sq = NULL;
FastMixerState *state = NULL;
bool didModify = false;
FastMixerStateQueue::block_t block = FastMixerStateQueue::BLOCK_UNTIL_PUSHED;
bool coldIdle = false;
if (mFastMixer != 0) {
sq = mFastMixer->sq();
state = sq->begin();
coldIdle = state->mCommand == FastMixerState::COLD_IDLE;
}
mMixerBufferValid = false; // mMixerBuffer has no valid data until appropriate tracks found.
mEffectBufferValid = false; // mEffectBuffer has no valid data until tracks found.
//遍历mActiveTracks
for (size_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {
const sp<Track> t = mActiveTracks[i];
//获取当前track
Track* const track = t.get();
//处理FastTrack
if (track->isFastTrack()) {
int j = track->mFastIndex;
FastTrack *fastTrack = &state->mFastTracks[j];
FastTrackDump *ftDump = &mFastMixerDumpState.mTracks[j];
FastTrackUnderruns underruns = ftDump->mUnderruns;
uint32_t recentFull = (underruns.mBitFields.mFull -
track->mObservedUnderruns.mBitFields.mFull) & UNDERRUN_MASK;
uint32_t recentPartial = (underruns.mBitFields.mPartial -
track->mObservedUnderruns.mBitFields.mPartial) & UNDERRUN_MASK;
uint32_t recentEmpty = (underruns.mBitFields.mEmpty -
track->mObservedUnderruns.mBitFields.mEmpty) & UNDERRUN_MASK;
uint32_t recentUnderruns = recentPartial + recentEmpty;
track->mObservedUnderruns = underruns;
if (!(track->isStopping() || track->isPausing() || track->isStopped()) &&
recentUnderruns > 0) {
track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->tallyUnderrunFrames(recentUnderruns * mFrameCount);
} else {
track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->tallyUnderrunFrames(0);
}
// This is similar to the state machine for normal tracks,
// with a few modifications for fast tracks.
bool isActive = true;
switch (track->mState) {
case TrackBase::STOPPING_1:
if (recentUnderruns > 0 || track->isTerminated()) {
track->mState = TrackBase::STOPPING_2;
}
break;
case TrackBase::PAUSING:
track->setPaused();
break;
case TrackBase::RESUMING:
track->mState = TrackBase::ACTIVE;
break;
case TrackBase::ACTIVE:
if (recentFull > 0 || recentPartial > 0) {
track->mRetryCount = kMaxTrackRetries;
}
if (recentUnderruns == 0) {
// no recent underruns: stay active
break;
}
// there has recently been an underrun of some kind
if (track->sharedBuffer() == 0) {
// were any of the recent underruns "empty" (no frames available)?
if (recentEmpty == 0) {
// no, then ignore the partial underruns as they are allowed indefinitely
break;
}
// there has recently been an "empty" underrun: decrement the retry counter
if (--(track->mRetryCount) > 0) {
break;
}
// indicate to client process that the track was disabled because of underrun;
// it will then automatically call start() when data is available
track->disable();
// remove from active list, but state remains ACTIVE [confusing but true]
isActive = false;
break;
}
FALLTHROUGH_INTENDED;
case TrackBase::STOPPING_2:
case TrackBase::PAUSED:
case TrackBase::STOPPED:
case TrackBase::FLUSHED: // flush() while active
// Check for presentation complete if track is inactive
// We have consumed all the buffers of this track.
// This would be incomplete if we auto-paused on underrun
{
uint32_t latency = 0;
status_t result = mOutput->stream->getLatency(&latency);
ALOGE_IF(result != OK,
"Error when retrieving output stream latency: %d", result);
size_t audioHALFrames = (latency * mSampleRate) / 1000;
int64_t framesWritten = mBytesWritten / mFrameSize;
if (!(mStandby || track->presentationComplete(framesWritten, audioHALFrames))) {
// track stays in active list until presentation is complete
break;
}
}
if (track->isStopping_2()) {
track->mState = TrackBase::STOPPED;
}
if (track->isStopped()) {
// Can't reset directly, as fast mixer is still polling this track
// track->reset();
// So instead mark this track as needing to be reset after push with ack
resetMask |= 1 << i;
}
isActive = false;
break;
case TrackBase::IDLE:
default:
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("unexpected track state %d", track->mState);
}
if (isActive) {
// was it previously inactive?
if (!(state->mTrackMask & (1 << j))) {
ExtendedAudioBufferProvider *eabp = track;
VolumeProvider *vp = track;
fastTrack->mBufferProvider = eabp;
fastTrack->mVolumeProvider = vp;
fastTrack->mChannelMask = track->mChannelMask;
fastTrack->mFormat = track->mFormat;
fastTrack->mGeneration++;
state->mTrackMask |= 1 << j;
didModify = true;
// no acknowledgement required for newly active tracks
}
sp<AudioTrackServerProxy> proxy = track->mAudioTrackServerProxy;
// cache the combined master volume and stream type volume for fast mixer; this
// lacks any synchronization or barrier so VolumeProvider may read a stale value
const float vh = track->getVolumeHandler()->getVolume(
proxy->framesReleased()).first;
float volume = masterVolume
* mStreamTypes[track->streamType()].volume
* vh;
track->mCachedVolume = volume;
gain_minifloat_packed_t vlr = proxy->getVolumeLR();
float vlf = volume * float_from_gain(gain_minifloat_unpack_left(vlr));
float vrf = volume * float_from_gain(gain_minifloat_unpack_right(vlr));
track->setFinalVolume((vlf + vrf) / 2.f);
++fastTracks;
} else {
// was it previously active?
if (state->mTrackMask & (1 << j)) {
fastTrack->mBufferProvider = NULL;
fastTrack->mGeneration++;
state->mTrackMask &= ~(1 << j);
didModify = true;
// If any fast tracks were removed, we must wait for acknowledgement
// because we're about to decrement the last sp<> on those tracks.
block = FastMixerStateQueue::BLOCK_UNTIL_ACKED;
} else {
// ALOGW rather than LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL because it seems there are cases where an
// AudioTrack may start (which may not be with a start() but with a write()
// after underrun) and immediately paused or released. In that case the
// FastTrack state hasn't had time to update.
// TODO Remove the ALOGW when this theory is confirmed.
ALOGW("fast track %d should have been active; "
"mState=%d, mTrackMask=%#x, recentUnderruns=%u, isShared=%d",
j, track->mState, state->mTrackMask, recentUnderruns,
track->sharedBuffer() != 0);
// Since the FastMixer state already has the track inactive, do nothing here.
}
tracksToRemove->add(track);
// Avoids a misleading display in dumpsys
track->mObservedUnderruns.mBitFields.mMostRecent = UNDERRUN_FULL;
}
continue;
}
{ // local variable scope to avoid goto warning
//准备数据块
audio_track_cblk_t* cblk = track->cblk();
int name = track->name();
//AudioMixer中不存在该Track,则创建一个
if (!mAudioMixer->exists(name)) {
status_t status = mAudioMixer->create(
name,
track->mChannelMask,
track->mFormat,
track->mSessionId);
if (status != OK) {
tracksToRemove->add(track);
track->invalidate(); // consider it dead.
continue;
}
}
size_t desiredFrames;
const uint32_t sampleRate = track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->getSampleRate();
AudioPlaybackRate playbackRate = track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->getPlaybackRate();
desiredFrames = sourceFramesNeededWithTimestretch(
sampleRate, mNormalFrameCount, mSampleRate, playbackRate.mSpeed);
desiredFrames += mAudioMixer->getUnreleasedFrames(track->name());
uint32_t minFrames = 1;
if ((track->sharedBuffer() == 0) && !track->isStopped() && !track->isPausing() &&
(mMixerStatusIgnoringFastTracks == MIXER_TRACKS_READY)) {
minFrames = desiredFrames;
}
size_t framesReady = track->framesReady();
if (ATRACE_ENABLED()) {
std::string traceName("nRdy");
traceName += std::to_string(track->name());
}
//数据已准备好
if ((framesReady >= minFrames) && track->isReady() &&
!track->isPaused() && !track->isTerminated())
{
mixedTracks++;
chain.clear();
if (track->mainBuffer() != mSinkBuffer &&
track->mainBuffer() != mMixerBuffer) {
if (mEffectBufferEnabled) {
mEffectBufferValid = true; // Later can set directly.
}
chain = getEffectChain_l(track->sessionId());
if (chain != 0) {
tracksWithEffect++;
} else {
ALOGW("prepareTracks_l(): track %d attached to effect but no chain found on "
"session %d",
name, track->sessionId());
}
}
int param = AudioMixer::VOLUME;
if (track->mFillingUpStatus == Track::FS_FILLED) {
track->mFillingUpStatus = Track::FS_ACTIVE;
if (track->mState == TrackBase::RESUMING) {
track->mState = TrackBase::ACTIVE;
param = AudioMixer::RAMP_VOLUME;
}
//AudioMixer设置参数
mAudioMixer->setParameter(name, AudioMixer::RESAMPLE, AudioMixer::RESET, NULL);
mLeftVolFloat = -1.0;
} else if (cblk->mServer != 0) {
param = AudioMixer::RAMP_VOLUME;
}
//计算Track的音量
uint32_t vl, vr; // in U8.24 integer format
float vlf, vrf, vaf; // in [0.0, 1.0] float format
float typeVolume = mStreamTypes[track->streamType()].volume;
float v = masterVolume * typeVolume;
if (track->isPausing() || mStreamTypes[track->streamType()].mute) {
vl = vr = 0;
vlf = vrf = vaf = 0.;
if (track->isPausing()) {
track->setPaused();
}
} else {
sp<AudioTrackServerProxy> proxy = track->mAudioTrackServerProxy;
gain_minifloat_packed_t vlr = proxy->getVolumeLR();
vlf = float_from_gain(gain_minifloat_unpack_left(vlr));
vrf = float_from_gain(gain_minifloat_unpack_right(vlr));
if (vlf > GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY) {
vlf = GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY;
}
if (vrf > GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY) {
vrf = GAIN_FLOAT_UNITY;
}
const float vh = track->getVolumeHandler()->getVolume(
track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->framesReleased()).first;
vlf *= v * vh;
vrf *= v * vh;
const float scaleto8_24 = MAX_GAIN_INT * MAX_GAIN_INT;
vl = (uint32_t) (scaleto8_24 * vlf);
vr = (uint32_t) (scaleto8_24 * vrf);
uint16_t sendLevel = proxy->getSendLevel_U4_12();
if (sendLevel > MAX_GAIN_INT) {
sendLevel = MAX_GAIN_INT;
}
vaf = v * sendLevel * (1. / MAX_GAIN_INT);
}
//设置音量
track->setFinalVolume((vrf + vlf) / 2.f);
if (chain != 0 && chain->setVolume_l(&vl, &vr)) {
param = AudioMixer::VOLUME;
vlf = (float)vl / (1 << 24);
vrf = (float)vr / (1 << 24);
track->mHasVolumeController = true;
} else {
if (track->mHasVolumeController) {
param = AudioMixer::VOLUME;
}
track->mHasVolumeController = false;
}
if ((mOutput->flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_VOIP_RX) != 0) {
v = mStreamTypes[track->streamType()].mute ? 0.0f : v;
if (v != mLeftVolFloat) {
status_t result = mOutput->stream->setVolume(v, v);
if (result == OK) {
mLeftVolFloat = v;
}
}
// if stream volume was successfully sent to the HAL, mLeftVolFloat == v here and we
// remove stream volume contribution from software volume.
if (v != 0.0f && mLeftVolFloat == v) {
vlf = min(1.0f, vlf / v);
vrf = min(1.0f, vrf / v);
vaf = min(1.0f, vaf / v);
}
}
// XXX: these things DON'T need to be done each time
mAudioMixer->setBufferProvider(name, track);
mAudioMixer->enable(name);
//通过AudioMixer设置音量
mAudioMixer->setParameter(name, param, AudioMixer::VOLUME0, &vlf);
mAudioMixer->setParameter(name, param, AudioMixer::VOLUME1, &vrf);
mAudioMixer->setParameter(name, param, AudioMixer::AUXLEVEL, &vaf);
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::FORMAT, (void *)track->format());
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::CHANNEL_MASK, (void *)(uintptr_t)track->channelMask());
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::MIXER_CHANNEL_MASK, (void *)(uintptr_t)mChannelMask);
uint32_t maxSampleRate = mSampleRate * AUDIO_RESAMPLER_DOWN_RATIO_MAX;
uint32_t reqSampleRate = track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->getSampleRate();
if (reqSampleRate == 0) {
reqSampleRate = mSampleRate;
} else if (reqSampleRate > maxSampleRate) {
reqSampleRate = maxSampleRate;
}
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::RESAMPLE,
AudioMixer::SAMPLE_RATE,
(void *)(uintptr_t)reqSampleRate);
AudioPlaybackRate playbackRate = track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->getPlaybackRate();
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TIMESTRETCH,
AudioMixer::PLAYBACK_RATE,
&playbackRate);
if (mMixerBufferEnabled
&& (track->mainBuffer() == mSinkBuffer
|| track->mainBuffer() == mMixerBuffer)) {
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::MIXER_FORMAT, (void *)mMixerBufferFormat);
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::MAIN_BUFFER, (void *)mMixerBuffer);
mMixerBufferValid = true;
} else {
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::MIXER_FORMAT, (void *)EFFECT_BUFFER_FORMAT);
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::MAIN_BUFFER, (void *)track->mainBuffer());
}
mAudioMixer->setParameter(
name,
AudioMixer::TRACK,
AudioMixer::AUX_BUFFER, (void *)track->auxBuffer());
track->mRetryCount = kMaxTrackRetries;
if (mMixerStatusIgnoringFastTracks != MIXER_TRACKS_READY ||
mixerStatus != MIXER_TRACKS_ENABLED) {
mixerStatus = MIXER_TRACKS_READY;
}
} else {
if (framesReady < desiredFrames && !track->isStopped() && !track->isPaused()) {
track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->tallyUnderrunFrames(desiredFrames);
} else {
track->mAudioTrackServerProxy->tallyUnderrunFrames(0);
}
chain = getEffectChain_l(track->sessionId());
if (chain != 0) {
chain->clearInputBuffer();
}
if ((track->sharedBuffer() != 0) || track->isTerminated() ||
track->isStopped() || track->isPaused()) {
size_t audioHALFrames = (latency_l() * mSampleRate) / 1000;
int64_t framesWritten = mBytesWritten / mFrameSize;
if (mStandby || track->presentationComplete(framesWritten, audioHALFrames)) {
if (track->isStopped()) {
track->reset();
}
tracksToRemove->add(track);
}
} else {
if (--(track->mRetryCount) <= 0) {
tracksToRemove->add(track);
track->disable();
} else if (mMixerStatusIgnoringFastTracks == MIXER_TRACKS_READY ||
mixerStatus != MIXER_TRACKS_READY) {
mixerStatus = MIXER_TRACKS_ENABLED;
}
}
mAudioMixer->disable(name);
}
} // local variable scope to avoid goto warning
}
bool pauseAudioWatchdog = false;
if (didModify) {
state->mFastTracksGen++;
if (kUseFastMixer == FastMixer_Dynamic &&
state->mCommand == FastMixerState::MIX_WRITE && state->mTrackMask <= 1) {
state->mCommand = FastMixerState::COLD_IDLE;
state->mColdFutexAddr = &mFastMixerFutex;
state->mColdGen++;
mFastMixerFutex = 0;
if (kUseFastMixer == FastMixer_Dynamic) {
mNormalSink = mOutputSink;
}
block = FastMixerStateQueue::BLOCK_UNTIL_ACKED;
pauseAudioWatchdog = true;
}
}
if (sq != NULL) {
sq->end(didModify);
sq->push(coldIdle ? FastMixerStateQueue::BLOCK_NEVER : block);
}
while (resetMask != 0) {
size_t i = __builtin_ctz(resetMask);
ALOG_ASSERT(i < count);
resetMask &= ~(1 << i);
sp<Track> track = mActiveTracks[i];
ALOG_ASSERT(track->isFastTrack() && track->isStopped());
track->reset();
}
for (const auto &track : *tracksToRemove) {
const int name = track->name();
if (mAudioMixer->exists(name)) { // Normal tracks here, fast tracks in FastMixer.
mAudioMixer->setBufferProvider(name, nullptr /* bufferProvider */);
}
}
removeTracks_l(*tracksToRemove);
if (getEffectChain_l(AUDIO_SESSION_OUTPUT_MIX) != 0) {
mEffectBufferValid = true;
}
if (mEffectBufferValid) {
memset(mEffectBuffer, 0, mEffectBufferSize);
}
if ((mBytesRemaining == 0) && ((mixedTracks != 0 && mixedTracks == tracksWithEffect) ||
(mixedTracks == 0 && fastTracks > 0))) {
// FIXME as a performance optimization, should remember previous zero status
if (mMixerBufferValid) {
memset(mMixerBuffer, 0, mMixerBufferSize);
}
memset(mSinkBuffer, 0, mNormalFrameCount * mFrameSize);
}
mMixerStatusIgnoringFastTracks = mixerStatus;
if (fastTracks > 0) {
mixerStatus = MIXER_TRACKS_READY;
}
return mixerStatus;
}
prepareTracks_l的流程很长,但目前只需要把握几点,即创建AudioMixer,并设置参数.但还没有传到HAL层,还需要调用thread_mix:
1
2
3
4
5
6
void AudioFlinger::MixerThread::threadLoop_mix()
{
//处理AudioMixer
mAudioMixer->process();
...
}
AudioMixer的process类似与钩子函数,在不同的场景将会调用不同的接口.
1
2
3
4
//frameworks/av/include/media/AudioMixer.h
void process() {
(this->*mHook)();
}
对应的场景接口包括:
| 接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|
process__nop() |
初始值 |
process__genericNoResampling |
不重采样 |
process__genericResampling |
需要重采样 |
process__noResampleOneTrack |
单路Track,不需要重采样 |
process__oneTrack16BitsStereoNoResampling |
单路16bit双通道不需要重采样 |
实际AudioMixer的操作在这里暂不讨论,后续深入学习后再进行总结.
4.3.4 addOutput
再回到AudioPolicyManager的流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
void AudioPolicyManager::addOutput(audio_io_handle_t output,
const sp<SwAudioOutputDescriptor>& outputDesc)
{
mOutputs.add(output, outputDesc);
applyStreamVolumes(outputDesc, AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE, 0 /* delayMs */, true /* force */);
updateMono(output); // update mono status when adding to output list
selectOutputForMusicEffects();
nextAudioPortGeneration();
}
4.3.5 setOutputDevice
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
uint32_t AudioPolicyManager::setOutputDevice(const sp<AudioOutputDescriptor>& outputDesc,
audio_devices_t device,
bool force,
int delayMs,
audio_patch_handle_t *patchHandle,
const char *address,
bool requiresMuteCheck)
{
AudioParameter param;
uint32_t muteWaitMs;
//假如outputDesc重复了,即mOutput1,mOuptut2都不为空,则分别进行设置,这里用了递归
if (outputDesc->isDuplicated()) {
muteWaitMs = setOutputDevice(outputDesc->subOutput1(), device, force, delayMs,
nullptr /* patchHandle */, nullptr /* address */, requiresMuteCheck);
muteWaitMs += setOutputDevice(outputDesc->subOutput2(), device, force, delayMs,
nullptr /* patchHandle */, nullptr /* address */, requiresMuteCheck);
return muteWaitMs;
}
if ((device != AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) &&
((device & outputDesc->supportedDevices()) == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE)) {
return 0;
}
//outputDesc获取支持的设备
device = (audio_devices_t)(device & outputDesc->supportedDevices());
audio_devices_t prevDevice = outputDesc->mDevice;
if (device != AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {
outputDesc->mDevice = device;
}
if (requiresMuteCheck) {
muteWaitMs = checkDeviceMuteStrategies(outputDesc, prevDevice, delayMs);
} else {
muteWaitMs = 0;
}
if ((device == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE || device == prevDevice) &&
!force &&
outputDesc->getPatchHandle() != 0) {
return muteWaitMs;
}
//假如device为AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE,需要进行routing,重新设置device
if (device == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {
resetOutputDevice(outputDesc, delayMs, NULL);
} else {
DeviceVector deviceList;
//获取deviceList
if ((address == NULL) || (strlen(address) == 0)) {
deviceList = mAvailableOutputDevices.getDevicesFromType(device);
} else {
deviceList = mAvailableOutputDevices.getDevicesFromTypeAddr(device, String8(address));
}
if (!deviceList.isEmpty()) {
struct audio_patch patch;
outputDesc->toAudioPortConfig(&patch.sources[0]);
patch.num_sources = 1;
patch.num_sinks = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < deviceList.size() && i < AUDIO_PATCH_PORTS_MAX; i++) {
deviceList.itemAt(i)->toAudioPortConfig(&patch.sinks[i]);
patch.num_sinks++;
}
ssize_t index;
if (patchHandle && *patchHandle != AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE) {
index = mAudioPatches.indexOfKey(*patchHandle);
} else {
index = mAudioPatches.indexOfKey(outputDesc->getPatchHandle());
}
sp< AudioPatch> patchDesc;
audio_patch_handle_t afPatchHandle = AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE;
if (index >= 0) {
patchDesc = mAudioPatches.valueAt(index);
afPatchHandle = patchDesc->mAfPatchHandle;
}
//创建AudioPatch
status_t status = mpClientInterface->createAudioPatch(&patch,
&afPatchHandle,
delayMs);
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
if (index < 0) {
patchDesc = new AudioPatch(&patch, mUidCached);
addAudioPatch(patchDesc->mHandle, patchDesc);
} else {
patchDesc->mPatch = patch;
}
patchDesc->mAfPatchHandle = afPatchHandle;
if (patchHandle) {
*patchHandle = patchDesc->mHandle;
}
//设置Patch的Handle值
outputDesc->setPatchHandle(patchDesc->mHandle);
nextAudioPortGeneration();
//调用回调通知Patch已经更新了
mpClientInterface->onAudioPatchListUpdate();
}
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < mInputs.size(); i++) {
const sp<AudioInputDescriptor> inputDescriptor = mInputs.valueAt(i);
if (!is_virtual_input_device(inputDescriptor->mDevice)) {
AudioParameter inputCmd = AudioParameter();
inputCmd.addInt(String8(AudioParameter::keyRouting),device);
//通知inptut
mpClientInterface->setParameters(inputDescriptor->mIoHandle,
inputCmd.toString(),
delayMs);
}
}
}
applyStreamVolumes(outputDesc, device, delayMs);
return muteWaitMs;
}
5. 小结
分析至此,仅仅是大致了解了音频系统的初始化流程,其中许多细节仍然是还不了解,需要再实际调试或者解问题中加深了解.本博客也会适时查漏补缺,及时更新.